Q9Y3E7
Gene name |
CHMP3 (CGI149, NEDF, VPS24) |
Protein name |
Charged multivesicular body protein 3 |
Names |
Chromatin-modifying protein 3, Neuroendocrine differentiation factor, Vacuolar protein sorting-associated protein 24, hVps24 |
Species |
Homo sapiens (Human) |
KEGG Pathway |
hsa:51652 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
CHARGED MULTIVESICULAR BODY PROTEIN (PTHR10476) |
Descriptions
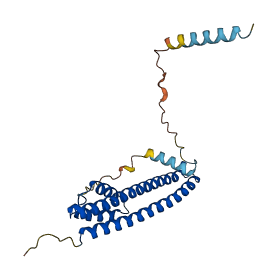
CHMP3 is a core component of the endosomal sorting required for transport complex III (ESCRT-III), which is involved in multivesicular bodies (MVBs) formation and sorting of endosomal cargo proteins into MVBs. The autoinhibition of CHMP3 is regulated through the intramolecular interactions between N-terminal basic domain and C-terminal acidic domain. The binding of the endosome-associated ubiquitin isopeptidase (AMSH) to the acidic half relieves the autoinhibition of CHMP3. CHMP3 can be induced to block HIV-1 release (Anti-HIV-1 budding activity) by coexpressing AMSH or by truncating the acidic domain.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-150 (N-terminal domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Zamborlini A et al. (2006) "Release of autoinhibition converts ESCRT-III components into potent inhibitors of HIV-1 budding", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 19140-5
- Bajorek M et al. (2009) "Structural basis for ESCRT-III protein autoinhibition", Nature structural & molecular biology, 16, 754-62
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure
155 variants for Q9Y3E7
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
CA347565883 rs1382997162 |
2 | G>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA347565851 rs1231402215 |
5 | G>E | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1286901822 CA347565857 |
5 | G>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1406757066 CA347565843 |
6 | K>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1253519911 CA347565822 |
7 | T>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs774481900 CA1750268 |
7 | T>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1468136327 CA347565820 |
8 | Q>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs759443052 COSM286472 CA1750267 |
9 | E>D | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
rs1425230936 CA347565804 |
9 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1558667032 CA347565784 |
10 | K>E | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA1750264 rs776458208 |
10 | K>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1259181723 CA347565770 |
11 | P>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs770666607 CA1750263 |
12 | P>A | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs770666607 CA51427674 |
12 | P>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA347565726 rs1558667007 |
15 | L>M | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA1750226 rs760712170 |
17 | N>S | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA347564628 rs760712170 |
17 | N>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA347564595 rs1238312283 |
19 | W>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA347564574 rs1333848460 |
20 | S>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA347564583 rs1430538203 |
20 | S>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs540948421 CA1750224 |
23 | I>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA51413409 rs1019126612 |
26 | E>A | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA51413413 rs548843054 |
26 | E>K | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
CA1750223 rs761505549 |
30 | V>I | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs774159726 CA1750222 |
31 | D>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA51413402 rs374031204 |
31 | D>V | No |
ClinGen ESP |
|
|
rs144255258 CA1750220 |
35 | R>K | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750202 rs757120612 |
36 | D>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1158342289 CA347564357 |
36 | D>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA347563102 rs1475865871 |
37 | I>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs572378103 CA1750200 |
38 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs762716183 CA1750199 |
39 | R>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs774832261 CA1750198 |
40 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1204304017 CA347563063 |
43 | K>E | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1390555044 CA347563060 |
43 | K>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs764835867 CA1750197 |
44 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs139320001 CA1750196 |
46 | R>* | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs139320001 CA1750195 |
46 | R>G | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs747374601 CA347563043 |
46 | R>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750193 rs747374601 |
46 | R>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
COSM197615 rs747374601 CA1750194 |
46 | R>Q | large_intestine [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated ExAC gnomAD |
|
rs1238197243 CA347563034 |
48 | V>L | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1339697638 CA347563023 |
49 | K>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs773687427 CA1750192 |
51 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs888272079 CA51406098 |
52 | A>T | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs139264120 CA1750191 |
52 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA347562979 rs1239678603 |
56 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs778806637 CA1750189 |
57 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA347562966 rs1573263744 |
58 | D>N | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA347562928 rs1479872895 |
64 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1004476833 CA51406055 |
65 | K>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs745732049 CA1750187 |
67 | M>T | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs377602911 CA1750186 |
68 | I>N | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1171339253 CA347562862 |
73 | A>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs897082944 CA51406027 |
75 | S>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1172942486 CA347562840 |
76 | K>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs757322286 CA1750185 |
78 | Y>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA51406011 rs764294745 |
80 | S>F | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA347562799 rs1244810285 |
83 | H>Y | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750181 rs752418529 |
84 | M>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750179 rs11548928 |
