Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1539-1677 (HD domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Cleavage |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Gordon WR et al. (2007) "Structural basis for autoinhibition of Notch", Nature structural & molecular biology, 14, 295-300
- Mango SE et al. (1991) "Carboxy-terminal truncation activates glp-1 protein to specify vulval fates in Caenorhabditis elegans", Nature, 352, 811-5
- Roehl H et al. (1996) "Roles of the RAM and ANK domains in signaling by the C. elegans GLP-1 receptor", The EMBO journal, 15, 7002-12
- Tiyanont K et al. (2011) "Evidence for increased exposure of the Notch1 metalloprotease cleavage site upon conversion to an activated conformation", Structure (London, England : 1993), 19, 546-54
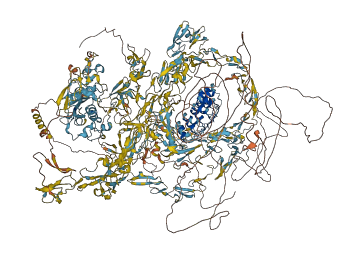
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9QW30
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9QW30-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q9QW30
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9QW30 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q9QW30
109 regional properties for Q9QW30
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 198 - 209 | IPR000152-1 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 275 - 286 | IPR000152-2 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 315 - 326 | IPR000152-3 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 353 - 364 | IPR000152-4 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 433 - 444 | IPR000152-5 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 471 - 482 | IPR000152-6 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 509 - 520 | IPR000152-7 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 547 - 558 | IPR000152-8 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 584 - 595 | IPR000152-9 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 622 - 633 | IPR000152-10 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 659 - 670 | IPR000152-11 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 697 - 708 | IPR000152-12 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 772 - 783 | IPR000152-13 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 810 - 821 | IPR000152-14 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 888 - 899 | IPR000152-15 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 926 - 937 | IPR000152-16 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 964 - 975 | IPR000152-17 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 1002 - 1013 | IPR000152-18 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 1040 - 1051 | IPR000152-19 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 1164 - 1175 | IPR000152-20 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 1202 - 1213 | IPR000152-21 |
| ptm | EGF-type aspartate/asparagine hydroxylation site | 1241 - 1252 | IPR000152-22 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 24 - 63 | IPR000742-1 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 64 - 102 | IPR000742-2 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 105 - 143 | IPR000742-3 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 144 - 180 | IPR000742-4 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 182 - 219 | IPR000742-5 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 221 - 258 | IPR000742-6 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 260 - 296 | IPR000742-7 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 298 - 336 | IPR000742-8 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 338 - 374 | IPR000742-9 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 375 - 413 | IPR000742-10 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 415 - 454 | IPR000742-11 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 456 - 492 | IPR000742-12 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 494 - 530 | IPR000742-13 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 532 - 568 | IPR000742-14 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 570 - 605 | IPR000742-15 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 607 - 643 | IPR000742-16 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 645 - 680 | IPR000742-17 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 682 - 718 | IPR000742-18 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 720 - 755 | IPR000742-19 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 757 - 793 | IPR000742-20 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 795 - 831 | IPR000742-21 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 833 - 871 | IPR000742-22 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 873 - 909 | IPR000742-23 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 911 - 947 | IPR000742-24 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 949 - 985 | IPR000742-25 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 987 - 1023 | IPR000742-26 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 1025 - 1061 | IPR000742-27 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 1063 - 1099 | IPR000742-28 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 1104 - 1147 | IPR000742-29 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 1149 - 1185 | IPR000742-30 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 1187 - 1223 | IPR000742-31 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 1225 - 1262 | IPR000742-32 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 1264 - 1302 | IPR000742-33 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 1304 - 1343 | IPR000742-34 |
