Q9VK34
Gene name |
Sirt1 |
Protein name |
NAD-dependent histone deacetylase sirtuin-1 |
Names |
Silent information regulator 2 |
Species |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
KEGG Pathway |
dme:Dmel_CG5216 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
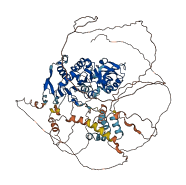
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9VK34
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9VK34-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q9VK34
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9VK34 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q9VK34
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nuclear inner membrane | The inner, i.e. lumen-facing, lipid bilayer of the nuclear envelope. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| rDNA heterochromatin | A region of heterochromatin located at the rDNA repeats in a chromosome. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| histone deacetylase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: histone N6-acetyl-L-lysine + H2O = histone L-lysine + acetate. This reaction represents the removal of an acetyl group from a histone, a class of proteins complexed to DNA in chromatin and chromosomes. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| NAD+ binding | Binding to the oxidized form, NAD, of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a coenzyme involved in many redox and biosynthetic reactions. |
| NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: histone N6-acetyl-L-lysine + H2O = histone L-lysine + acetate. This reaction requires the presence of NAD, and represents the removal of an acetyl group from a histone. |
| p53 binding | Binding to one of the p53 family of proteins. |
| protein lysine deacetylase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: H2O + N6-acetyl-L-lysyl- |
| transcription corepressor activity | A transcription coregulator activity that represses or decreases the transcription of specific gene sets via binding to a DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factor, either on its own or as part of a complex. Corepressors often act by altering chromatin structure and modifications. For example, one class of transcription corepressors modifies chromatin structure through covalent modification of histones. A second class remodels the conformation of chromatin in an ATP-dependent fashion. A third class modulates interactions of DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factors with other transcription coregulators. |
| transcription factor binding | Binding to a transcription factor, a protein required to initiate or regulate transcription. |
| transferase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a group, e.g. a methyl group, glycosyl group, acyl group, phosphorus-containing, or other groups, from one compound (generally regarded as the donor) to another compound (generally regarded as the acceptor). Transferase is the systematic name for any enzyme of EC class 2. |
16 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| behavioral response to ethanol | Any process that results in a change in the behavior of an organism as a result of an ethanol stimulus. |
| cellular response to insulin stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| determination of adult lifespan | The pathways that regulate the duration of the adult phase of the life-cycle of an animal. |
| heterochromatin assembly | An epigenetic gene silencing mechanism in which chromatin is compacted into heterochromatin, resulting in a chromatin conformation refractory to transcription. This process starts with heterochromatin nucleation, its spreading, and ends with heterochromatin boundary formation. |
| histone deacetylation | The modification of histones by removal of acetyl groups. |
| histone H3 deacetylation | The modification of histone H3 by the removal of one or more acetyl groups. |
| lateral inhibition | Signaling between cells of equivalent developmental potential that results in these cells adopting different developmental fates. An example is the suppression by cells with a particular fate of the adoption of the same fate by surrounding cells. |
| negative regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| peptidyl-lysine deacetylation | The removal of an acetyl group from an acetylated lysine residue in a peptide or protein. |
| positive regulation of feeding behavior | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of feeding behavior. |
| positive regulation of Notch signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the Notch signaling pathway. |
| protein deacetylation | The removal of an acetyl group from a protein amino acid. An acetyl group is CH3CO-, derived from acetic |
| regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that modulates the occurrence or rate of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| regulation of histone acetylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of an acetyl group to a histone protein. |
| regulation of response to ethanol | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of response to ethanol. |
4 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9I7I7 | Sirt2 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase Sirt2 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q96EB6 | SIRT1 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q923E4 | Sirt1 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q68FX9 | Sirt5 | NAD-dependent protein deacylase sirtuin-5, mitochondrial | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MMENYEEIRL | GHIRSKDLGN | QVPDTTQFYP | PTKFDFGAEI | LASTSTEAEA | EAEATATTTE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PATSELAGKA | NGEIKTKTLA | AREEQEIGAN | LEHKTKNPTK | SMGEDEDDEE | EEEEDDEEEE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| EDDEEGITGT | SNEDEDSSSN | CSSSVEPDWK | LRWLQREFYT | GRVPRQVIAS | IMPHFATGLA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GDTDDSVLWD | YLAHLLNEPK | RRNKLASVNT | FDDVISLVKK | SQKIIVLTGA | GVSVSCGIPD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| FRSTNGIYAR | LAHDFPDLPD | PQAMFDINYF | KRDPRPFYKF | AREIYPGEFQ | PSPCHRFIKM |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LETKGKLLRN | YTQNIDTLER | VAGIQRVIEC | HGSFSTASCT | KCRFKCNADA | LRADIFAQRI |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| PVCPQCQPNK | EQSVDASVAV | TEEELRQLVE | NGIMKPDIVF | FGEGLPDEYH | TVMATDKDVC |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| DLLIVIGSSL | KVRPVAHIPS | SIPATVPQIL | INREQLHHLK | FDVELLGDSD | VIINQICHRL |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| SDNDDCWRQL | CCDESVLTES | KELMPPEHSN | HHLHHHLLHH | RHCSSESERQ | SQLDTDTQSI |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| KSNSSADYIL | GSAGTCSDSG | FESSTFSCGK | RSTAAEAAAI | ERIKTDILVE | LNETTALSCD |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| RLGLEGPQTT | VESYRHLSID | SSKDSGIEQC | DNEATPSYVR | PSNLVQETKT | VAPSLTPIPQ |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| QRGKRQTAAE | RLQPGTFYSH | TNNYSYVFPG | AQVFWDNDYS | DDDDEEEERS | HNRHSDLFGN |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| VGHNYKDDDE | DACDLNAVPL | SPLLPPSLEA | HIVTDIVNGS | NEPLPNSSPG | QKRTACIIEQ |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | ||
| QPTPAIETEI | PPLKKRRPSE | ENKQQTQIER | SEESPPPGQL | AAV |