88 | L>F | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs911237858 CA51405990 |
89 | M>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs753416661 CA1750178 |
90 | G>E | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs766860986 CA1750177 |
93 | N>Y | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1212501940 CA347562713 |
95 | L>F | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs368950086 CA1750150 |
96 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs775671590 CA1750147 |
97 | V>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs770016809 CA1750146 |
99 | R>* | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs746864912 CA1750145 |
99 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1204057476 CA347561254 |
100 | V>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750141 rs754597514 |
103 | S>C | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs754597514 CA1750140 |
103 | S>F | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs754597514 CA1750142 |
103 | S>Y | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs753507067 CA1750139 |
104 | L>M | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750138 rs779478429 |
104 | L>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
rs753507067 CA51393858 |
104 | L>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750136 rs749965778 |
105 | Q>P | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA347561224 rs1481158555 |
106 | K>N | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750135 rs768053993 |
106 | K>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC |
|
|
CA347561219 rs1309107963 |
107 | S>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
CA347561211 rs1239426479 |
108 | T>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1573236753 CA347561195 |
110 | V>G | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs757752779 CA1750134 |
111 | M>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs151030608 CA1750133 |
112 | K>N | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750132 rs764585197 |
116 | S>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA347561153 rs1254623189 |
116 | S>N | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs376633964 CA1750131 |
118 | V>M | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA347561125 rs1216872800 |
120 | I>T | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA347561117 rs1316876854 |
121 | P>L | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA347561109 rs1282713848 |
122 | E>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA347561110 rs1282713848 |
122 | E>D | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1006124257 CA51393830 |
124 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs770818481 CA51393825 |
126 | T>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750130 rs148511443 |
127 | M>V | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs540945205 CA1750129 |
129 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA347560924 rs1573236614 |
136 | K>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs766405014 CA1750108 |
140 | I>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs761747904 CA1750107 |
141 | E>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA347559948 rs1462177835 |
144 | L>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750105 rs774273747 |
145 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA347559869 rs1469334620 |
147 | T>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1481680405 CA347559841 |
148 | F>S | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750103 rs199633699 |
152 | D>E | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs144721613 CA1750102 |
153 | D>N | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1305929078 CA347559699 |
154 | Q>R | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750101 rs367837051 |
155 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750100 rs745536967 |
156 | E>D | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA347559603 rs1205641112 |
158 | E>A | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1358705124 CA347559556 |
160 | E>A | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1326612180 CA347559529 |
162 | E>K | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs780703545 CA1750099 |
163 | M>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs912806492 CA51392344 |
164 | E>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA1750097 rs578080094 |
167 | R>I | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA347559437 rs578080094 |
167 | R>T | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA51392316 rs201616389 |
169 | L>I | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA347559410 rs1298238295 |
171 | E>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs553362782 CA51392314 |
173 | T>I | No |
ClinGen 1000Genomes |
|
|
CA347559192 rs932718886 |
176 | A>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA347559195 rs1328266785 |
176 | A>S | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA347559199 rs1328266785 |
176 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA51391558 rs932718886 |
176 | A>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA347559189 rs1364842745 |
177 | L>V | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1471681654 CA347559180 |
178 | G>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1200503151 CA347559155 |
182 | S>G | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750077 rs370256030 |
185 | T>P | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750074 rs754290630 |
189 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1573230781 CA347559085 |
192 | E>D | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
CA1750072 rs756370546 |
192 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs372637780 CA1750071 |
194 | P>L | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750070 rs751335215 |
195 | G>R | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs762838113 CA347559064 |
196 | A>G | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1472946034 CA347559067 |
196 | A>P | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs762838113 CA1750069 |
196 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs765024225 CA1750067 |
197 | M>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA51391521 rs896090722 |
197 | M>L | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1465903669 CA347559055 |
198 | A>T | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
COSM364504 rs1376898188 CA347559030 |
202 | D>N | lung [Cosmic] | No |
ClinGen cosmic curated TOPMed |
|
rs759236870 CA1750066 |
203 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs1386110607 CA347559020 |
203 | E>V | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750065 rs776553670 |
