Q9Z2D3
Gene name |
Gsdme |
Protein name |
Gasdermin-E |
Names |
Non-syndromic hearing impairment protein 5 homolog |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:54722 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
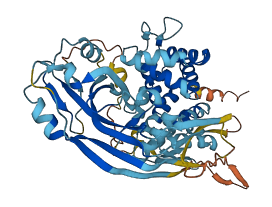
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-246 (N-terminal gasdermin domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Cleavage |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9Z2D3
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9Z2D3-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
6 variants for Q9Z2D3
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs29690906 | 90 | G>E | No | Ensembl | |
| rs225299816 | 184 | V>M | No | Ensembl | |
| rs30713457 | 269 | L>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs29663382 | 287 | Q>E | No | Ensembl | |
| rs29667555 | 373 | H>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs242951588 | 436 | N>D | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q9Z2D3
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| integral component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cardiolipin binding | Binding to cardiolipin. |
| phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding | Binding to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, a derivative of phosphatidylinositol in which the inositol ring is phosphorylated at the 4' and 5' positions. |
| wide pore channel activity | Enables the transport of a solute across a membrane via a large pore, un-gated channel. Examples include gap junctions, which transport substances from one cell to another; and porins which transport substances in and out of bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell death | Any biological process that results in permanent cessation of all vital functions of a cell. A cell should be considered dead when any one of the following molecular or morphological criteria is met: (1) the cell has lost the integrity of its plasma membrane; (2) the cell, including its nucleus, has undergone complete fragmentation into discrete bodies (frequently referred to as apoptotic bodies). The cell corpse (or its fragments) may be engulfed by an adjacent cell in vivo, but engulfment of whole cells should not be considered a strict criteria to define cell death as, under some circumstances, live engulfed cells can be released from phagosomes (see PMID:18045538). |
| cellular response to tumor necrosis factor | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a tumor necrosis factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to virus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a virus. |
| granzyme-mediated programmed cell death signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals induced by granzymes which triggers the cell death of a cell. The pathway starts with reception of a granzyme signal, and ends when the execution phase of cell death is triggered. Granzymes are serine proteases that are secreted by cytotoxic T cells and natural killer cells to induce cell death in target cells. |
| inner ear receptor cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features of inner ear receptor cells. Inner ear receptor cells are mechanorecptors found in the inner ear responsible for transducing signals involved in balance and sensory perception of sound. |
| necrotic cell death | A type of cell death that is morphologically characterized by an increasingly translucent cytoplasm, swelling of organelles, minor ultrastructural modifications of the nucleus (specifically, dilatation of the nuclear membrane and condensation of chromatin into small, irregular, circumscribed patches) and increased cell volume (oncosis), culminating in the disruption of the plasma membrane and subsequent loss of intracellular contents. Necrotic cells do not fragment into discrete corpses as their apoptotic counterparts do. Moreover, their nuclei remain intact and can aggregate and accumulate in necrotic tissues. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of immune response to tumor cell | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of an immune response to tumor cell. |
| positive regulation of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPK cascade. |
| pyroptosis | A caspase-1-dependent cell death subroutine that is associated with the generation of pyrogenic mediators such as IL-1beta and IL-18. |
| sensory perception of sound | The series of events required for an organism to receive an auditory stimulus, convert it to a molecular signal, and recognize and characterize the signal. Sonic stimuli are detected in the form of vibrations and are processed to form a sound. |
1 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q7YS54 | GSDME | Gasdermin-E | Equus caballus (Horse) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MFAKATRNFL | KEVDAGGDLI | SVSHLNDSDK | LQLLSLVTKK | KRYWCWQRPK | YQILSATLED |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| VLTEGHCLSP | VVVESDFVKY | ESKCENHKSG | AIGTVVGKVK | LNVGGKGVVE | SHSSFGTLRK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QEVDVQQLIQ | DAVKRTVNMD | NLVLQQVLES | RNEVLCVLTQ | KIMTTQKCVI | SEHVQSEETC |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GGMVGIQTKT | IQVSATEDGT | VTTDTNVVLE | IPAATTIAYG | IMELFVKQDG | QFEFCLLQGK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| HGGFEHERKL | DSVYLDPLAY | REFAFLDMLD | GGQGISSQDG | PLRVVKQATL | HLERSFHPFA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| VLPAQQQRAL | FCVLQKILFD | EELLRALEQV | CDDVAGGLWS | SQAVLAMEEL | TDSQQQDLTA |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| FLQLVGYRIQ | GEHPGPQDEV | SNQKLFATAY | FLVSALAEMP | DNATVFLGTC | CKLHVISSLC |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| CLLHALSDDS | VCDFHNPTLA | PLRDTERFGI | VQRLFASADI | ALERMQFSAK | ATILKDSCIF |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | |||
| PLILHITLSG | LSTLSKEHEE | ELCQSGHATG | QD |