Q9Z138
Gene name |
Ror2 |
Protein name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2 |
Names |
mROR2, Neurotrophic tyrosine kinase, receptor-related 2 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
|
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
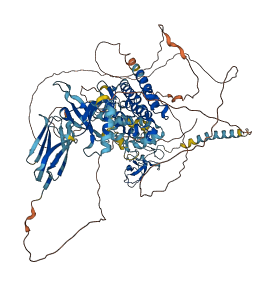
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
473-746 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Others |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Artim SC et al. (2012) "Assessing the range of kinase autoinhibition mechanisms in the insulin receptor family", The Biochemical journal, 448, 213-20
- Shen J et al. (2019) "Extracellular Juxtamembrane Motif Critical for TrkB Preformed Dimer and Activation", Cells, 8,
- Arevalo JC et al. (2000) "TrkA immunoglobulin-like ligand binding domains inhibit spontaneous activation of the receptor", Molecular and cellular biology, 20, 5908-16
- Hubbard SR (2004) "Juxtamembrane autoinhibition in receptor tyrosine kinases", Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology, 5, 464-71
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9Z138
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9Z138-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q9Z138
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9Z138 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q9Z138
No regional properties for Q9Z138
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for Q9Z138 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| microtubule | Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| frizzled binding | Binding to a frizzled (fz) receptor. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase binding | Binding to a mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase kinase, a protein that can phosphorylate a MAP kinase kinase. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | Combining with a signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate. |
| Wnt-protein binding | Binding to a Wnt-protein, a secreted growth factor involved in signaling. |
33 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| astrocyte development | The process aimed at the progression of an astrocyte over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell. An astrocyte is the most abundant type of glial cell. Astrocytes provide support for neurons and regulate the environment in which they function. |
| BMP signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of a member of the BMP (bone morphogenetic protein) family to a receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| bone mineralization | The deposition of hydroxyapatite, a form of calcium phosphate with the formula Ca10(PO4)6(OH)2, in bone tissue. |
| cartilage condensation | The condensation of mesenchymal cells that have been committed to differentiate into chondrocytes. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cell fate commitment | The commitment of cells to specific cell fates and their capacity to differentiate into particular kinds of cells. Positional information is established through protein signals that emanate from a localized source within a cell (the initial one-cell zygote) or within a developmental field. |
| embryonic digit morphogenesis | The process, occurring in the embryo, by which the anatomical structures of the digit are generated and organized. A digit is one of the terminal divisions of an appendage, such as a finger or toe. |
| embryonic genitalia morphogenesis | The process, occurring in the embryo, by which the anatomical structures of the genitalia are generated and organized. |
| inner ear morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the inner ear are generated and organized. The inner ear is the structure in vertebrates that contains the organs of balance and hearing. It consists of soft hollow sensory structures (the membranous labyrinth) containing fluid (endolymph) surrounded by fluid (perilymph) and encased in a bony cavity (the bony labyrinth). It consists of two chambers, the sacculus and utriculus, from which arise the cochlea and semicircular canals respectively. |
| JNK cascade | An intracellular protein kinase cascade containing at least a JNK (a MAPK), a JNKK (a MAPKK) and a JUN3K (a MAP3K). The cascade can also contain an additional tier: the upstream MAP4K. The kinases in each tier phosphorylate and activate the kinases in the downstream tier to transmit a signal within a cell. |
| macrophage migration | The orderly movement of a macrophage from one site to another. |
| male genitalia development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the male genitalia over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| negative regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| negative regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of JUN kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of JUN kinase activity. |
| positive regulation of kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| positive regulation of macrophage differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of macrophage differentiation. |
| positive regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPK cascade. |
| positive regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase cascade. |
| positive regulation of protein kinase C activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase C activity. |
| positive regulation of synaptic transmission, glutamatergic | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of glutamatergic synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to another neuron across a synapse using the neurotransmitter glutamate. |
| positive regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| skeletal system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skeleton is the bony framework of the body in vertebrates (endoskeleton) or the hard outer envelope of insects (exoskeleton or dermoskeleton). |
| SMAD protein signal transduction | The cascade of processes by which a signal interacts with a receptor, causing a change in the activity of a SMAD protein, and ultimately effecting a change in the functioning of the cell. |
| smoothened signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of activation of the transmembrane protein Smoothened. |
| somitogenesis | The formation of mesodermal clusters that are arranged segmentally along the anterior posterior axis of an embryo. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| Wnt signaling pathway, calcium modulating pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where activated receptors leads to an increase in intracellular calcium and activation of protein kinase C (PKC). |
| Wnt signaling pathway, planar cell polarity pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where activated receptors signal via downstream effectors including C-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) to modulate cytoskeletal elements and control cell polarity. |
78 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q91044 | NTRK3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q91987 | NTRK2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q91009 | NTRK1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8AXY6 | MUSK | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine protein kinase | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q5IS37 | NTRK3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | SS |
