Q9Z1N5
Gene name |
Ddx39b (Bat1, Bat1a, Uap56) |
Protein name |
Spliceosome RNA helicase Ddx39b |
Names |
56 kDa U2AF65-associated protein, DEAD box protein UAP56, HLA-B-associated transcript 1 protein |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:53817 |
EC number |
3.6.4.13: Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
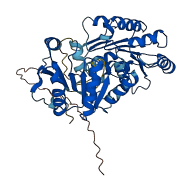
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9Z1N5
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9Z1N5-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
17 variants for Q9Z1N5
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3389409012 | 72 | Q>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3389450244 | 82 | G>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3407674470 | 93 | M>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389371672 | 119 | M>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389475126 | 159 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389371677 | 169 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389459415 | 196 | D>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3407545531 | 219 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389460489 | 232 | S>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3389460489 | 232 | S>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389462195 | 238 | V>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3407698349 | 309 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3407631337 | 325 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389453760 | 331 | Q>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389475121 | 347 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389460442 | 355 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389460506 | 415 | P>S | No | EVA |
1 associated diseases with Q9Z1N5
Without disease ID
1 regional properties for Q9Z1N5
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Centrosomal protein of 290kDa, coiled-coil region | 1283 - 1410 | IPR032321 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.4.13 | Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nuclear matrix | The dense fibrillar network lying on the inner side of the nuclear membrane. |
| nuclear speck | A discrete extra-nucleolar subnuclear domain, 20-50 in number, in which splicing factors are seen to be localized by immunofluorescence microscopy. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
| spliceosomal complex | Any of a series of ribonucleoprotein complexes that contain snRNA(s) and small nuclear ribonucleoproteins (snRNPs), and are formed sequentially during the spliceosomal splicing of one or more substrate RNAs, and which also contain the RNA substrate(s) from the initial target RNAs of splicing, the splicing intermediate RNA(s), to the final RNA products. During cis-splicing, the initial target RNA is a single, contiguous RNA transcript, whether mRNA, snoRNA, etc., and the released products are a spliced RNA and an excised intron, generally as a lariat structure. During trans-splicing, there are two initial substrate RNAs, the spliced leader RNA and a pre-mRNA. |
| transcription export complex | The transcription export (TREX) complex couples transcription elongation by RNA polymerase II to mRNA export. The complex associates with the polymerase and travels with it along the length of the transcribed gene. TREX is composed of the THO transcription elongation complex as well as other proteins that couple THO to mRNA export proteins. The TREX complex is known to be found in a wide range of eukaryotes, including S. cerevisiae and metazoans. |
| U4 snRNP | A ribonucleoprotein complex that contains small nuclear RNA U4, a heptameric ring of Sm proteins, as well as several proteins that are unique to the U4 snRNP, most of which remain associated with the U4 snRNA both while the U4 snRNP is free or assembled into the U4/U6 snRNP or into a series of spliceosomal complexes. |
| U6 snRNP | A ribonucleoprotein complex that contains small nuclear RNA U6, the Lsm2-8 heptameric ring complex, as well as several proteins that are unique to the U6 snRNP, most of which remain associated with the U6 snRNA both while the U6 snRNP is free or assembled into the U4/U6 snRNP or into a series of spliceosomal complexes. |
10 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| ATP-dependent activity, acting on RNA | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate; this reaction requires the presence of RNA, and it drives another reaction. |
| ATP-dependent protein binding | Binding to a protein or protein complex using energy from ATP hydrolysis. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| RNA binding | Binding to an RNA molecule or a portion thereof. |
| RNA helicase activity | Unwinding of an RNA helix, driven by ATP hydrolysis. |
| U4 snRNA binding | Binding to a U4 small nuclear RNA (U4 snRNA). |
| U6 snRNA binding | Binding to a U6 small nuclear RNA (U6 snRNA). |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| mRNA export from nucleus | The directed movement of mRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm. |
| mRNA splicing, via spliceosome | The joining together of exons from one or more primary transcripts of messenger RNA (mRNA) and the excision of intron sequences, via a spliceosomal mechanism, so that mRNA consisting only of the joined exons is produced. |
| negative regulation of DNA damage checkpoint | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of a DNA damage checkpoint. |
