Help
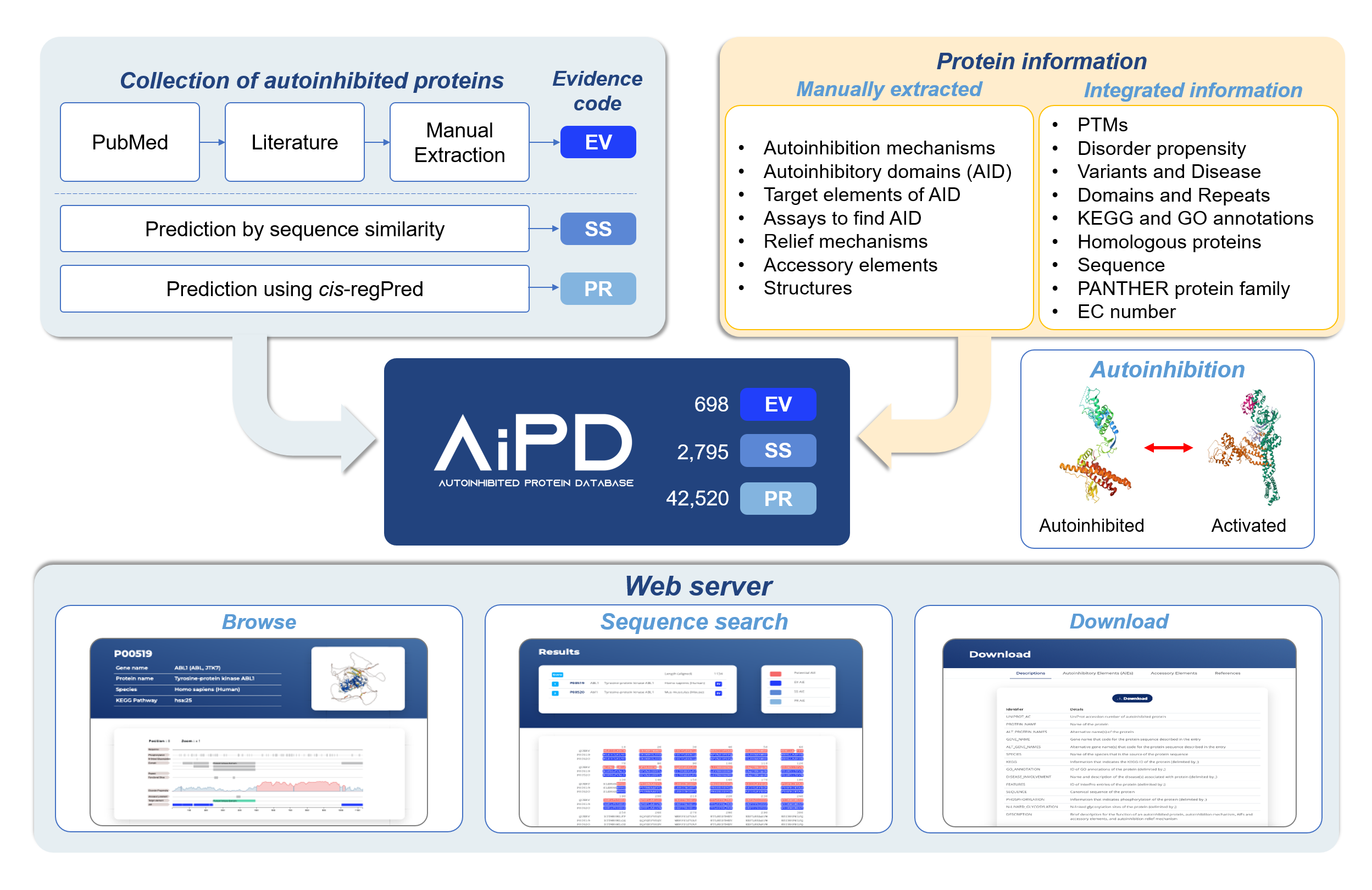
Manually extracted contents
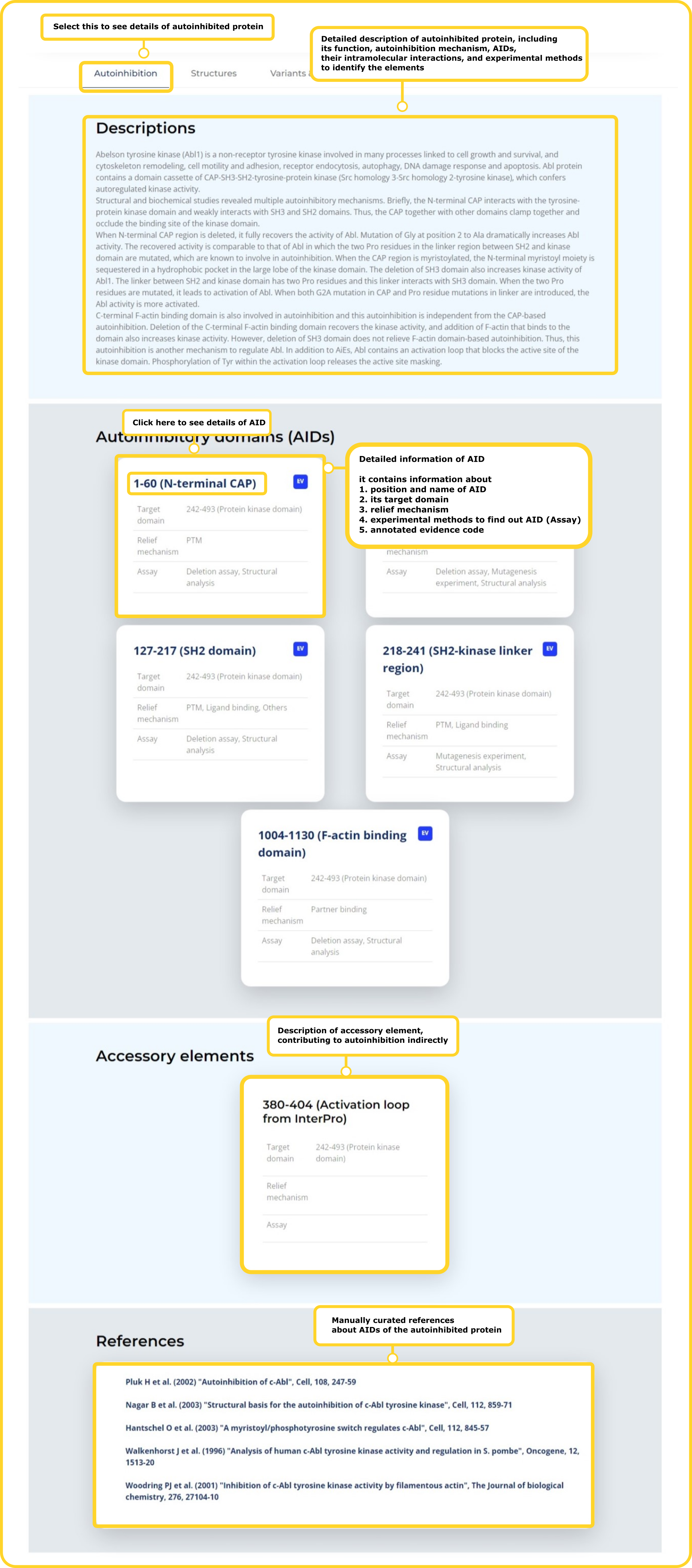
Autoinhibitory Domains (AIDs)
The domains or sequence segments that play a crucial role in modulating the activity of the target domain in cis.
The mechanisms that the autoinhibited state of the protein is relieved.
It contains the post-translational modifications (PTMs), partner binding, ligand binding, cleavage, etc.
The experimental methods to identify the AIDs when the evidence code of the autoinhibited protein is annotated with 'EV'.
It contains the deletion assay, mutagenesis experiment, split protein assay, peptide inhibitor test, structural anaylsis, etc..
The annotations based on the identification of an AID. There are three types of Evidence Codes.
Target Domains
The domains or regions regulated by AID.
Accessory Elements
The regions involved in autoinhibition but does not make direct contact with a target domain or is a regulatory region within a catalytic domain, such as an activation loop within the kinase domain.
Description
The detailed description about the autoinhibted protein.
It describes comprehensive information about autoinhibited protein such as AIDs, target domain, and relief mechanism.