Q9R097
Gene name |
Spint1 (Hai1) |
Protein name |
Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 1 |
Names |
Hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1, HAI-1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:20732 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
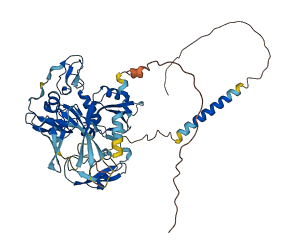
Descriptions
Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 1 (HAI-1) is important in the integrity of the basement membrane during placental development and maintaining postnatal tissue homeostasis including keratinization of the epidermis, hair development, colonic epithelium integrity, proliferation and cell fate of neural progenitor cells, and tissue injury and repair. HAI-1 is a membrane-bound multidomain protein containing an extracellular region that consists of a MANEC (motif at N terminus with eight cysteines, or MANSC) PAN-apple-like domain, an internal PKD-like domain, a Kunitz domain 1, a low-density lipoprotein receptor class A (LDLRA) domain, and a Kunitz domain 2 followed by a C-terminal single-span transmembrane region.
HAI-1 inhibits a number of serine proteases, including matriptase, HGFA, hepsin, trypsin, and prostasin. The full-length extracellular portion of HAI-1 (sHAI-1) shows weaker inhibitory activity toward target proteases than the smaller fragments, suggesting autoinhibition of HAI-1. The full-length extracellular domain of HAI-1 (sHAI-1) has a compact conformation mediated by the MANEC domain and a long but well-ordered linker (365-linker), which sterically blocks the active site in Kunitz domain 1. Kunitz domain 2 also slightly inhibits the inhibitory activity of sHAI-1 in synergy with MANEC domain.
Also, an N-linked glycan moiety in the MANEC domain (Asn66) can block an additionally larger surrounding area from protease accessibility and the deglycosylation of Asn66 leads to stronger protease suppressive activity by releasing the autoinhibition.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
241-295 (Kunitz domain 1) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Target domain |
241-295 (Kunitz domain 1) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Structural analysis |
Target domain |
241-295 (Kunitz domain 1) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Liu M et al. (2017) "The crystal structure of a multidomain protease inhibitor (HAI-1) reveals the mechanism of its auto-inhibition", The Journal of biological chemistry, 292, 8412-8423
- Kojima K et al. (2008) "Roles of functional and structural domains of hepatocyte growth factor activator inhibitor type 1 in the inhibition of matriptase", The Journal of biological chemistry, 283, 2478-87
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9R097
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9R097-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
24 variants for Q9R097
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388582461 | 7 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388571735 | 16 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388580009 | 18 | L>H | No | EVA | |
| rs219964095 | 33 | S>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388582521 | 62 | S>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388580664 | 68 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388576026 | 78 | G>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388571742 | 153 | G>W | No | EVA | |
| rs3388579988 | 196 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs241977671 | 198 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388580100 | 246 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3391955263 | 272 | F>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3392079849 | 272 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3392157241 | 272 | F>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3388580477 | 284 | Y>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3391825166 | 331 | E>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3392157240 | 333 | D>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3410618022 | 334 | D>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388576023 | 340 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388580465 | 344 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388578800 | 412 | E>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388577058 | 417 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3388576016 | 421 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388580661 | 431 | R>L | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q9R097
1 regional properties for Q9R097
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Zinc finger, RING-type | 617 - 660 | IPR001841 |
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
1 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| serine-type endopeptidase inhibitor activity | Binds to and stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a serine-type endopeptidase. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| branching involved in labyrinthine layer morphogenesis | The process in which the branches of the fetal placental villi are generated and organized. The villous part of the placenta is called the labyrinth layer. |
| cellular response to BMP stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) stimulus. |
| embryonic placenta development | The embryonically driven process whose specific outcome is the progression of the placenta over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The placenta is an organ of metabolic interchange between fetus and mother, partly of embryonic origin and partly of maternal origin. |
| epidermis development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the epidermis over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The epidermis is the outer epithelial layer of an animal, it may be a single layer that produces an extracellular material (e.g. the cuticle of arthropods) or a complex stratified squamous epithelium, as in the case of many vertebrate species. |
| epithelium development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of an epithelium over time, from its formation to the mature structure. An epithelium is a tissue that covers the internal or external surfaces of an anatomical structure. |
| extracellular matrix organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of an extracellular matrix. |
| negative regulation of neural precursor cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neural precursor cell proliferation. |
| negative regulation of peptidase activity | Any process that stops or reduces the rate of peptidase activity, the hydrolysis of peptide bonds within proteins. |
| neural tube closure | The last step in the formation of the neural tube, where the paired neural folds are brought together and fuse at the dorsal midline. |
| placenta blood vessel development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a blood vessel of the placenta over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| positive regulation of glial cell differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of glia cell differentiation. |
| viral entry into host cell | The process that occurs after viral attachment by which a virus, or viral nucleic acid, breaches the plasma membrane or cell envelope and enters the host cell. The process ends when the viral nucleic acid is released into the host cell cytoplasm. |
13 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q7YRQ8 | TFPI2 | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q868Z9 | Ppn | Papilin | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| M9PE65 | axo | Axotactin | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P49223 | SPINT3 | Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P48307 | TFPI2 | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P10646 | TFPI | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O43291 | SPINT2 | Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O43278 | SPINT1 | Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O35536 | Tfpi2 | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9WU03 | Spint2 | Kunitz-type protease inhibitor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O54819 | Tfpi | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q02445 | Tfpi | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q28864 | TFPI | Tissue factor pathway inhibitor | Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAGRRLARAS | ISAVGVWLLC | ALGLQATEAE | LPSAPAELPG | GAACLSRFTS | GVPSFVLDTE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ASVSNGATFL | GSPTARRGWD | CVRSCCTTQN | CNLALVELQP | DGGEDAISAC | FLMNCLYEQN |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| FVCKFAPKEG | FINYLTQELY | RSYRELRTRG | FGGSRIPRIW | MGIDLKVQLQ | KPLVLNEADN |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| TDWHLLQGDS | DVRVERKRPE | EVELWGLKEG | TYLFQLTRTD | SDQPEETANL | TITVLTAKQT |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| EDYCLASYKV | GRCRGSFPRW | YYDPKEQICK | SFTFGGCLGN | KNNYLREEEC | MLACKDVQGI |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| SPKRHHPVCS | GSCHATQFRC | SNGCCIDGFL | ECDDTPDCPD | GSDEATCEKY | TSGFDELQNI |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| HFLSDKGYCA | ELPDTGFCKE | NIPRWYYNPF | SERCARFTYG | GCYGNKNNFE | EEQQCLESCR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| GISKKDVFGL | RREGSIPTVG | SAEVAIAVFL | VICIIVVLTI | LGYCFFKNQR | KEFHSPLHHP |
| 490 | 500 | ||||
| PPTPASSTVS | TTEDTEHLVY | NHTTQPL |