Q9JJZ4
Gene name |
Ube2j1 (Ncube1) |
Protein name |
Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 J1 |
Names |
E2 ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme J1, Non-canonical ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme 1, NCUBE-1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:56228 |
EC number |
2.3.2.23: Aminoacyltransferases |
Protein Class |
|
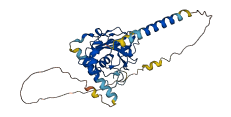
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9JJZ4
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9JJZ4-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
14 variants for Q9JJZ4
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388680111 | 34 | L>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3388664072 | 45 | V>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388680112 | 76 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388664038 | 97 | H>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388676131 | 97 | H>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3388680084 | 99 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs259282008 | 166 | G>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388676660 | 197 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs27774249 | 204 | C>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3388676153 | 218 | F>S | No | EVA | |
| rs27774215 | 233 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3394133823 | 287 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3393846454 | 289 | M>V | No | EVA | |
| rs253584875 | 312 | Y>S | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q9JJZ4
1 regional properties for Q9JJZ4
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 | 10 - 168 | IPR000608 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.3.2.23 | Aminoacyltransferases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| endoplasmic reticulum membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| integral component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ubiquitin conjugating enzyme activity | Isoenergetic transfer of ubiquitin from one protein to another via the reaction X-ubiquitin + Y -> Y-ubiquitin + X, where both the X-ubiquitin and Y-ubiquitin linkages are thioester bonds between the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin and a sulfhydryl side group of a cysteine residue. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase binding | Binding to a ubiquitin protein ligase enzyme, any of the E3 proteins. |
7 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| negative regulation of retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of retrograde protein transport, ER to cytosol. |
| protein N-linked glycosylation via asparagine | The glycosylation of protein via the N4 atom of peptidyl-asparagine forming N4-glycosyl-L-asparagine; the most common form is N-acetylglucosaminyl asparagine; N-acetylgalactosaminyl asparagine and N4 glucosyl asparagine also occur. This modification typically occurs in extracellular peptides with an N-X-(ST) motif. Partial modification has been observed to occur with cysteine, rather than serine or threonine, in the third position; secondary structure features are important, and proline in the second or fourth positions inhibits modification. |
| protein polyubiquitination | Addition of multiple ubiquitin groups to a protein, forming a ubiquitin chain. |
| regulation of macrophage cytokine production | Any process that modulates the rate, frequency or extent of macrophage cytokine production. Macrophage cytokine production is the appearance of a chemokine due to biosynthesis or secretion following a cellular stimulus, resulting in an increase in its intracellular or extracellular levels. |
| regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of tumor necrosis factor production. |
| spermatid development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a spermatid over time, from its formation to the mature structure. |
| ubiquitin-dependent ERAD pathway | The series of steps necessary to target endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-resident proteins for degradation by the cytoplasmic proteasome. Begins with recognition of the ER-resident protein, includes retrotranslocation (dislocation) of the protein from the ER to the cytosol, protein ubiquitination necessary for correct substrate transfer, transport of the protein to the proteasome, and ends with degradation of the protein by the cytoplasmic proteasome. |
11 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9Y385 | UBE2J1 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 J1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9CQ37 | Ube2t | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 T | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P52483 | Ube2e3 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 E3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q921J4 | Ube2s | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 S | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9D1C1 | Ube2c | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P61087 | Ube2k | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 K | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P61079 | Ube2d3 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 D3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q64362 | Aktip | AKT-interacting protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q7TSS2 | Ube2q1 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 Q1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| A0PJN4 | Ube2ql1 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2Q-like protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9LSP7 | UBC32 | Ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme E2 32 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| METRYNLKSP | AVKRLMKEAA | ELKDPTDHYH | AQPLEDNLFE | WHFTVRGPPD | SDFDGGVYHG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| RIVLPPEYPM | KPPSIILLTA | NGRFEVGKKI | CLSISGHHPE | TWQPSWSIRT | ALLAIIGFMP |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| TKGEGAIGSL | DYTPEERRAL | AKKSQDFCCE | GCGSAMKDVL | LPLKSGSGSS | QADQEAKELA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| RQISFKAEVN | SSGKTIAESD | LNQCFSLNDS | QDDLPTTFQG | ATASTSYGAQ | NPSGAPLPQP |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| TQPAPKNTSM | SPRQRRAQQQ | SQRRPSTSPD | VLQGQPPRAH | HTEHGGSAML | IIILTLALAA |
| 310 | |||||
| LIFRRIYLAN | EYIFDFEL |