Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
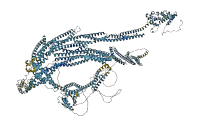
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9QWN8
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9QWN8-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q9QWN8
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9QWN8 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q9QWN8
36 regional properties for Q9QWN8
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| conserved_site | Actinin-type actin-binding domain, conserved site | 59 - 68 | IPR001589-1 |
| conserved_site | Actinin-type actin-binding domain, conserved site | 133 - 157 | IPR001589-2 |
| domain | Pleckstrin homology domain, spectrin-type | 2221 - 2240 | IPR001605-1 |
| domain | Pleckstrin homology domain, spectrin-type | 2241 - 2262 | IPR001605-2 |
| domain | Pleckstrin homology domain, spectrin-type | 2283 - 2300 | IPR001605-3 |
| domain | Pleckstrin homology domain, spectrin-type | 2303 - 2321 | IPR001605-4 |
| domain | Calponin homology domain | 57 - 161 | IPR001715-1 |
| domain | Calponin homology domain | 176 - 281 | IPR001715-2 |
| domain | Pleckstrin homology domain | 2218 - 2330 | IPR001849 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 306 - 414 | IPR002017-1 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 427 - 527 | IPR002017-2 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 532 - 639 | IPR002017-3 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 642 - 744 | IPR002017-4 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 749 - 849 | IPR002017-5 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 856 - 954 | IPR002017-6 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 960 - 1063 | IPR002017-7 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 1066 - 1169 | IPR002017-8 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 1174 - 1266 | IPR002017-9 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 1279 - 1379 | IPR002017-10 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 1384 - 1485 | IPR002017-11 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 1489 - 1586 | IPR002017-12 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 1589 - 1692 | IPR002017-13 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 1696 - 1797 | IPR002017-14 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 1801 - 1904 | IPR002017-15 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 1910 - 2010 | IPR002017-16 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 2017 - 2078 | IPR002017-17 |
| repeat | Spectrin/alpha-actinin | 306 - 528 | IPR018159-1 |
| repeat | Spectrin/alpha-actinin | 534 - 746 | IPR018159-2 |
| repeat | Spectrin/alpha-actinin | 749 - 958 | IPR018159-3 |
| repeat | Spectrin/alpha-actinin | 961 - 1172 | IPR018159-4 |
| repeat | Spectrin/alpha-actinin | 1174 - 1383 | IPR018159-5 |
| repeat | Spectrin/alpha-actinin | 1384 - 1588 | IPR018159-6 |
| repeat | Spectrin/alpha-actinin | 1589 - 1801 | IPR018159-7 |
| repeat | Spectrin/alpha-actinin | 1802 - 2010 | IPR018159-8 |
| repeat | Spectrin/alpha-actinin | 2016 - 2256 | IPR018159-9 |
| domain | Pleckstrin homology domain 9 | 2222 - 2327 | IPR041681 |
19 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| cell junction | A cellular component that forms a specialized region of connection between two or more cells, or between a cell and the extracellular matrix, or between two membrane-bound components of a cell, such as flagella. |
| cell projection | A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon. |
| cortical actin cytoskeleton | The portion of the actin cytoskeleton, comprising filamentous actin and associated proteins, that lies just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| Golgi membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding any of the compartments of the Golgi apparatus. |
| neuronal cell body | The portion of a neuron that includes the nucleus, but excludes cell projections such as axons and dendrites. |
| nuclear matrix | The dense fibrillar network lying on the inner side of the nuclear membrane. |
| parallel fiber to Purkinje cell synapse | An excitatory synapse formed by the parallel fibers of granule cells synapsing onto the dendrites of Purkinje cells. |
| paranodal junction | A highly specialized cell-cell junction found in vertebrates, which forms between a neuron and a glial cell, and has structural similarity to Drosophila septate junctions. It flanks the node of Ranvier in myelinated nerve and electrically isolates the myelinated from unmyelinated nerve segments and physically separates the voltage-gated sodium channels at the node from the cluster of potassium channels underneath the myelin sheath. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic spectrin-associated cytoskeleton | The portion of the spectrin-associated cytoskeleton contained within the postsynapse. |