| domain | EGF-like domain | 1375 - 1412 | IPR000742-35 |
| domain | Notch domain | 1418 - 1544 | IPR000800 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 64 - 102 | IPR001881-1 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 109 - 143 | IPR001881-2 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 146 - 180 | IPR001881-3 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 182 - 219 | IPR001881-4 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 225 - 258 | IPR001881-5 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 260 - 296 | IPR001881-6 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 298 - 336 | IPR001881-7 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 338 - 374 | IPR001881-8 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 415 - 454 | IPR001881-9 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 456 - 492 | IPR001881-10 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 494 - 530 | IPR001881-11 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 532 - 568 | IPR001881-12 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 570 - 605 | IPR001881-13 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 607 - 643 | IPR001881-14 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 645 - 680 | IPR001881-15 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 682 - 718 | IPR001881-16 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 720 - 755 | IPR001881-17 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 757 - 793 | IPR001881-18 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 795 - 831 | IPR001881-19 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 837 - 871 | IPR001881-20 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 873 - 909 | IPR001881-21 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 911 - 947 | IPR001881-22 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 949 - 985 | IPR001881-23 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 987 - 1023 | IPR001881-24 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 1025 - 1061 | IPR001881-25 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 1064 - 1099 | IPR001881-26 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 1105 - 1147 | IPR001881-27 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 1149 - 1185 | IPR001881-28 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 1187 - 1223 | IPR001881-29 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 1225 - 1262 | IPR001881-30 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 1264 - 1302 | IPR001881-31 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 1306 - 1343 | IPR001881-32 |
| domain | EGF-like calcium-binding domain | 1370 - 1412 | IPR001881-33 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 1827 - 1939 | IPR002110-1 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 1943 - 2041 | IPR002110-2 |
| domain | Notch, NOD domain | 1539 - 1595 | IPR010660 |
| domain | Notch, NODP domain | 1617 - 1677 | IPR011656 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like, conserved site | 230 - 252 | IPR013032-1 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like, conserved site | 347 - 367 | IPR013032-2 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like, conserved site | 579 - 599 | IPR013032-3 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like, conserved site | 729 - 749 | IPR013032-4 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like calcium-binding, conserved site | 182 - 207 | IPR018097-1 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like calcium-binding, conserved site | 260 - 284 | IPR018097-2 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like calcium-binding, conserved site | 456 - 480 | IPR018097-3 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like calcium-binding, conserved site | 532 - 556 | IPR018097-4 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like calcium-binding, conserved site | 682 - 706 | IPR018097-5 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like calcium-binding, conserved site | 911 - 935 | IPR018097-6 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like calcium-binding, conserved site | 1025 - 1049 | IPR018097-7 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like calcium-binding, conserved site | 1149 - 1173 | IPR018097-8 |
| conserved_site | EGF-like calcium-binding, conserved site | 1225 - 1250 | IPR018097-9 |
| domain | Notch, C-terminal | 2380 - 2445 | IPR024600 |
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| cilium | A specialized eukaryotic organelle that consists of a filiform extrusion of the cell surface and of some cytoplasmic parts. Each cilium is largely bounded by an extrusion of the cytoplasmic (plasma) membrane, and contains a regular longitudinal array of microtubules, anchored to a basal body. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| extracellular matrix | A structure lying external to one or more cells, which provides structural support, biochemical or biomechanical cues for cells or tissues. |
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| calcium ion binding | Binding to a calcium ion (Ca2+). |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| NF-kappaB binding | Binding to NF-kappaB, a transcription factor for eukaryotic RNA polymerase II promoters. |
