Q9JJN1
Gene name |
Fgf21 |
Protein name |
Fibroblast growth factor 21 |
Names |
FGF-21 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:56636 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
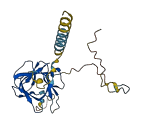
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9JJN1
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9JJN1-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
5 variants for Q9JJN1
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388912679 | 106 | Q>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388903609 | 154 | N>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388909536 | 157 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388906183 | 199 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs244122204 | 204 | R>Q | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q9JJN1
No regional properties for Q9JJN1
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for Q9JJN1 | |||
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| extracellular space | That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| fibroblast growth factor receptor binding | Binding to a fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR). |
| growth factor activity | The function that stimulates a cell to grow or proliferate. Most growth factors have other actions besides the induction of cell growth or proliferation. |
14 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| animal organ morphogenesis | Morphogenesis of an animal organ. An organ is defined as a tissue or set of tissues that work together to perform a specific function or functions. Morphogenesis is the process in which anatomical structures are generated and organized. Organs are commonly observed as visibly distinct structures, but may also exist as loosely associated clusters of cells that work together to perform a specific function or functions. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a fibroblast growth factor receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands. |
| negative regulation of endothelial cell apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of endothelial cell apoptotic process. |
| negative regulation of neuron death | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neuron death. |
| positive regulation of cell population proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the rate or extent of cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of cold-induced thermogenesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cold-induced thermogenesis. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of gene expression | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| positive regulation of glucose import | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the import of the hexose monosaccharide glucose into a cell or organelle. |
| positive regulation of MAPKKK cascade by fibroblast growth factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a fibroblast growth factor receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands resulting in an increase in the rate or frequency of a MAPKKK cascade. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of triglyceride catabolic process | Any process that increases the frequency, rate, or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of triglyceride. |
| regulation of cell migration | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
28 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P48801 | FGF3 | Fibroblast growth factor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P08620 | FGF4 | Fibroblast growth factor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NP95 | FGF20 | Fibroblast growth factor 20 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9HCT0 | FGF22 | Fibroblast growth factor 22 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P10767 | FGF6 | Fibroblast growth factor 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O15520 | FGF10 | Fibroblast growth factor 10 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q92914 | FGF11 | Fibroblast growth factor 11 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P11487 | FGF3 | Fibroblast growth factor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P31371 | FGF9 | Fibroblast growth factor 9 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O43320 | FGF16 | Fibroblast growth factor 16 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV SS |
| Q9NSA1 | FGF21 | Fibroblast growth factor 21 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O35565 | Fgf10 | Fibroblast growth factor 10 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P11403 | Fgf4 | Fibroblast growth factor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P21658 | Fgf6 | Fibroblast growth factor 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54130 | Fgf9 | Fibroblast growth factor 9 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9ESL8 | Fgf16 | Fibroblast growth factor 16 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9ESL9 | Fgf20 | Fibroblast growth factor 20 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9ESS2 | Fgf22 | Fibroblast growth factor 22 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P61329 | Fgf12 | Fibroblast growth factor 12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P05524 | Fgf3 | Fibroblast growth factor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q95L12 | FGF9 | Fibroblast growth factor 9 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q9EST9 | Fgf20 | Fibroblast growth factor 20 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O54769 | Fgf16 | Fibroblast growth factor 16 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P36364 | Fgf9 | Fibroblast growth factor 9 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P70492 | Fgf10 | Fibroblast growth factor 10 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q6PBT8 | fgf1 | Putative fibroblast growth factor 1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| Q2HXK8 | fgf16 | Fibroblast growth factor 16 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| P48802 | fgf3 | Fibroblast growth factor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEWMRSRVGT | LGLWVRLLLA | VFLLGVYQAY | PIPDSSPLLQ | FGGQVRQRYL | YTDDDQDTEA |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| HLEIREDGTV | VGAAHRSPES | LLELKALKPG | VIQILGVKAS | RFLCQQPDGA | LYGSPHFDPE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| ACSFRELLLE | DGYNVYQSEA | HGLPLRLPQK | DSPNQDATSW | GPVRFLPMPG | LLHEPQDQAG |
| 190 | 200 | ||||
| FLPPEPPDVG | SSDPLSMVEP | LQGRSPSYAS |