| presynapse | The part of a synapse that is part of the presynaptic cell. |
| spectrin | Membrane associated dimeric protein (240 and 220 kDa) of erythrocytes. Forms a complex with ankyrin, actin and probably other components of the membrane cytoskeleton, so that there is a mesh of proteins underlying the plasma membrane, potentially restricting the lateral mobility of integral proteins. |
| synaptic vesicle | A secretory organelle, typically 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and secretes these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament binding | Binding to an actin filament, also known as F-actin, a helical filamentous polymer of globular G-actin subunits. |
| phospholipid binding | Binding to a phospholipid, a class of lipids containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester. |
| structural constituent of cytoskeleton | The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a cytoskeletal structure. |
| structural constituent of synapse | The action of a molecule that contributes to the structural integrity of a synapse. |
12 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| actin filament capping | The binding of a protein or protein complex to the end of an actin filament, thus preventing the addition, exchange or removal of further actin subunits. |
| adult behavior | Behavior in a fully developed and mature organism. |
| cellular response to ethanol | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ethanol stimulus. |
| cerebellar Purkinje cell layer morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structure of the cerebellar Purkinje cell layer is generated and organized. The Purkinje cell layer lies just underneath the molecular layer of the cerebellar cortex. It contains the neuronal cell bodies of the Purkinje cells that are arranged side by side in a single layer. Candelabrum interneurons are vertically oriented between the Purkinje cells. Purkinje neurons are inhibitory and provide the output of the cerebellar cortex through axons that project into the white matter. Extensive dendritic trees from the Purkinje cells extend upward in a single plane into the molecular layer where they synapse with parallel fibers of granule cells. |
| multicellular organism growth | The increase in size or mass of an entire multicellular organism, as opposed to cell growth. |
| postsynapse organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of a postsynapse. |
| regulation of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of calcium ion-dependent exocytosis. |
| synapse assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a synapse. This process ends when the synapse is mature (functional). |
| synaptic vesicle docking | The initial (indirect) attachment of a synaptic vesicle membrane to the presynaptic active zone membrane, mediated by proteins protruding from the membrane and proteins of the presynaptic active zone cytoplasmic component. Synaptic vesicle tethering is the first step in this process. |
| synaptic vesicle exocytosis | Fusion of intracellular membrane-bounded vesicles with the pre-synaptic membrane of the neuronal cell resulting in release of neurotransmitter into the synaptic cleft. |
| vesicle-mediated transport | A cellular transport process in which transported substances are moved in membrane-bounded vesicles; transported substances are enclosed in the vesicle lumen or located in the vesicle membrane. The process begins with a step that directs a substance to the forming vesicle, and includes vesicle budding and coating. Vesicles are then targeted to, and fuse with, an acceptor membrane. |
7 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q01082 | SPTBN1 | Spectrin beta chain, non-erythrocytic 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P11277 | SPTB | Spectrin beta chain, erythrocytic | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O15020 | SPTBN2 | Spectrin beta chain, non-erythrocytic 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P15508 | Sptb | Spectrin beta chain, erythrocytic | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62261 | Sptbn1 | Spectrin beta chain, non-erythrocytic 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9QXQ0 | Actn4 | Alpha-actinin-4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9Z1P2 | Actn1 | Alpha-actinin-1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSSTLSPTDF | DSLEIQGQYS | DINNRWDLPD | SDWDNDSSSA | RLFERSRIKA | LADEREAVQK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KTFTKWVNSH | LARVTCRVGD | LYSDLRDGRN | LLRLLEVLSG | ETLPKPTKGR | MRIHCLENVD |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KALQFLKEQK | VHLENMGSHD | IVDGNHRLTL | GLVWTIILRF | QIQDISVETE | DNKEKKSAKD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| ALLLWCQMKT | AGYPNVNVHN | FTTSWRDGLA | FNAIVHKHRP | DLLDFESLKK | CNAHYNLQNA |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| FNLAEKELGL | TKLLDPEDVN | VDQPDEKSII | TYVATYYHYF | SKMKALAVEG | KRIGKVLDHA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| MEAEHLVEKY | ESLASELLQW | IEQTIVTLND | RQLANSLSGV | QNQLQSFNSY | RTVEKPPKFT |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| EKGNLEVLLF | TIQSKLRANN | QKVYTPREGR | LISDINKAWE | RLEKAEHERE | LALRTELIRQ |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| EKLEQLAARF | DRKAAMRETW | LSENQRLVSQ | DNFGLELAAV | EAAVRKHEAI | ETDIVAYSGR |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| VQAVDAVAAE | LAAEHYHDIK | RIAARQNNVA | RLWDFLREMV | AARRERLLLN | LELQKVFQDL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LYLMDWMAEM | KGRLQSQDLG | KHLAGVEDLL | QLHELVEADI | AVQAERVRAV | SASALRFCDP |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| GKEYRPCDPQ | LVSERVATLE | QSYEALCELA | ATRRARLEES | RRLWRFLWEV | GEAEAWVREQ |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| QHLLASAETG | RDLTGVLRLL | NKHTALRGEM | SGRLGPLKLT | LEQGQQLVAE | GHPGANQAST |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| RAAELQAQWE | RLEALAEERA | QRLAQAASLY | QFQADANDME | AWLVDALRLV | SSPEVGHDEF |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| STQALARQHR | ALEEEIRAHR | PTLDALREQA | AALPPALSHT | PEVQGRVPTL | EQHYEELQAR |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| AGERARALEA | ALAFYTMLSE | AGACGLWVEE | KEQWLNGLAL | PERLEDLEVV | QQRFETLEPE |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| MNALAARVTA | VSDIAEQLLK | ASPPGKDRII | GTQEQLNQRW | QQFRSLADGK | KAALTSALSI |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| QNYHLECTET | QAWMREKTKV | IESTQDLGND | LAGVLALQRK | LAGTERDLEA | ISARVGELTQ |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| EANALAAGHP | AQAPAINTRL | GEVQTGWEDL | RATMRRREES | LGEARRLQDF | LRSLDDFQAW |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| LGRTQTAVAS | EEGPATLPEA | EALLAQHAAL | RGEVERAQSE | YSRLRTLGEE | VTRDQADPQC |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| LFLRQRLEAL | GTGWEELGRM | WESRQGRLAQ | AHGFQGFLRD | ARQAEGVLSS | QEYFLSHTEM |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| PGTLQAADAA | IKKLEDFMST | MDANGERIRG | LLEAGRQLVS | KGNIHAEKIQ | EKADSIEKRH |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| RKNQEAVQQL | LGRLRDNREQ | QHFLQDCQEL | KLWIDEKMLT | AQDVSYDEAR | NLHTKWQKHQ |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 | 1380 |
| AFMAELAANK | DWLDKVDKEG | RELTLEKPEL | KVLVSEKLED | LHRRWDELET | TTQAKARSLF |
| 1390 | 1400 | 1410 | 1420 | 1430 | 1440 |
| DANRAELFAQ | SCSALESWLE | SLQAQLHSDD | YGKDLTSVNI | LLKKQQMLER | EMAVREKEVE |
| 1450 | 1460 | 1470 | 1480 | 1490 | 1500 |
| AIQAQAKALA | QEDQSAGEVE | RTSRAVEEKF | RALCQPMKDR | CRRLQASREQ | HQFHRDVEDE |
| 1510 | 1520 | 1530 | 1540 | 1550 | 1560 |
| ILWVTERLPM | ASSLEHGKDL | PSVQLLMKKN | QTLQKEIQGH | EPRIADLKER | QRTLGTAAAG |
| 1570 | 1580 | 1590 | 1600 | 1610 | 1620 |
| PELAELQEMW | KRLSHELELR | GKRLEEALRA | QQFYRDAAEA | EAWMGEQELH | MMGQEKAKDE |
| 1630 | 1640 | 1650 | 1660 | 1670 | 1680 |
| LSAQAEVKKH | QVLEQALADY | AQTIKQLAAS | SQDMIDHEHP | ESTRLTIRQA | QVDKLYAGLK |
| 1690 | 1700 | 1710 | 1720 | 1730 | 1740 |
| ELAGERRERL | QEHLRLCQLR | RELDDLEQWI | QEREVVAASH | ELGQDYEHVT | MLRDKFREFS |
| 1750 | 1760 | 1770 | 1780 | 1790 | 1800 |
| RDTSTIGQER | VDSANALANG | LIAGGHAARA | TVAEWKDSLN | EAWADLLELL | DTRGQVLAAA |
| 1810 | 1820 | 1830 | 1840 | 1850 | 1860 |
| YELQRFLHGA | RQALARVQHK | QQQLPDGTGR | DLNAAEALQR | RHCAYEHDIQ | ALSTQVQQVQ |
| 1870 | 1880 | 1890 | 1900 | 1910 | 1920 |
| DDGLRLQKAY | AGDKAEEIGR | HMQAVAEAWA | QLQGSSAARR | QLLLDTTDKF | RFFKAVRELM |
| 1930 | 1940 | 1950 | 1960 | 1970 | 1980 |
| LWMDGINLQM | DAQERPRDVS | SADLVIKNQQ | GIKAEIEARA | DRFSACIDMG | QELLARNHYA |
| 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 2030 | 2040 |
| AEEISEKLSQ | LQSRRQETAE | KWQEKMDWLQ | LVLEVLVFGR | DAGMAEAWLC | SQEPLVRSAE |
| 2050 | 2060 | 2070 | 2080 | 2090 | 2100 |
| LGCTVDEVES | LIKRHEAFQK | SAVAWEERFS | ALEKLTALEE | RENEQKRKRE | EEERRKQPPT |
| 2110 | 2120 | 2130 | 2140 | 2150 | 2160 |
| SEPMASQPEG | SLVDGQRVLD | TAWDGTQSKL | PPSTQAPSIN | GVCTDTESSQ | PLLEQQRLEQ |
| 2170 | 2180 | 2190 | 2200 | 2210 | 2220 |
| SNVPEGPGSG | TGDESSGPRG | ERQTLPRGPA | PSPMPQSRSS | ESAHVATLPA | RGAELSAQEQ |
| 2230 | 2240 | 2250 | 2260 | 2270 | 2280 |
| MEGTLCRKQE | MEAFNKKAAN | RSWQNVYCVL | RRGSLGFYKD | ARAASAGVPY | HGEVPVSLAR |
| 2290 | 2300 | 2310 | 2320 | 2330 | 2340 |
| AQGSVAFDYR | KRKHVFKLGL | QDGKEYLFQA | KDEAEMSSWL | RVVNAAIATA | SSASGEPEEP |
| 2350 | 2360 | 2370 | 2380 | ||
| VVPSASRGLT | RAMTMPPVSQ | PEGSIVLRSK | DGREREREKR | FSFFKKNK |