| signaling receptor activity | Receiving a signal and transmitting it in the cell to initiate a change in cell activity. A signal is a physical entity or change in state that is used to transfer information in order to trigger a response. |
48 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| animal organ morphogenesis | Morphogenesis of an animal organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process in which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions. |
| atrial septum morphogenesis | The developmental process in which atrial septum is generated and organized. The atrial septum separates the upper chambers (the atria) of the heart from one another. |
| bone remodeling | The continuous turnover of bone matrix and mineral that involves first, an increase in resorption (osteoclastic activity) and later, reactive bone formation (osteoblastic activity). The process of bone remodeling takes place in the adult skeleton at discrete foci. The process ensures the mechanical integrity of the skeleton throughout life and plays an important role in calcium homeostasis. An imbalance in the regulation of bone resorption and bone formation results in many of the metabolic bone diseases, such as osteoporosis. |
| cell fate determination | A process involved in cell fate commitment. Once determination has taken place, a cell becomes committed to differentiate down a particular pathway regardless of its environment. |
| cellular response to tumor cell | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a tumor cell. |
| central nervous system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the central nervous system over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The central nervous system is the core nervous system that serves an integrating and coordinating function. In vertebrates it consists of the brain and spinal cord. In those invertebrates with a central nervous system it typically consists of a brain, cerebral ganglia and a nerve cord. |
| cholangiocyte proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of cholangiocytes, resulting in the expansion of the cholangiocyte population. A cholangiocyte is an epithelial cell that is part of the bile duct. Cholangiocytes contribute to bile secretion via net release of bicarbonate and water. |
| ciliary body morphogenesis | The process in which the ciliary body generated and organized. The ciliary body is the circumferential tissue inside the eye composed of the ciliary muscle and ciliary processes. |
| defense response to bacterium | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a bacterium that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| determination of left/right symmetry | The establishment of an organism's body plan or part of an organism with respect to the left and right halves. The pattern can either be symmetric, such that the halves are mirror images, or asymmetric where the pattern deviates from this symmetry. |
| embryonic limb morphogenesis | The process, occurring in the embryo, by which the anatomical structures of the limb are generated and organized. A limb is an appendage of an animal used for locomotion or grasping. |
| glomerular capillary formation | The process that gives rise to a glomerular capillary. This process pertains to the initial formation of a structure from unspecified parts. |
| glomerular visceral epithelial cell development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a glomerular visceral epithelial cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A glomerular visceral epithelial cell is a specialized epithelial cell that contains 'feet' that interdigitate with the 'feet' of other glomerular epithelial cells. |
| heart looping | The tube morphogenesis process in which the primitive heart tube loops asymmetrically. This looping brings the primitive heart chambers into alignment preceding their future integration. Heart looping begins with dextral-looping and ends when the main regional divisions of the mature heart and primordium of the great arterial trunks become established preceeding septation. |
| hepatocyte proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of hepatocytes, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. Hepatocytes form the main structural component of the liver. They are specialized epithelial cells that are organized into interconnected plates called lobules. |
| humoral immune response | An immune response mediated through a body fluid. |
| in utero embryonic development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the embryo in the uterus over time, from formation of the zygote in the oviduct, to birth. An example of this process is found in Mus musculus. |
| inflammatory response to antigenic stimulus | An inflammatory response to an antigenic stimulus, which can be include any number of T cell or B cell epitopes. |
| intrahepatic bile duct development | The progression of the intrahepatic bile ducts over time, from their formation to the mature structure. Intrahepatic bile ducts (bile ducts within the liver) collect bile from bile canaliculi in the liver, and connect to the extrahepatic bile ducts (bile ducts outside the liver). |
| left/right axis specification | The establishment, maintenance and elaboration of the left/right axis. The left/right axis is defined by a line that runs orthogonal to both the anterior/posterior and dorsal/ventral axes. Each side is defined from the viewpoint of the organism rather of the observer (as per anatomical axes). |
