Q9SU24
Gene name |
ORC1B |
Protein name |
Origin of replication complex subunit 1B |
Names |
AtORC1b, Origin recognition complex 1b protein, Protein UNFERTILIZED EMBRYO SAC 13 |
Species |
Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) |
KEGG Pathway |
ath:AT4G12620 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

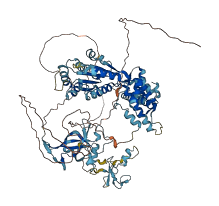
2 structures for Q9SU24
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5HH7 | X-ray | 190 A | A | 118-349 | PDB |
| AF-Q9SU24-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
88 variants for Q9SU24
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSVATH06634590 | 6 | R>K | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634588 | 10 | F>C | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH14157297 | 11 | K>E | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634586 | 14 | T>A | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7462213_G_T | 14 | T>N | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7462204_G_A | 17 | P>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634585 | 18 | S>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634583 | 28 | P>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7462157_G_A | 33 | H>Y | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634582 | 34 | T>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH14157296 | 38 | P>A | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634581 | 40 | T>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586489 | 43 | P>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586488 | 52 | S>Y | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634580 | 55 | I>F | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7462082_C_G | 58 | G>R | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586487 | 59 | N>H | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7462076_C_A | 60 | D>Y | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH02805226 | 61 | P>Q | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH02805225 | 82 | A>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7462009_G_A | 82 | A>V | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7462007_G_C | 83 | P>A | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634579 | 86 | P>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586486 | 92 | P>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7461970_G_A | 95 | S>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH02805224 | 99 | E>D | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH02805223 | 107 | I>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586434 | 113 | V>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634578 | 114 | S>P | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634577 | 121 | I>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634576 | 123 | K>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586433 | 124 | T>M | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586433 | 124 | T>R | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586431 | 160 | E>K | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7461764_G_A | 164 | P>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH14157295 | 178 | N>Y | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634574 | 197 | P>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7461569_G_T | 229 | P>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7461563_C_G | 231 | G>R | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH02805207 | 237 | T>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634573 | 238 | M>K | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7461502_C_T | 251 | R>Q | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7461469_C_G | 262 | G>A | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7461422_C_T | 278 | V>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH02805194 | 365 | V>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH14157275 | 378 | V>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634571 | 385 | G>R | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7461061_C_T | 398 | G>E | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7461034_C_T | 407 | G>E | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7461013_T_C | 414 | H>R | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634570 | 420 | Q>H | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586426 | 426 | A>V | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586425 | 449 | I>V | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH00496017 | 452 | F>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH00496017 | 452 | F>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634569 | 467 | M>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586354 | 511 | A>P | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460672_G_C | 528 | R>G | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460671_C_A | 528 | R>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460614_C_G | 547 | R>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460499_G_C | 585 | N>K | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH02805176 | 586 | S>C | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460407_A_T | 616 | L>Q | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460386_T_C | 623 | H>R | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH02805174 | 627 | Q>H | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634567 | 632 | T>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586353 | 635 | N>D | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460350_T_C | 635 | N>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460257_C_G | 666 | C>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460254_C_T | 667 | R>K | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH00496015 | 673 | A>V | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460218_G_A | 679 | T>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634565 | 683 | A>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460200_T_G | 685 | N>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634564 | 689 | I>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH02805172 | 691 | A>V | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460180_C_T | 692 | D>N | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH11586352 | 693 | V>A | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634563 | 695 | A>E | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634561 | 711 | S>G | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460119_A_G | 712 | V>A | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH08332859 | 715 | L>R | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH14157252 | 725 | H>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634556 | 745 | S>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7460005_G_C | 750 | T>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH14157251 | 752 | G>R | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_4_7459985_C_T | 757 | G>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06634555 | 758 | W>S | No | 1000Genomes |
