Q9U280
Gene name |
tat-1 (Y49E10.11) |
Protein name |
Phospholipid-transporting ATPase tat-1 |
Names |
TAT-1 |
Species |
Caenorhabditis elegans |
KEGG Pathway |
cel:CELE_Y49E10.11 |
EC number |
7.6.2.1: Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate |
Protein Class |
|
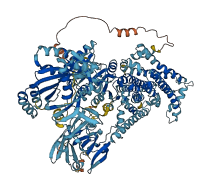
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9U280
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9U280-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q9U280
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9U280 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q9U280
1 regional properties for Q9U280
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Fork head domain | 174 - 266 | IPR001766 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 7.6.2.1 | Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
12 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| basolateral plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane that includes the basal end and sides of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| early endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an early endosome. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| late endosome | A prelysosomal endocytic organelle differentiated from early endosomes by lower lumenal pH and different protein composition. Late endosomes are more spherical than early endosomes and are mostly juxtanuclear, being concentrated near the microtubule organizing center. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| recycling endosome | An organelle consisting of a network of tubules that functions in targeting molecules, such as receptors transporters and lipids, to the plasma membrane. |
| recycling endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a recycling endosome. |
| trans-Golgi network | The network of interconnected tubular and cisternal structures located within the Golgi apparatus on the side distal to the endoplasmic reticulum, from which secretory vesicles emerge. The trans-Golgi network is important in the later stages of protein secretion where it is thought to play a key role in the sorting and targeting of secreted proteins to the correct destination. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| ATPase-coupled intramembrane lipid transporter activity | Catalysis of the movement of lipids from one membrane leaflet to the other, driven by ATP hydrolysis. This includes flippases and floppases. |
| magnesium ion binding | Binding to a magnesium (Mg) ion. |
| phosphatidylserine floppase activity | Catalysis of the movement of phosphatidylserine from the cytosolic to the exoplasmic leaftlet of a membrane, using energy from the hydrolysis of ATP. |
6 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| endocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process in which cells take up external materials or membrane constituents by the invagination of a small region of the plasma membrane to form a new membrane-bounded vesicle. |
| lysosome organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a lysosome. A lysosome is a cytoplasmic, membrane-bounded organelle that is found in most animal cells and that contains a variety of hydrolases. |
| negative regulation of phagocytosis, engulfment | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the internalization of bacteria, immune complexes and other particulate matter or of an apoptotic cell by phagocytosis. |
| phospholipid translocation | The movement of a phospholipid molecule from one leaflet of a membrane bilayer to the opposite leaflet. |
| phospholipid transport | The directed movement of phospholipids into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. Phospholipids are any lipids containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester. |
| positive regulation of phagocytosis, engulfment | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the internalization of bacteria, immune complexes and other particulate matter or of an apoptotic cell by phagocytosis. |
11 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P39524 | DRS2 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase DRS2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | EV |
| Q9P241 | ATP10D | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase VD | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8TF62 | ATP8B4 | Probable phospholipid-transporting ATPase IM | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P98198 | ATP8B2 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase ID | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O43520 | ATP8B1 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase IC | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9Y2Q0 | ATP8A1 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase IA | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q148W0 | Atp8b1 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase IC | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P98199 | Atp8b2 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase ID | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P70704 | Atp8a1 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase IA | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| D4AA47 | Atp8b1 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase IC | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q5BL50 | atp8b1 | Phospholipid-transporting ATPase IC | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPTEARDNNR | HIHLGKVRDP | HHQHAQRFCS | NRISTCKYNG | FSFLPRFLYE | QFRRYNNIFF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LAIALLQQIP | DVSPTGRYTT | AVPFLIILSV | SALKEIFEDV | KRRRSDNKVN | AFSVEILVDG |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| HWIEKQWKDV | SVGDFIRIDN | DSLFPADLLL | LASSEQQGMA | YIETSNLDGE | TNLKIKQALD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| ITSTMTSPEK | LSQFESEITC | EPPSRHVNEF | NGNIEINGVA | RHFGIDQLLL | RGARLKNTAW |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| IFGAVIYTGH | DSKLLMNSKR | APLKSGTIDV | QTNYRIIFLF | FVLVALALIS | ATGSEIWRGN |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| NIPQAWYLSF | LEHDPKGSFL | WGVLTFFILY | NNLIPISLQV | TLEVVRFFQA | IYINNDIEMY |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| DVNSDSCAIA | RTSNLNEELG | QVKFIMSDKT | GTLTRNVMKF | KRLSIGSRNY | GNNEDDEFAD |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| ASLIEDYRQG | DEHSTSILEV | LKMMAVCHTV | VPENKDGQLI | YQSSSPDEAA | LVRGAASQSV |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| SFHTRQPQKV | ICNVFGEDET | IEILDVIDFT | SDRKRMSVIV | RDGAGGDIKL | YTKGADTVIF |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| ERLEHGKEQE | EAVEYCTEHL | EDYASFGYRT | LCFSMRHLTE | QEYSQWAPEY | KKAILAIDNR |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| AKLLADAAEK | LERNMILVGA | TAIEDKLQEW | VPETIQALMA | ADIRVWMLTG | DKRETAINIA |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| HSCALCHTNT | ELLIVDKTTY | EETYQKLEQF | VARAIELEKQ | EKGFAMVIDG | KSLLHALTGE |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| ARKHFGDLAL | RCHAVVCCRM | SPMQKAEVVE | MVRKLAKHVV | LAIGDGANDV | AMIQAANVGV |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| GISGEEGLQA | ASASDYAIPR | FHFLRRLLLV | HGAWNHDRSV | KVILYSFYKN | ICLYIIELWF |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| AMFSAWSGQT | IFERWTIGMF | NVIFTAWPPV | VLGLFDHPVP | AEQIMKYPAL | YASFQNRAFS |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| IGNFSLWIGL | AIVHSLSLFF | LTYATMEHQV | VWDNGLTGGW | LMLGNCAYTF | VVATVCFKAL |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| LECDSWTWPV | VVACIGSIGL | WIVFVIVYSL | VFPHIGGIGA | DMAGMAAIMM | SSYTFWLALL |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| FIPLATLLWD | LVIKSLFTIA | MPTPRELAVM | YNKRTTSFNG | FERLASYSSN | VLENMRLLTS |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | |
| SLRGSTTGST | RSRTASEASL | ALAEQTRYGF | AFSQDESSAV | AQTELIRNVD | STREKPTGR |