| liver development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the liver over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The liver is an exocrine gland which secretes bile and functions in metabolism of protein and carbohydrate and fat, synthesizes substances involved in the clotting of the blood, synthesizes vitamin A, detoxifies poisonous substances, stores glycogen, and breaks down worn-out erythrocytes. |
| liver morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the liver are generated and organized. |
| marginal zone B cell differentiation | The process in which a B cell in the spleen acquires the specialized features of a marginal zone B cell. Marginal zone B cells are localized in a distinct anatomical region of the spleen that represents the major antigen-filtering and scavenging area (by specialized macrophages resident there). It appears that they are preselected to express a BCR repertoire similar to B-1 B cells, biased toward bacterial cell wall constituents and senescent self-components (such as oxidized LDL). |
| morphogenesis of an epithelial sheet | The process in which the anatomical structures of an epithelial sheet are generated and organized. An epithelial sheet is a flat surface consisting of closely packed epithelial cells. |
| multicellular organism growth | The increase in size or mass of an entire multicellular organism, as opposed to cell growth. |
| myeloid dendritic cell differentiation | The process in which a monocyte acquires the specialized features of a dendritic cell, an immunocompetent cell of the lymphoid and hemopoietic systems and skin. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of growth rate | Any process that reduces the rate of growth of all or part of an organism. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| Notch signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to the receptor Notch on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| placenta blood vessel development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a blood vessel of the placenta over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| placenta development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the placenta over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The placenta is an organ of metabolic interchange between fetus and mother, partly of embryonic origin and partly of maternal origin. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of BMP signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of BMP signaling pathway activity. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of keratinocyte proliferation | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of keratinocyte proliferation. Keratinocyte proliferation is the multiplication or reproduction of keratinocytes, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. |
| positive regulation of osteoclast differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of osteoclast differentiation. |
| positive regulation of Ras protein signal transduction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of Ras protein signal transduction. |
| proximal tubule development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the proximal tubule over time, from its formation to the mature structure. In mammals, the proximal tubule is a nephron tubule that connects Bowman's capsule to the descending thin limb of the loop of Henle. It has a brush border epithelial morphology. |
| pulmonary valve morphogenesis | The process in which the structure of the pulmonary valve is generated and organized. |
| regulation of actin cytoskeleton reorganization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of actin cytoskeleton reorganization. |
| regulation of cell cycle | Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle. |
| regulation of osteoclast development | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of osteoclast development. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| skeletal system development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the skeleton over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The skeleton is the bony framework of the body in vertebrates (endoskeleton) or the hard outer envelope of insects (exoskeleton or dermoskeleton). |
| tissue regeneration | The regrowth of lost or destroyed tissues. |
| wound healing | The series of events that restore integrity to a damaged tissue, following an injury. |
13 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q868Z9 | Ppn | Papilin | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P46531 | NOTCH1 | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P21941 | MATN1 | Cartilage matrix protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q04721 | NOTCH2 | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q6GUQ1 | Egfl8 | Epidermal growth factor-like protein 8 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q01705 | Notch1 | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q91V88 | Npnt | Nephronectin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P51942 | Matn1 | Cartilage matrix protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O35516 | Notch2 | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q07008 | Notch1 | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P13508 | glp-1 | Protein glp-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | EV |