No associated diseases with Q9SU24
7 regional properties for Q9SU24
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Bromo adjacent homology (BAH) domain | 200 - 344 | IPR001025 |
| domain | Zinc finger, PHD-type | 168 - 213 | IPR001965 |
| domain | AAA+ ATPase domain | 463 - 617 | IPR003593 |
| domain | ATPase, AAA-type, core | 467 - 613 | IPR003959 |
| conserved_site | Zinc finger, PHD-type, conserved site | 169 - 212 | IPR019786 |
| domain | Zinc finger, PHD-finger | 166 - 215 | IPR019787 |
| domain | AAA lid domain | 641 - 676 | IPR041083 |
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| nuclear origin of replication recognition complex | A multisubunit complex that is located at the replication origins of a chromosome in the nucleus. |
| origin recognition complex | A multisubunit complex that is located at the replication origins of a chromosome. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| DNA replication origin binding | Binding to a DNA replication origin, a unique DNA sequence of a replicon at which DNA replication is initiated and proceeds bidirectionally or unidirectionally. |
| double-stranded methylated DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded methylated DNA. Methylation of cytosine or adenine in DNA is an important mechanism for establishing stable heritable epigenetic marks. |
| histone binding | Binding to a histone, any of a group of water-soluble proteins found in association with the DNA of eukaryotic or archaeal chromosomes. They are involved in the condensation and coiling of chromosomes during cell division and have also been implicated in gene regulation and DNA replication. They may be chemically modified (methylated, acetlyated and others) to regulate gene transcription. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
5 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA replication | The cellular metabolic process in which a cell duplicates one or more molecules of DNA. DNA replication begins when specific sequences, known as origins of replication, are recognized and bound by initiation proteins, and ends when the original DNA molecule has been completely duplicated and the copies topologically separated. The unit of replication usually corresponds to the genome of the cell, an organelle, or a virus. The template for replication can either be an existing DNA molecule or RNA. |
| DNA replication initiation | The process in which DNA-dependent DNA replication is started; this begins with the ATP dependent loading of an initiator complex onto the DNA, this is followed by DNA melting and helicase activity. In bacteria, the gene products that enable the helicase activity are loaded after the initial melting and in archaea and eukaryotes, the gene products that enable the helicase activity are inactive when they are loaded and subsequently activate. |
| double fertilization forming a zygote and endosperm | Fertilization where one of the two sperm nuclei from the pollen tube fuses with the egg nucleus to form a 2n zygote, and the other fuses with the two polar nuclei to form the 3n primary endosperm nucleus and then develops into the endosperm. The ploidy level of the 2n zygote and 3n primary endosperm nucleus is determined by the ploidy level of the parents involved. An example of this component is found in Arabidopsis thaliana. |
| mitotic DNA replication checkpoint signaling | A signal transduction process that contributes to a mitotic DNA replication checkpoint. |
| regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
7 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P54784 | ORC1 | Origin recognition complex subunit 1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q58DC8 | ORC1 | Origin recognition complex subunit 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| O16810 | Orc1 | Origin recognition complex subunit 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | EV |
| Q13415 | ORC1 | Origin recognition complex subunit 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9Z1N2 | Orc1 | Origin recognition complex subunit 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q80Z32 | Orc1 | Origin recognition complex subunit 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q710E8 | ORC1A | Origin of replication complex subunit 1A | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MASTPRAKTF | KSPTKTPSNI | YRKSYLSPSS | TSHTPQTPET | HTPLRRSARH | VSRKIDLGND |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| PIDAPGNDPI | EGMNLIRKRE | RAPRKPTTDV | VPSKSKKTET | PKKKKKIDSF | TPVSPIRSET |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| IKKTKKKKRV | YYNKVEFDET | EFEIGDDVYV | KRREDSNSDE | EEDPEIEDCQ | ICFKSDTNIM |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| IECDDCLGGF | HLKCLKPPLK | EVPEGDWICQ | FCEVKKSGQS | QTLDLPKPPE | GKKLARTMRE |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| KLLSGDLWAA | RIDKLWKEVD | DGVYWIRARW | YMIPEETVSG | RQPHNLKREL | YLTNDFADIE |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| MECILRHCSV | KCPKEFSKAS | NDGDDVFLCE | YEYDVHWRSF | KRLAELADGD | SDSDQEWNGR |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KEEEVDDSDE | EMELDDEVLK | SKRGGLTSAR | GGANSRKGRF | FGVEKVGMKL | IPEHVRCHKQ |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SELEKAKATL | LLATRPKSLP | CRSKEMEEIT | SFIKGSISDD | QCLGRCMYIH | GVPGTGKTIS |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| VLSVMKNLKA | EVEEGSVSPY | CFVEINGLKL | ASPENIYSVI | YEALSGHRVG | WKKALQCLNE |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| RFAEGKRIGK | EDEKPCILLI | DELDLLVTRN | QSVLYNILDW | PTKPNSKLVV | LGIANTMDLP |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| EKLLPRISSR | MGIQRLCFGP | YNHTQLQEII | STRLNGIDAF | EKTAIEFASR | KVAAISGDAR |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| RALEICRRAA | EVADHRLNTN | KSAKNQLVIM | ADVEAAIQEM | FQAPHIQVMK | SVSKLSKIFL |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| TAMVHELYKT | GMAETTFDRV | ATTVSSICLT | NGEAFPGWDI | LLKIGCDLGE | CRIILCEPGE |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | |||
| KHRLQKLQLN | FPSDDVAFAL | KDNKDLPWLA | NYL |