Q9V9J3
Gene name |
Src42A (Src41, TK5, CG44128) |
Protein name |
Tyrosine-protein kinase Src42A |
Names |
EC 2.7.10.2 , Tyrosine-protein kinase Src41 , Dsrc41 |
Species |
Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) |
KEGG Pathway |
dme:Dmel_CG44128 |
EC number |
2.7.10.2: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
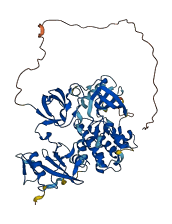
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
248-504 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
248-504 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Target domain |
248-504 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
387-411 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
248-504 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
387-411 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
248-504 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Hong E et al. (2004) "Solution structure and backbone dynamics of the non-receptor protein-tyrosine kinase-6 Src homology 2 domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 29700-8
- Ko S et al. (2009) "Structural basis of the auto-inhibition mechanism of nonreceptor tyrosine kinase PTK6", Biochemical and biophysical research communications, 384, 236-42
- Qiu H et al. (2002) "Regulation of the nonreceptor tyrosine kinase Brk by autophosphorylation and by autoinhibition", The Journal of biological chemistry, 277, 34634-41
- Williams JC et al. (1997) "The 2.35 A crystal structure of the inactivated form of chicken Src: a dynamic molecule with multiple regulatory interactions", Journal of molecular biology, 274, 757-75
- Boggon TJ et al. (2004) "Structure and regulation of Src family kinases", Oncogene, 23, 7918-27
- Meng Y et al. (2014) "Locking the active conformation of c-Src kinase through the phosphorylation of the activation loop", Journal of molecular biology, 426, 423-35
- Register AC et al. (2014) "SH2-catalytic domain linker heterogeneity influences allosteric coupling across the SFK family", Biochemistry, 53, 6910-23
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9V9J3
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9V9J3-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q9V9J3
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9V9J3 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q9V9J3
7 regional properties for Q9V9J3
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 248 - 504 | IPR000719 |
| domain | SH2 domain | 128 - 222 | IPR000980 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 248 - 500 | IPR001245 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 63 - 124 | IPR001452 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 366 - 378 | IPR008266 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 254 - 276 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 248 - 500 | IPR020635 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.2 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The component of a plasma membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to its cytoplasmic surface, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| non-membrane spanning protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| signaling receptor binding | Binding to one or more specific sites on a receptor molecule, a macromolecule that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
28 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament bundle assembly | The assembly of actin filament bundles; actin filaments are on the same axis but may be oriented with the same or opposite polarities and may be packed with different levels of tightness. |
| adherens junction organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an adherens junction. An adherens junction is a cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex at which the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane is attached to actin filaments. |
| apoptotic cell clearance | The recognition and removal of an apoptotic cell by a neighboring cell or by a phagocyte. |
| axon guidance | The chemotaxis process that directs the migration of an axon growth cone to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| cell differentiation | The cellular developmental process in which a relatively unspecialized cell, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cell, acquires specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize a specific cell. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. |
| compound eye development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the compound eye over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The compound eye is an organ of sight that contains multiple repeating units, often arranged hexagonally. Each unit has its own lens and photoreceptor cell(s) and can generate either a single pixelated image or multiple images, per eye. |
| defense response to bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| dorsal closure | The process during Drosophila embryogenesis whereby the ectodermal cells of the lateral epithelium stretch in a coordinated fashion to internalize the amnioserosa cells and close the embryo dorsally. |
| dorsal closure, spreading of leading edge cells | Dorsally-directed movement of a cell at the leading edge of the epithelium over the amnioserosa. |
| epithelial cell-cell adhesion | The attachment of an epithelial cell to another epithelial cell via adhesion molecules. |
| hydrogen peroxide mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals mediated by the detection of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). |
| imaginal disc fusion, thorax closure | The joining of the parts of the wing imaginal discs, giving rise to the adult thorax. |
| imaginal disc-derived wing morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the imaginal disc-derived wing are generated and organized. The wing is an appendage modified for flying. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| intestinal stem cell homeostasis | Any biological process involved in the maintenance of the steady-state number of intestinal stem cells within a population of cells. |
| negative regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway activity. |
| negative regulation of synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of synaptic assembly at neuromuscular junction. |
| open tracheal system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an open tracheal system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. An open tracheal system is a respiratory system, a branched network of epithelial tubes that supplies oxygen to target tissues via spiracles. An example of this is found in Drosophila melanogaster. |
| peptidyl-tyrosine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-tyrosine to form peptidyl-O4'-phospho-L-tyrosine. |
| positive regulation of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling pathway activity. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of inflammatory response to wounding | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response to wounding. |
| positive regulation of sevenless signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the sevenless signaling pathway. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of synaptic plasticity | A process that modulates synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to change as circumstances require. They may alter function, such as increasing or decreasing their sensitivity, or they may increase or decrease in actual numbers. |