204 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs770673887 CA1750064 |
205 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs770673887 CA347559007 |
205 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs760450254 CA1750063 |
206 | E>K | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
rs937688635 CA347558987 |
207 | E>D | No |
ClinGen TOPMed |
|
|
rs1177172351 CA347558994 |
207 | E>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA347558993 rs1177172351 |
207 | E>Q | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1573230637 CA347558968 |
210 | L>R | No |
ClinGen Ensembl |
|
|
rs1208087749 CA347558945 |
213 | M>I | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1326914668 CA347558942 |
214 | Q>* | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
rs1326914668 CA347558944 |
214 | Q>K | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750057 rs369026092 |
216 | R>Q | No |
ClinGen ESP ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs748612866 CA1750058 |
216 | R>W | No |
ClinGen ExAC TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
CA1750056 rs769276177 |
218 | A>V | No |
ClinGen ExAC gnomAD |
|
|
CA347558906 rs1432424342 |
220 | L>R | No |
ClinGen TOPMed gnomAD |
|
|
rs1327456483 CA347558902 |
221 | R>H | No |
ClinGen gnomAD |
No associated diseases with Q9Y3E7
No regional properties for Q9Y3E7
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for Q9Y3E7 | |||
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | ||
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR10476 | CHARGED MULTIVESICULAR BODY PROTEIN |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR10476:SF1 | CHARGED MULTIVESICULAR BODY PROTEIN 3 |
| PANTHER Protein Class | membrane traffic protein | |
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
15 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| amphisome membrane | Any membrane that is part of an amphisome. |
| autophagosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an autophagosome, a double-membrane-bounded vesicle in which endogenous cellular material is sequestered. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| ESCRT III complex | A complex with membrane scission activity that plays a major role in many processes where membranes are remodelled - including endosomal transport (vesicle budding), nuclear envelope organisation (membrane closure, mitotic bridge cleavage), and cytokinesis (abscission). |
| extracellular exosome | A vesicle that is released into the extracellular region by fusion of the limiting endosomal membrane of a multivesicular body with the plasma membrane. Extracellular exosomes, also simply called exosomes, have a diameter of about 40-100 nm. |
| kinetochore | A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules. |
| kinetochore microtubule | Any of the spindle microtubules that attach to the kinetochores of chromosomes by their plus ends, and maneuver the chromosomes during mitotic or meiotic chromosome segregation. |
| late endosome | A prelysosomal endocytic organelle differentiated from early endosomes by lower lumenal pH and different protein composition. Late endosomes are more spherical than early endosomes and are mostly juxtanuclear, being concentrated near the microtubule organizing center. |
| lysosomal membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the lysosome and separating its contents from the cell cytoplasm. |
| midbody | A thin cytoplasmic bridge formed between daughter cells at the end of cytokinesis. The midbody forms where the contractile ring constricts, and may persist for some time before finally breaking to complete cytokinesis. |
| multivesicular body | A type of endosome in which regions of the limiting endosomal membrane invaginate to form internal vesicles; membrane proteins that enter the internal vesicles are sequestered from the cytoplasm. |
| multivesicular body membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a multivesicular body. |
| nuclear pore | A protein complex providing a discrete opening in the nuclear envelope of a eukaryotic cell, where the inner and outer nuclear membranes are joined. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| phosphatidylcholine binding | Binding to a phosphatidylcholine, a glycophospholipid in which a phosphatidyl group is esterified to the hydroxyl group of choline. |
| ubiquitin-specific protease binding | Binding to a ubiquitin-specific protease. |
26 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| autophagosome maturation | Removal of PI3P and Atg8/LC3 after the closure of the phagophore and before the fusion with the endosome/lysosome (e.g. mammals and insects) or vacuole (yeast), and that very likely destabilizes other Atg proteins and thus enables their efficient dissociation and recycling. |
| autophagy | The cellular catabolic process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm; allows for both recycling of macromolecular constituents under conditions of cellular stress and remodeling the intracellular structure for cell differentiation. |
| endosome transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway | The directed movement of substances from endosomes to lysosomes or vacuoles by a pathway in which molecules are sorted into multivesicular bodies, which then fuse with the target compartment. |
| late endosome to lysosome transport | The directed movement of substances from late endosome to lysosome. |
| late endosome to vacuole transport | The directed movement of substances from late endosomes to the vacuole. In yeast, after transport to the prevacuolar compartment, endocytic content is delivered to the late endosome and on to the vacuole. This pathway is analogous to endosome to lysosome transport. |
| macroautophagy | The major inducible pathway for the general turnover of cytoplasmic constituents in eukaryotic cells, it is also responsible for the degradation of active cytoplasmic enzymes and organelles during nutrient starvation. Macroautophagy involves the formation of double-membrane-bounded autophagosomes which enclose the cytoplasmic constituent targeted for degradation in a membrane-bounded structure. Autophagosomes then fuse with a lysosome (or vacuole) releasing single-membrane-bounded autophagic bodies that are then degraded within the lysosome (or vacuole). Some types of macroautophagy, e.g. pexophagy, mitophagy, involve selective targeting of the targets to be degraded. |
| midbody abscission | The process by which the midbody, the cytoplasmic bridge that connects the two prospective daughter cells, is severed at the end of mitotic cytokinesis, resulting in two separate daughter cells. |
| mitotic metaphase plate congression | The cell cycle process in which chromosomes are aligned at the metaphase plate, a plane halfway between the poles of the mitotic spindle, during mitosis. |