| A2RUV0 | notch1 | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| P46530 | notch1a | Neurogenic locus notch homolog protein 1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MPALRPAALR | ALLWLWLCGA | GPAHALQCRG | GQEPCVNEGT | CVTYHNGTGY | CRCPEGFLGE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| YCQHRDPCEK | NRCQNGGTCV | TQAMLGKATC | RCAPGFTGED | CQYSTSHPCF | VSRPCQNGGT |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| CHMLSWDTYE | CTCQVGFTGK | QCQWTDVCLS | HPCENGSTCS | SVANQFSCRC | PAGITGQKCD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| ADINECDIPG | RCQHGGTCLN | LPGSYRCQCP | QRFTGQHCDS | PYVPCAPSPC | VNGGTCRQTG |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| DFTSECHCLP | GFEGSNCERN | IDDCPNHKCQ | NGGVCVDGVN | TYNCRCPPQW | TGQFCTEDVD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| ECLLQPNACQ | NGGTCTNRNG | GYGCVCVNGW | SGDDCSENID | DCAFASCTPG | STCIDRVASF |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| SCLCPEGKAG | LLCHLDDACI | SNPCHKGALC | DTNPLNGQYI | CTCPQAYKGA | DCTEDVDECA |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| MANSNPCEHA | GKCVNTDGAF | HCECLKGYAG | PRCEMDINEC | HSDPCQNDAT | CLDKIGGFTC |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LCMPGFKGVH | CELEVNECQS | NPCVNNGQCV | DKVNRFQCLC | PPGFTGPVCQ | IDIDDCSSTP |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| CLNGAKCIDH | PNGYECQCAT | GFTGTLCDEN | IDNCDPDPCH | HGQCQDGIDS | YTCICNPGYM |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| GAICSDQIDE | CYSSPCLNDG | RCIDLVNGYQ | CNCQPGTSGL | NCEINFDDCA | SNPCLHGACV |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| DGINRYSCVC | SPGFTGQRCN | IDIDECASNP | CRKDATCIND | VNGFRCMCPE | GPHHPSCYSQ |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| VNECLSSPCI | HGNCTGGLSG | YKCLCDAGWV | GINCEVDKNE | CLSNPCQNGG | TCNNLVNGYR |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| CTCKKGFKGY | NCQVNIDECA | SNPCLNQGTC | LDDVSGYTCH | CMLPYTGKNC | QTVLAPCSPN |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| PCENAAVCKE | APNFESFTCL | CAPGWQGQRC | TVDVDECVSK | PCMNNGICHN | TQGSYMCECP |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| PGFSGMDCEE | DINDCLANPC | QNGGSCVDKV | NTFSCLCLPG | FVGDKCQTDM | NECLSEPCKN |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| GGTCSDYVNS | YTCTCPAGFH | GVHCENNIDE | CTESSCFNGG | TCVDGINSFS | CLCPVGFTGP |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| FCLHDINECS | SNPCLNSGTC | VDGLGTYRCT | CPLGYTGKNC | QTLVNLCSPS | PCKNKGTCAQ |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| EKARPRCLCP | PGWDGAYCDV | LNVSCKAAAL | QKGVPVEHLC | QHSGICINAG | NTHHCQCPLG |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| YTGSYCEEQL | DECASNPCQH | GATCSDFIGG | YRCECVPGYQ | GVNCEYEVDE | CQNQPCQNGG |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| TCIDLVNHFK | CSCPPGTRGL | LCEENIDDCA | GAPHCLNGGQ | CVDRIGGYSC | RCLPGFAGER |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| CEGDINECLS | NPCSSEGSLD | CIQLKNNYQC | VCRSAFTGRH | CETFLDVCPQ | KPCLNGGTCA |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 | 1380 |
| VASNVPDGFI | CRCPPGFSGA | RCQSSCGQVK | CRRGEQCVHT | ASGPHCFCPN | HKDCESGCAS |
| 1390 | 1400 | 1410 | 1420 | 1430 | 1440 |
| NPCQHGGTCY | PQRQPPYYSC | RCSPPFWGSH | CESYTAPTST | PPATCLSQYC | ADKARDGICD |
| 1450 | 1460 | 1470 | 1480 | 1490 | 1500 |
| EACNSHACQW | DGGDCSLTME | DPWANCTSSL | RCWEYINNQC | DELCNTAECL | FDNFECQRNS |
| 1510 | 1520 | 1530 | 1540 | 1550 | 1560 |
| KTCKYDKYCA | DHFKDNHCDK | GCNNEECGWD | GLDCAADQPE | NLAEGILVIV | VLLPPEQLLQ |
| 1570 | 1580 | 1590 | 1600 | 1610 | 1620 |
| DSRSFLRALG | TLLHTNLRIK | QDSQGALMVY | PYYGEKSAAM | KKQKVARRSL | PDEQEQEIIG |
| 1630 | 1640 | 1650 | 1660 | 1670 | 1680 |
| SKVFLEIDNR | QCVQDSDQCF | KNTDAAAALL | ASHAIQGTLS | YPLVSVVSES | EDPRNTPLLY |
| 1690 | 1700 | 1710 | 1720 | 1730 | 1740 |
| LLAVAVVIIL | FLILLGVIMA | KRKRKHGFLW | LPEGFTLRRD | SSNHKRREPV | GQDAVGLKNL |
| 1750 | 1760 | 1770 | 1780 | 1790 | 1800 |
| SVQVSEANLI | GSTTSEHWGD | DEGPQPKKAK | AEDDEALLSE | DDPVDRRPWT | QQHLEAADIR |
| 1810 | 1820 | 1830 | 1840 | 1850 | 1860 |
| RTPSLALTPP | QAEQEVDVLD | VNVRGPDGCT | PLMLASLRGG | SSDLSDEDED | AEDSSANIIT |
| 1870 | 1880 | 1890 | 1900 | 1910 | 1920 |
| DLVYQGASLQ | AQTDRTGEMA | LHLAARYSRA | DAAKRLLDAG | ADANAQDNMG | RCPLHAAVAA |
| 1930 | 1940 | 1950 | 1960 | 1970 | 1980 |
| DAQGVFQILI | RNRVTDLDAR | MNDGTTPLIL | AARLAVEGMV | AELINCQADV | NAVDDHGKSA |
| 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 2030 | 2040 |
| LHWAAAVNNV | EATLLLLKNG | ANRDMQDNKE | ETPLFLAARE | GSYEAAKILL | DHFANRDITD |
| 2050 | 2060 | 2070 | 2080 | 2090 | 2100 |
| HMDRLPRDVA | RDRMHHDIVR | LLDEYNVTPS | PPGTVLTSAL | SPVLCGPNRS | FLSLKHTPMG |
| 2110 | 2120 | 2130 | 2140 | 2150 | 2160 |
| KKARRPNTKS | TMPTSLPNLA | KEAKDVKGSR | RKKCLNEKVQ | LSESSVTLSP | VDSLESPHTY |
| 2170 | 2180 | 2190 | 2200 | 2210 | 2220 |
| VSDATSSPMI | TSPGILQASP | TPLLAAAPAA | PVHAQHALSF | SNLHEMQPLR | PGASTVLPSV |
| 2230 | 2240 | 2250 | 2260 | 2270 | 2280 |
| SQLLSHHHIV | PPGSGSAGSL | GRLHSVPVPS | DWMNRVEMSE | TQYSEMFGMV | LAPAEGTHPG |
| 2290 | 2300 | 2310 | 2320 | 2330 | 2340 |
| MAAPQSRAPE | GKPIPTQREP | LPPIVTFQLI | PKGSLAQAAG | APQTQSGCPP | AVAGPLPSMY |
| 2350 | 2360 | 2370 | 2380 | 2390 | 2400 |
| QIPEMARLPS | VAFPPTMMPQ | QEGQVAQTIV | PTYHPFPASV | GKYPTPPSQH | SYASSNAAER |
| 2410 | 2420 | 2430 | 2440 | 2450 | 2460 |
| TPNHGGHLQG | EHPYLTPSPE | SPDQWSSSSP | HSASDWSDVT | TSPTPGGGGG | GQRGPGTHMS |
| 2470 | |||||
| EPPHSNMQVY | A |