| salivary gland morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the salivary gland are generated and organized. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
78 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q0VBZ0 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3ZC95 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase | Bos taurus (Bovine) | EV SS |
| A0JNB0 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| P41239 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q8JH64 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q75R65 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P00523 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | EV |
| P09324 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q02977 | YRK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Yrk | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P42683 | LCK | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q05876 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q24592 | hop | Tyrosine-protein kinase hopscotch | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P00528 | Src64B | Tyrosine-protein kinase Src64B | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P00522 | Abl | Tyrosine-protein kinase Abl | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P08630 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Btk | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P41240 | CSK | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P23458 | JAK1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P51813 | BMX | Cytoplasmic tyrosine-protein kinase BMX | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42680 | TEC | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O60674 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P42679 | MATK | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P52333 | JAK3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q08881 | ITK | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P29597 | TYK2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13882 | PTK6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q06187 | BTK | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P06239 | LCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lck | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P06241 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P07948 | LYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P08631 | HCK | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P12931 | SRC | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P07947 | YES1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P09769 | FGR | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P51451 | BLK | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P42685 | FRK | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9R117 | Tyk2 | Non-receptor tyrosine-protein kinase TYK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62270 | Srms | Tyrosine-protein kinase Srms | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q64434 | Ptk6 | Protein-tyrosine kinase 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P35991 | Btk | Tyrosine-protein kinase BTK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P41241 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q62137 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62120 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P24604 | Tec | Tyrosine-protein kinase Tec | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P52332 | Jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03526 | Itk | Tyrosine-protein kinase ITK/TSK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P41242 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P08103 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P25911 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P39688 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P05480 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P06240 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P14234 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P16277 | Blk | Tyrosine-protein kinase Blk | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q04736 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q922K9 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| A1Y2K1 | FYN | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| O19064 | JAK2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q62689 | Jak2 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q63272 | Jak3 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P32577 | Csk | Tyrosine-protein kinase CSK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P41243 | Matk | Megakaryocyte-associated tyrosine-protein kinase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P50545 | Hck | Tyrosine-protein kinase HCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q07014 | Lyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Lyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9WUD9 | Src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| F1LM93 | Yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase Yes | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62662 | Frk | Tyrosine-protein kinase FRK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q62844 | Fyn | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fyn | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6P6U0 | Fgr | Tyrosine-protein kinase Fgr | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q01621 | Lck | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase LCK | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G5ECJ6 | csk-1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase csk-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| G5EE56 | src-1 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| O45539 | src-2 | Tyrosine protein-kinase src-2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q2MHE4 | HT1 | Serine/threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase HT1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O12990 | jak1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase JAK1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q6EWH2 | fyna | Tyrosine-protein kinase fyna | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| A1A5H8 | yes1 | Tyrosine-protein kinase yes | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| F1RDG9 | fynb | Tyrosine-protein kinase fynb | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q1JPZ3 | src | Proto-oncogene tyrosine-protein kinase Src | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGNCLTTQKG | EPDKPADRIK | LDDPPTIGVG | VGVPQIPMPS | HAGQPPEQIR | PVPQIPESET |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AGANAKIFVA | LYDYDARTDE | DLSFRKGEHL | EILNDTQGDW | WLARSKKTRS | EGYIPSNYVA |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KLKSIEAEPW | YFRKIKRIEA | EKKLLLPENE | HGAFLIRDSE | SRHNDYSLSV | RDGDTVKHYR |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| IRQLDEGGFF | IARRTTFRTL | QELVEHYSKD | SDGLCVNLCK | PCVQIEKPVT | EGLSHRTRDQ |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| WEIDRTSLKF | VRKLGSGQFG | DVWEGLWNNT | TPVAIKTLKS | GTMDPKDFLA | EAQIMKKLRH |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TKLIQLYAVC | TVEEPIYIIT | ELMKHGSLLE | YLQAIAGKGR | SLKMQTLIDM | AAQIAAGMAY |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LESQNYIHRD | LAARNVLVGD | GNIVKIADFG | LARLIKEDEY | EARVGARFPI | KWTAPEAANY |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SKFSIKSDVW | SFGILLTELV | TYGRIPYPGM | TNAEVLTQVE | HGYRMPQPPN | CEPRLYEIML |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | |||
| ECWHKDPMRR | PTFETLQWKL | EDFYTSDQSD | YKEAQAY |