| positive regulation of cell growth involved in cardiac muscle cell development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the growth of a cardiac muscle cell, where growth contributes to the progression of the cell over time from its initial formation to its mature state. |
| positive regulation of DNA biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA biosynthetic process. |
| positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription elongation, the extension of an RNA molecule after transcription initiation and promoter clearance by the addition of ribonucleotides catalyzed by a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. |
| positive regulation of translation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of proteins by the translation of mRNA or circRNA. |
| positive regulation of vascular associated smooth muscle cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation. |
| RNA secondary structure unwinding | The process in which a secondary structure of RNA are broken or 'melted'. |
| RNA splicing | The process of removing sections of the primary RNA transcript to remove sequences not present in the mature form of the RNA and joining the remaining sections to form the mature form of the RNA. |
| spliceosomal complex assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a spliceosomal complex, a ribonucleoprotein apparatus that catalyzes nuclear mRNA splicing via transesterification reactions. |
| viral mRNA export from host cell nucleus | The directed movement of intronless viral mRNA from the host nucleus to the cytoplasm for translation. |
28 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q07478 | SUB2 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase SUB2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q3T147 | DDX39B | Spliceosome RNA helicase DDX39B | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q5ZHZ0 | DDX39B | Spliceosome RNA helicase DDX39B | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P60024 | DDX39B | Spliceosome RNA helicase DDX39B | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | PR |
| Q5WR10 | DDX39B | Spliceosome RNA helicase DDX39B | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| O00148 | DDX39A | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX39A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q13838 | DDX39B | Spliceosome RNA helicase DDX39B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q62167 | Ddx3x | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX3X | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q99MJ9 | Ddx50 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX50 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91VC3 | Eif4a3 | Eukaryotic initiation factor 4A-III | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P16381 | D1Pas1 | Putative ATP-dependent RNA helicase Pl10 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62095 | Ddx3y | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX3Y | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61496 | Ddx4 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9QY15 | Ddx25 | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX25 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61655 | Ddx19a | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX19A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q501J6 | Ddx17 | Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX17 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VDW0 | Ddx39a | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX39A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91VN6 | Ddx41 | Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX41 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61656 | Ddx5 | Probable ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q29024 | DDX39B | Spliceosome RNA helicase DDX39B | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| Q5U216 | Ddx39a | ATP-dependent RNA helicase DDX39A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q63413 | Ddx39b | Spliceosome RNA helicase Ddx39b | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q5TM17 | DDX39B | Spliceosome RNA helicase DDX39B | Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque) | PR |
| Q5JK84 | AIP2 | DEAD-box ATP-dependent RNA helicase 15 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q0JM17 | AIP1 | DEAD-box ATP-dependent RNA helicase 56 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q18212 | hel-1 | Spliceosome RNA helicase DDX39B homolog | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q56XG6 | RH15 | DEAD-box ATP-dependent RNA helicase 15 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LFN6 | RH56 | DEAD-box ATP-dependent RNA helicase 56 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAENDVDNEL | LDYEDDEVET | AAGADGTEAP | AKKDVKGSYV | SIHSSGFRDF | LLKPELLRAI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| VDCGFEHPSE | VQHECIPQAI | LGMDVLCQAK | SGMGKTAVFV | LATLQQLEPV | TGQVSVLVMC |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| HTRELAFQIS | KEYERFSKYM | PNVKVAVFFG | GLSIKKDEEV | LKKNCPHIVV | GTPGRILALA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| RNKSLNLKHI | KHFILDECDK | MLEQLDMRRD | VQEIFRMTPH | EKQVMMFSAT | LSKEIRPVCR |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| KFMQDPMEIF | VDDETKLTLH | GLQQYYVKLK | DNEKNRKLFD | LLDVLEFNQV | VIFVKSVQRC |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| IALAQLLVEQ | NFPAIAIHRG | MPQEERLSRY | QQFKDFQRRI | LVATNLFGRG | MDIERVNIAF |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| NYDMPEDSDT | YLHRVARAGR | FGTKGLAITF | VSDENDAKIL | NDVQDRFEVN | ISELPDEIDI |
| SSYIEQTR |