Q9Z2A0
Gene name |
Pdpk1 (Pdk1) |
Protein name |
3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 |
Names |
mPDK1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:18607 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
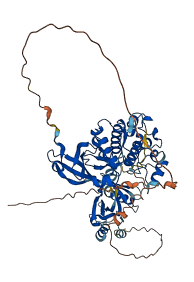
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
85-345 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM, Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
225-250 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
85-345 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9Z2A0
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9Z2A0-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
6 variants for Q9Z2A0
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs248533077 | 29 | V>M | No | Ensembl | |
| rs230000791 | 60 | R>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs46825835 | 289 | N>H | No | Ensembl | |
| rs264880737 | 410 | R>W | No | Ensembl | |
| rs13465575 | 546 | W>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs1131753902 | 557 | A>V | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q9Z2A0
8 regional properties for Q9Z2A0
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | C2 domain | 1 - 98 | IPR000008-1 |
| domain | C2 domain | 668 - 794 | IPR000008-2 |
| domain | C2 domain | 1535 - 1664 | IPR000008-3 |
| domain | Protein kinase C-like, phorbol ester/diacylglycerol-binding domain | 562 - 612 | IPR002219 |
| domain | MUN domain | 1002 - 1521 | IPR010439 |
| domain | Munc13 homology 1 | 1102 - 1245 | IPR014770 |
| domain | Mammalian uncoordinated homology 13, domain 2 | 1354 - 1521 | IPR014772 |
| domain | Protein Unc-13, C2B domain | 685 - 811 | IPR037302 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell projection | A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perikaryon | The portion of the cell soma (neuronal cell body) that excludes the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic density | An electron dense network of proteins within and adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane of an asymmetric, neuron-neuron synapse. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize them such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase activity | Phosphatidylinositol-3-phosphate-dependent catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein = ADP + a phosphoprotein. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| insulin receptor binding | Binding to an insulin receptor. |
| phospholipase activator activity | Increases the activity of a phospholipase, an enzyme that catalyzes of the hydrolysis of a glycerophospholipid. |
| phospholipase binding | Binding to a phospholipase. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
29 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of protein kinase B activity | Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme protein kinase B. |
| calcium-mediated signaling | Any intracellular signal transduction in which the signal is passed on within the cell via calcium ions. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cellular response to epidermal growth factor stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an epidermal growth factor stimulus. |
| cellular response to insulin stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a ligand to the tyrosine kinase receptor EGFR (ERBB1) on the surface of a cell. The pathway ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| extrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals in which a signal is conveyed from the cell surface to trigger the apoptotic death of a cell. The pathway starts with either a ligand binding to a cell surface receptor, or a ligand being withdrawn from a cell surface receptor (e.g. in the case of signaling by dependence receptors), and ends when the execution phase of apoptosis is triggered. |
| focal adhesion assembly | The aggregation and bonding together of a set of components to form a focal adhesion, a complex of intracellular signaling and structural proteins that provides a structural link between the internal actin cytoskeleton and the ECM, and also function as a locus of signal transduction activity. |
| hyperosmotic response | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of detection of, or exposure to, a hyperosmotic environment, i.e. an environment with a higher concentration of solutes than the organism or cell. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| negative regulation of cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process | Any process that decreases the rate or extent of cardiac cell apoptotic process, a form of programmed cell death induced by external or internal signals that trigger the activity of proteolytic caspases whose actions dismantle a cardiac muscle cell and result in its death. |
| negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of endothelial cell apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process in neurons. |
| negative regulation of protein kinase activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase activity. |
| negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of toll-like receptor signaling pathway. |
| negative regulation of transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of any TGF-beta receptor signaling pathway. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| positive regulation of blood vessel endothelial cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the migration of the endothelial cells of blood vessels. |
| positive regulation of phospholipase activity | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of phospholipase activity, the hydrolysis of a phospholipid. |
| positive regulation of protein localization to plasma membrane | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to plasma membrane. |
| positive regulation of release of sequestered calcium ion into cytosol | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the release into the cytosolic compartment of calcium ions sequestered in the endoplasmic reticulum or mitochondria. |
| positive regulation of sprouting angiogenesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of sprouting angiogenesis. |
| positive regulation of vascular endothelial cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of vascular endothelial cell proliferation. |
| regulation of endothelial cell migration | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of the orderly movement of an endothelial cell into the extracellular matrix to form an endothelium. |
| regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that modulates I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| regulation of mast cell degranulation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate, or extent of mast cell degranulation. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| type B pancreatic cell development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a type B pancreatic cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A type B pancreatic cell is a cell located towards center of the islets of Langerhans that secretes insulin. |
26 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q03407 | PKH1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PKH1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q9W0V1 | Pdk1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| O15530 | PDPK1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q6A1A2 | PDPK2P | Putative 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q02956 | Prkcz | Protein kinase C zeta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62074 | Prkci | Protein kinase C iota type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70268 | Pkn1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8K045 | Pkn3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8BWW9 | Pkn2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase N2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P23298 | Prkch | Protein kinase C eta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P16054 | Prkce | Protein kinase C epsilon type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q02111 | Prkcq | Protein kinase C theta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P28867 | Prkcd | Protein kinase C delta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P20444 | Prkca | Protein kinase C alpha type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P63318 | Prkcg | Protein kinase C gamma type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P68404 | Prkcb | Protein kinase C beta type | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60823 | Akt2 | RAC-beta serine/threonine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P31750 | Akt1 | RAC-alpha serine/threonine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9WUA6 | Akt3 | RAC-gamma serine/threonine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9ERE3 | Sgk3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Sgk3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8QZV4 | Stk32c | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 32C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91VJ4 | Stk38 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 38 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q7TSE6 | Stk38l | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 38-like | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O55173 | Pdpk1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9Y1J3 | pdk-1 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q4V3C8 | PDPK2 | 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MARTTSQLYD | AVPIQSSVVL | CSCPSPSMVR | SQTEPGSSPG | IPSGVSRQGS | TMDGTTAEAR |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PSTNPLQQHP | AQLPPQPRKK | RPEDFKFGKI | LGEGSFSTVV | LARELATSRE | YAIKILEKRH |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| IIKENKVPYV | TRERDVMSRL | DHPFFVKLYF | TFQDDEKLYF | GLSYAKNGEL | LKYIRKIGSF |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| DETCTRFYTA | EIVSALEYLH | GKGIIHRDLK | PENILLNEDM | HIQITDFGTA | KVLSPESKQA |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| RANSFVGTAQ | YVSPELLTEK | SACKSSDLWA | LGCIIYQLVA | GLPPFRAGNE | YLIFQKIIKL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| EYHFPEKFFP | KARDLVEKLL | VLDATKRLGC | EEMEGYGPLK | AHPFFETITW | ENLHQQTPPK |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LTAYLPAMSE | DDEDCYGNYD | NLLSQFGFMQ | VSSSSSSHSL | STVETSLPQR | SGSNIEQYIH |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| DLDTNSFELD | LQFSEDEKRL | LLEKQAGGNP | WHQFVENNLI | LKMGPVDKRK | GLFARRRQLL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LTEGPHLYYV | DPVNKVLKGE | IPWSQELRPE | AKNFKTFFVH | TPNRTYYLMD | PSGNAHKWCR |
| 550 | |||||
| KIQEVWRQQY | QSNPDAAVQ |