| multivesicular body assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a multivesicular body, a type of late endosome in which regions of the limiting endosomal membrane invaginate to form internal vesicles; membrane proteins that enter the internal vesicles are sequestered from the cytoplasm. |
| multivesicular body sorting pathway | A vesicle-mediated transport process in which transmembrane proteins are ubiquitylated to facilitate their entry into luminal vesicles of multivesicular bodies (MVBs); upon subsequent fusion of MVBs with lysosomes or vacuoles, the cargo proteins are degraded. |
| multivesicular body-lysosome fusion | The organelle membrane fusion process in which the membrane of a multivesicular body fuses with a lysosome to create a hybrid organelle. |
| negative regulation of cell death | Any process that decreases the rate or frequency of cell death. Cell death is the specific activation or halting of processes within a cell so that its vital functions markedly cease, rather than simply deteriorating gradually over time, which culminates in cell death. |
| nuclear membrane reassembly | The reformation of the nuclear membranes following their breakdown in the context of a normal process. |
| nucleus organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane repair | The resealing of a cell plasma membrane after cellular wounding due to, for instance, mechanical stress. |
| protein polymerization | The process of creating protein polymers, compounds composed of a large number of component monomers; polymeric proteins may be made up of different or identical monomers. Polymerization occurs by the addition of extra monomers to an existing poly- or oligomeric protein. |
| protein transport | The directed movement of proteins into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| regulation of centrosome duplication | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of centrosome duplication. Centrosome duplication is the replication of a centrosome, a structure comprised of a pair of centrioles and peri-centriolar material from which a microtubule spindle apparatus is organized. |
| regulation of early endosome to late endosome transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of early endosome to late endosome transport. |
| regulation of mitotic spindle assembly | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of mitotic spindle assembly. |
| suppression of viral release by host | A process in which a host organism stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the release of a virus with which it is infected, from its cells. |
| ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide covalently tagged with ubiquitin, via the multivesicular body (MVB) sorting pathway; ubiquitin-tagged proteins are sorted into MVBs, and delivered to a lysosome/vacuole for degradation. |
| viral budding from plasma membrane | A viral budding that starts with formation of a membrane curvature in the host plasma membrane. |
| viral budding via host ESCRT complex | Viral budding which uses a host ESCRT protein complex, or complexes, to mediate the budding process. |
| viral release from host cell | The dissemination of mature viral particles from the host cell, e.g. by cell lysis or the budding of virus particles from the cell membrane. |
25 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q58CS7 | CHMP3 | Charged multivesicular body protein 3 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q9VE61 | CG7694 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF181 homolog | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q9Y3E7 | CHMP3 | Charged multivesicular body protein 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O00237 | RNF103 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF103 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q86Y13 | DZIP3 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase DZIP3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q7LBR1 | CHMP1B | Charged multivesicular body protein 1b | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O43633 | CHMP2A | Charged multivesicular body protein 2a | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9R1W3 | Rnf103 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF103 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9CQ10 | Chmp3 | Charged multivesicular body protein 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9EPZ8 | Rnf103 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RNF103 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q8CGS4 | Chmp3 | Charged multivesicular body protein 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9SI09 | XERICO | Probable E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase XERICO | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9ZV51 | ATL56 | RING-H2 finger protein ATL56 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SKK8 | ATL22 | RING-H2 finger protein ATL22 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P0CH02 | ATL21B | Putative RING-H2 finger protein ATL21B | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| P0CH01 | ATL21A | Putative RING-H2 finger protein ATL21A | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O22255 | ATL64 | RING-H2 finger protein ATL64 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RXX9 | ATL6 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ATL6 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8GYT9 | SIS3 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SIS3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LZJ6 | ATL5 | RING-H2 finger protein ATL5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8GXF8 | SGR9 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SGR9, amyloplastic | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8LGA5 | ATL31 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ATL31 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LUZ9 | ATL63 | RING-H2 finger protein ATL63 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q5BKM3 | chmp3 | Charged multivesicular body protein 3 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| Q6NY88 | chmp3 | Charged multivesicular body protein 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGLFGKTQEK | PPKELVNEWS | LKIRKEMRVV | DRQIRDIQRE | EEKVKRSVKD | AAKKGQKDVC |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| IVLAKEMIRS | RKAVSKLYAS | KAHMNSVLMG | MKNQLAVLRV | AGSLQKSTEV | MKAMQSLVKI |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PEIQATMREL | SKEMMKAGII | EEMLEDTFES | MDDQEEMEEE | AEMEIDRILF | EITAGALGKA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | ||
| PSKVTDALPE | PEPPGAMAAS | EDEEEEEEAL | EAMQSRLATL | RS |