| Q24488 | Ror | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor Ror | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9V6K3 | Nrk | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor Ror2 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| O15146 | MUSK | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P04629 | NTRK1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q01973 | ROR1 | Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q16288 | NTRK3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q16620 | NTRK2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q01974 | ROR2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q3UFB7 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z139 | Ror1 | Inactive tyrosine-protein kinase transmembrane receptor ROR1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q00993 | Axl | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor UFO | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q03145 | Epha2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60805 | Mertk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Mer | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9WTL4 | Insrr | Insulin receptor-related protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60629 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60750 | Epha1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P97793 | Alk | ALK tyrosine kinase receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15208 | Insr | Insulin receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54761 | Ephb4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35546 | Ret | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Ret | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61006 | Musk | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62371 | Ddr2 | Discoidin domain-containing receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03146 | Ddr1 | Epithelial discoidin domain-containing receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P15209 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6VNS1 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35917 | Flt4 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35969 | Flt1 | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35918 | Kdr | Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60751 | Igf1r | Insulin-like growth factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16092 | Fgfr1 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P21803 | Fgfr2 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03142 | Fgfr4 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62190 | Mst1r | Macrophage-stimulating protein receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P55144 | Tyro3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor TYRO3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P70424 | Erbb2 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61527 | Erbb4 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61526 | Erbb3 | Receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01279 | Egfr | Epidermal growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q01887 | Ryk | Tyrosine-protein kinase RYK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q02858 | Tek | Angiopoietin-1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q06806 | Tie1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor Tie-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05532 | Kit | Mast/stem cell growth factor receptor Kit | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P05622 | Pdgfrb | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor beta | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P09581 | Csf1r | Macrophage colony-stimulating factor 1 receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26618 | Pdgfra | Platelet-derived growth factor receptor alpha | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q00342 | Flt3 | Receptor-type tyrosine-protein kinase FLT3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16056 | Met | Hepatocyte growth factor receptor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61851 | Fgfr3 | Fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P24786 | NTRK3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q62838 | Musk | Muscle, skeletal receptor tyrosine protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P35739 | Ntrk1 | High affinity nerve growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q03351 | Ntrk3 | NT-3 growth factor receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63604 | Ntrk2 | BDNF/NT-3 growth factors receptor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G5EGK5 | cam-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase receptor cam-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9SXB5 | At1g11303 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g11303 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LPZ9 | SD113 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-13 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64783 | At1g61370 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61370 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64770 | At1g61490 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61490 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9SYA0 | At1g61500 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61500 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O81833 | SD11 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWZ5 | SD25 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD2-5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SXB4 | At1g11300 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g11300 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64778 | At1g61420 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61420 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64776 | At1g61440 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61440 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64780 | At1g61400 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61400 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9SY95 | At1g61550 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61550 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64782 | SD129 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD1-29 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| O64774 | At1g61460 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61460 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64477 | At2g19130 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At2g19130 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9SXB8 | At1g11330 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g11330 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64793 | At1g67520 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g67520 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O64784 | At1g61360 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase At1g61360 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q39203 | SD22 | G-type lectin S-receptor-like serine/threonine-protein kinase SD2-2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MARGWVRPSR | VPLCARAVWT | AAALLLWTPW | TAGEVEDSEA | IDTLGQPDGP | DSPLPTLKGY |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| FLNFLEPVNN | ITIVQGQTAI | LHCKVAGNPP | PNVRWLKNDA | PVVQEPRRVI | IRKTEYGSRL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RIQDLDTTDT | GYYQCVATNG | LKTITATGVL | YVRLGPTHSP | NHNFQDDDQE | DGFCQPYRGI |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| ACARFIGNRT | IYVDSLQMQG | EIENRITAAF | TMIGTSTQLS | DQCSQFAIPS | FCHFVFPLCD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| ARSRAPKPRE | LCRDECEVLE | NDLCRQEYTI | ARSNPLILMR | LQLPKCEALP | MPESPDAANC |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| MRIGIPAERL | GRYHQCYNGS | GADYRGMAST | TKSGHQCQPW | ALQHPHSHRL | SSTEFPELGG |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| GHAYCRNPGG | QVEGPWCFTQ | NKNVRVELCD | VPPCSPRDGS | KMGILYILVP | SIAIPLVIAC |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LFFLVCMCRN | KQKASASTPQ | RRQLMASPSQ | DMEMPLISQH | KQAKLKEISL | STVRFMEELG |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| EDRFGKVYKG | HLFGPAPGEP | TQAVAIKTLK | DKAEGPLREE | FRQEAMLRAR | LQHPNIVCLL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| GVVTKDQPLS | MIFSYCSHGD | LHEFLVMRSP | HSDVGSTDDD | RTVKSALEPP | DFVHVVAQIA |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| AGMEFLSSHH | VVHKDLATRN | VLVYDKLNVR | ISDLGLFREV | YSADYYKLMG | NSLLPIRWMS |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| PEAVMYGKFS | IDSDIWSYGV | VLWEVFSYGL | QPYCGYSNQD | VVEMIRSRQV | LPCPDDCPAW |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| VYALMIECWN | EFPSRRPRFK | DIHSRLRSWG | NLSNYNSSAQ | TSGASNTTQT | SSLSTSPVSN |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| VSNARYMAPK | QKAQPFPQPQ | FIPMKGQIRP | LVPPAQLYIP | VNGYQPVPAY | GAYLPNFYPV |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| QIPMQMAPQQ | VPPQMVPKPS | SHHSGSGSTS | TGYVTTAPSN | TSVADRAALL | SEGTEDAQNI |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | ||
| AEDVAQSPVQ | EAEEEEEGSV | PETELLGDND | TLQVTEAAHV | QLEA |