Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
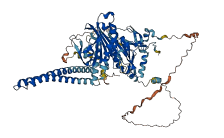
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9WV63
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9WV63-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q9WV63
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9WV63 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q9WV63
Functions
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| centriolar subdistal appendage | A protein complex which assembles on the mother centriole during cilium formation, adjacent and proximal to a centriolar distal appendage. In human, it contains ODF2, CNTRL, NIN, CCDC120c and CCDC68. |
| centriole | A cellular organelle, found close to the nucleus in many eukaryotic cells, consisting of a small cylinder with microtubular walls, 300-500 nm long and 150-250 nm in diameter. It contains nine short, parallel, peripheral microtubular fibrils, each fibril consisting of one complete microtubule fused to two incomplete microtubules. Cells usually have two centrioles, lying at right angles to each other. At division, each pair of centrioles generates another pair and the twin pairs form the pole of the mitotic spindle. |
| centrosome | A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| kinesin complex | Any complex that includes a dimer of molecules from the kinesin superfamily, a group of related proteins that contain an extended region of predicted alpha-helical coiled coil in the main chain that likely produces dimerization. The native complexes of several kinesin family members have also been shown to contain additional peptides, often designated light chains as all of the noncatalytic subunits that are currently known are smaller than the chain that contains the motor unit. Kinesin complexes generally possess a force-generating enzymatic activity, or motor, which converts the free energy of the gamma phosphate bond of ATP into mechanical work. |
| microtubule | Any of the long, generally straight, hollow tubes of internal diameter 12-15 nm and external diameter 24 nm found in a wide variety of eukaryotic cells; each consists (usually) of 13 protofilaments of polymeric tubulin, staggered in such a manner that the tubulin monomers are arranged in a helical pattern on the microtubular surface, and with the alpha/beta axes of the tubulin subunits parallel to the long axis of the tubule; exist in equilibrium with pool of tubulin monomers and can be rapidly assembled or disassembled in response to physiological stimuli; concerned with force generation, e.g. in the spindle. |
| sperm principal piece | The segment of the sperm flagellum where the mitochondrial sheath ends, and the outer dense fibers (ODFs) associated with outer axonemal doublets 3 and 8 are replaced by the 2 longitudinal columns of the fibrous sheath (FS) which run the length of the principal piece and are stabilized by circumferential ribs. The principal piece makes up ~2/3 of the length of the sperm flagellum and is defined by the presence of the FS and of only 7 (rather than 9) ODFs which taper and then terminate near the distal end of the principal piece. |
| spindle | The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart. |
| spindle pole | Either of the ends of a spindle, where spindle microtubules are organized; usually contains a microtubule organizing center and accessory molecules, spindle microtubules and astral microtubules. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| microtubule binding | Binding to a microtubule, a filament composed of tubulin monomers. |
| microtubule motor activity | A motor activity that generates movement along a microtubule, driven by ATP hydrolysis. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
8 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cell division | The process resulting in division and partitioning of components of a cell to form more cells; may or may not be accompanied by the physical separation of a cell into distinct, individually membrane-bounded daughter cells. |
| microtubule cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising microtubules and their associated proteins. |
| microtubule-based movement | A microtubule-based process that results in the movement of organelles, other microtubules, or other cellular components. Examples include motor-driven movement along microtubules and movement driven by polymerization or depolymerization of microtubules. |
| mitotic spindle assembly | Mitotic bipolar spindle assembly begins with spindle microtubule nucleation from the separated spindle pole body, includes spindle elongation during prometaphase, and is complete when all kinetochores are stably attached the spindle, and the spindle assembly checkpoint is satisfied. |
| mitotic spindle organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the microtubule spindle during a mitotic cell cycle. |
| nervous system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of nervous tissue over time, from its formation to its mature state. |
| regulation of cell migration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q2NL05 | KIF2A | Kinesin-like protein KIF2A | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| O00139 | KIF2A | Kinesin-like protein KIF2A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6QLM7 | Kif5a | Kinesin heavy chain isoform 5A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1M5N7 | Kif21b | Kinesin-like protein KIF21B | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q2PQA9 | Kif5b | Kinesin-1 heavy chain | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q7M6Z5 | Kif27 | Kinesin-like protein KIF27 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MATANFGKIQ | IGIYVEIKRS | DGRIHQAMVT | SLNEDNESVT | VEWIENGDTK | GKEIDLESIF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| SLNPDLVPDE | DIEPSPEIPP | PSSSSKVNKI | VKNRRTVASI | KNDPPPRDNR | VVGSARARPS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QLPEQSSSAQ | QNGSVSDISP | VQAAKKEFGP | PSRRKSNCVK | EVEKLQEKRE | KRRLQQQELR |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| EKRAQDVDAT | NPNYEIMCMI | RDFRGSLDYR | PLTTADPIDE | HRICVCVRKR | PLNKKETQMK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| DLDVITIPSK | DVVMVHEPKQ | KVDLTRYLEN | QTFRFDYAFD | DSAPNEMVYR | FTARPLVETI |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| FERGMATCFA | YGQTGSGKTH | TMGGDCSGKN | QDCSKGIYAL | AARDVFLMLK | KPNYKKLELQ |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| VYATFFEIYS | GKVFDLLNRK | TKLRVLEDGK | QQVQVVGLQE | REVKCVEDVL | KLIDIGNSCR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| TSGQTSANAH | SSRSHAVFQI | ILRRKGKLHG | KFSLIDLAGN | ERGADTSSAD | RQTRLEGAEI |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| NKSLLALKEC | IRALGRNKPH | TPFRASKLTQ | VLRDSFIGEN | SRTCMIATIS | PGMASCENTL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| NTLRYANRVK | ELTVDPTAAG | DVRPIMHHPP | SQIDDLETQW | GVGSSPQRDD | LKLLCEQNEE |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| EVSPQLFTFH | EAVSQMVEME | EQVVEDHRAV | FQESIRWIED | EKALLEMTEE | VDYDVDSYAT |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | ||
| QLEAILEQKI | DILTELRDKV | KSFRAALQEE | EQASKQINPK | RPRAL |