Q9VL72
Gene name |
Etl1 (CG5899) |
Protein name |
SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A containing DEAD/H box 1 homolog |
Names |
Enhancer trap locus homolog 1, Etl-1 |
Species |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
KEGG Pathway |
dme:Dmel_CG5899 |
EC number |
3.6.4.12: Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
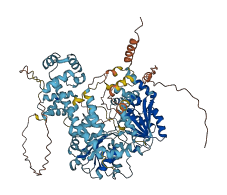
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9VL72
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9VL72-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q9VL72
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9VL72 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q9VL72
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.4.12 | Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
1 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA | Catalytic activity that acts to modify DNA, driven by ATP hydrolysis. |
| ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity | An activity, driven by ATP hydrolysis, that modulates the contacts between histones and DNA, resulting in a change in chromosome architecture within the nucleosomal array, leading to chromatin remodeling. |
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| DNA helicase activity | Unwinding of a DNA helix, driven by ATP hydrolysis. |
3 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| defense response to Gram-negative bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a Gram-negative bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| DNA repair | The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway. |
| positive regulation of innate immune response | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the innate immune response, the organism's first line of defense against infection. |
3 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P31380 | FUN30 | ATP-dependent helicase FUN30 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q24368 | Iswi | Chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase chain Iswi | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9H4L7 | SMARCAD1 | SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A containing DEAD/H box 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSDSTVAASA | SASASSSAKS | SLSDLRQFRI | NKNASSVVAS | PSRTERVPGK | KRIQVMADSD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| SDGNDSQTPK | KTKLELTVKE | KEERYMAAAK | ISPHFDTMAI | QESLSRTNWD | VAASVRYLRE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| NCKPKGHNGP | LAKSKLKPRS | NGISGGNFSD | NDHSDDDDVK | QSKDQVYDSD | DSDSEMSTKM |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TGQRKKVFQF | MNEASLIELQ | SVKTLSEKKA | LAIIDVRPFS | DWSDLRQKLE | SIRMSGDLLN |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| YAQELINKQN | TVAAILSKCN | NMVSRLEKAI | SNGAGIVEQP | KLLSSGLQLA | DYQIIGLNWL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TVMHKQEMNG | ILADEMGLGK | TIQVIAFLAY | LKENGLSQAA | HLIVVPSSTL | DNWEAEISRW |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| CPELVVEKYH | GSQDERRRMR | GRFAKDGFTG | FDVLLTTYHI | VGSTPEERKM | FRVCKLDYVI |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| FDEAHMLKNM | TTQRYANLIT | INARMRILLT | GTPLQNNLLE | LISLLCFVMP | KFFAKSIEDI |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| KSLFAKKGKS | DGDQDEVSQF | QETQIQRAKR | IMKPFVLRRL | KKDVLKNLPK | KLSLVEKVPM |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| SSQQKIYYHE | LVDYYSNNKG | EVCSSSERAG | IAIMMEMRRI | ANHPLLMRHY | FTDANLRGFS |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| KRLANASSFK | KTNEQYIFEE | LAVMSDFQVY | QMMNKHEFYD | VKIPDNLICD | SGKFLYLDTL |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| LPKLKAEGHR | VLLFSQFTMM | LDIVEEYLRI | RKFGFCRLDG | ATAVNVRQDL | ITDFNGDDSI |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| FVFLLSTKAG | GVGINLTAAD | TCVIHDIDFN | PYNDKQAEDR | CHRMGQQRPV | TIYRLISEST |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| IEEGILMAAE | EKLKLEKDIT | SNEKGEVHEQ | RCVVKLLTTA | LGLDKDQEEQ | LNNSLNNSIA |
| SPAK |