Q9Z1N2
Gene name |
Orc1 (Orc1l) |
Protein name |
Origin recognition complex subunit 1 |
Names |
|
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:18392 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
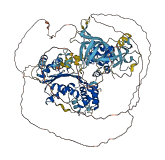
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

3 structures for Q9Z1N2
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4DOV | X-ray | 170 A | A/C | 9-170 | PDB |
| 4DOW | X-ray | 195 A | A/B | 9-170 | PDB |
| AF-Q9Z1N2-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
58 variants for Q9Z1N2
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388698609 | 20 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388689296 | 22 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388705633 | 26 | Q>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388700929 | 74 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3394661245 | 108 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388701932 | 144 | P>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388702243 | 145 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs233632970 | 146 | D>N | No | EVA | |
| rs257017073 | 148 | K>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388705618 | 159 | W>C | No | EVA | |
| rs263390725 | 165 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388705604 | 166 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs229834318 | 176 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388701943 | 197 | S>C | No | EVA | |
| rs245309750 | 203 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs214751271 | 214 | H>R | No | EVA | |
| rs224611844 | 228 | I>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3413106483 | 230 | N>K | No | EVA | |
| rs28129823 | 230 | N>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388701909 | 246 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3394565094 | 254 | S>T | No | EVA | |
| rs257600251 | 280 | K>R | No | EVA | |
| rs263786545 | 281 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3394708504 | 282 | N>D | No | EVA | |
| rs28129817 | 284 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs28129817 | 284 | P>T | No | EVA | |
| rs212122146 | 297 | V>F | No | EVA | |
| rs28129816 | 309 | S>G | No | EVA | |
| rs253854760 | 312 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs219052914 | 313 | L>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388687200 | 315 | A>S | No | EVA | |
| rs237883714 | 328 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388700899 | 347 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs263266082 | 352 | Y>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3394617087 | 355 | R>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388701290 | 356 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388701893 | 366 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs247790906 | 395 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388697346 | 400 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs224353324 | 416 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs28129804 | 422 | N>K | No | EVA | |
| rs255035710 | 466 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388695644 | 521 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388701367 | 524 | H>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3388698234 | 525 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs216012210 | 537 | D>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388701336 | 558 | V>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388689305 | 564 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3394617066 | 575 | H>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388695671 | 589 | S>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3388698617 | 616 | F>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3388704591 | 645 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388705575 | 649 | R>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3388679694 | 660 | Y>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3394660868 | 713 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs265348702 | 718 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs228018032 | 719 | G>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388698659 | 730 | L>* | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q9Z1N2
3 regional properties for Q9Z1N2
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | HECT domain | 587 - 942 | IPR000569 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 64 - 195 | IPR002110-1 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 196 - 257 | IPR002110-2 |
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chromosome, telomeric region | The end of a linear chromosome, required for the integrity and maintenance of the end. A chromosome telomere usually includes a region of telomerase-encoded repeats the length of which rarely exceeds 20 bp each and that permits the formation of a telomeric loop (T-loop). The telomeric repeat region is usually preceded by a sub-telomeric region that is gene-poor but rich in repetitive elements. Some telomeres only consist of the latter part (for eg. D. melanogaster telomeres). |
| nuclear origin of replication recognition complex | A multisubunit complex that is located at the replication origins of a chromosome in the nucleus. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| origin recognition complex | A multisubunit complex that is located at the replication origins of a chromosome. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA replication origin binding | Binding to a DNA replication origin, a unique DNA sequence of a replicon at which DNA replication is initiated and proceeds bidirectionally or unidirectionally. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
5 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA replication | The cellular metabolic process in which a cell duplicates one or more molecules of DNA. DNA replication begins when specific sequences, known as origins of replication, are recognized and bound by initiation proteins, and ends when the original DNA molecule has been completely duplicated and the copies topologically separated. The unit of replication usually corresponds to the genome of the cell, an organelle, or a virus. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA. |
| DNA replication initiation | The process in which DNA-dependent DNA replication is started; this begins with the ATP dependent loading of an initiator complex onto the DNA, this is followed by DNA melting and helicase activity. In bacteria, the gene products that enable the helicase activity are loaded after the initial melting and in archaea and eukaryotes, the gene products that enable the helicase activity are inactive when they are loaded and subsequently activate. |
| mitotic DNA replication checkpoint signaling | A signal transduction process that contributes to a mitotic DNA replication checkpoint. |
| positive regulation of G0 to G1 transition | A cell cycle process that activates or increases the rate or extent of the transition from the G0 quiescent state to the G1 phase. |
| positive regulation of smooth muscle cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of smooth muscle cell proliferation. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P54784 | ORC1 | Origin recognition complex subunit 1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q58DC8 | ORC1 | Origin recognition complex subunit 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| O16810 | Orc1 | Origin recognition complex subunit 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | EV |
| Q13415 | ORC1 | Origin recognition complex subunit 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O89033 | Cdc6 | Cell division control protein 6 homolog | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q80Z32 | Orc1 | Origin recognition complex subunit 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q710E8 | ORC1A | Origin of replication complex subunit 1A | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SU24 | ORC1B | Origin of replication complex subunit 1B | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPSYLTRQKT | RQTFSWVGRP | LPNRKQFQQM | YREICMKIND | GSEIHIKVGQ | FVLIQGEDNK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KPYVAKLIEL | FQNGAEVPPK | KCARVQWFVR | FLEIPVSKRH | LLGRSPPAQE | IFWYDCSDWD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| NKINVETIIG | PVQVVALAPE | EVIPVDQKSE | ETLFVKLSWN | KKDFAPLPPE | VLAALREQED |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SPEWQKPLKA | KIKNVKSPAR | NTTEQEVKGI | KSNHSTSKFH | QTPANIVIPN | AKKSLELDGL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| GFTRKPNTRW | SKKSSCDSLD | YQKTSKRRAA | FSETTSPPKK | PNKPREIKPS | SALETRVKNG |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| QTQPFCAKSS | VVLRARNPAM | TTTKLGVDNT | LSPIRNGLRS | SVVPSGGLTP | VYIRRKAKEQ |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| ETHKEPIRTS | RVHRKSSLLT | LKRIRQQLCL | LDGDDRDQEE | EESVDSESEE | EDEFISSLPT |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| RNSLGQSRTR | QTPSKSPQKN | PKPRTPHRAT | PQIRDRNLAV | QEPASALEEA | RLRLHVSAVP |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| DSLPCREQEF | QDIYSFVESK | LLDGTGGCMY | ISGVPGTGKT | ATVHEVIRCL | QQAAETDDVP |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| PFQYVEVNGM | KLTEPHQVYV | QILKKLTGQK | ATANHAAELL | AKQFCGQGSQ | KETTVLLVDE |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| LDLLWTHKQD | VMYNLFDWPT | HKGAHLIVLT | IANTMDLPER | IMMNRVSSRL | GLTRMSFQPY |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| SHSQLKQILV | SRLRNLRAFE | DDAIQLVARK | VAALSGDARR | CLDICRRATE | ICELSHLRGD |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| SLSLVTVAHL | MEAIDEMFSS | SYITAIKNSS | VVEQSFLRAI | IAEFRRSGLE | EATFQQIYSQ |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | |
| HVALCRMEGL | PYPTMSETMA | VCSRLGSCRL | LLVEPSRNDL | LLRVRLNVSQ | NDVLFALKEE |