Q9JIH7
Gene name |
Wnk1 |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK1 |
Names |
Protein kinase lysine-deficient 1, Protein kinase with no lysine 1 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:116477 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
SERINE/THREONINE-PROTEIN KINASE WNK WITH NO LYSINE -RELATED (PTHR13902) |
Descriptions
WNK family protein kinases are large enzymes that contain the catalytic lysine in a unique position compared with all other protein kinases. The activity of the Wnk1 kinase domain is controlled by its autoinhibitory domain, which is relieved through specific mutations of key residues in the domain. Activation of Wnk1 requires autophosphorylaiton of Ser382 within its activation loop, and phosphorylation of Ser378 enhances its kinase activity.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
221-479 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
Deletion assay, Mutagenesis experiment |
Accessory elements
367-388 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
221-479 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
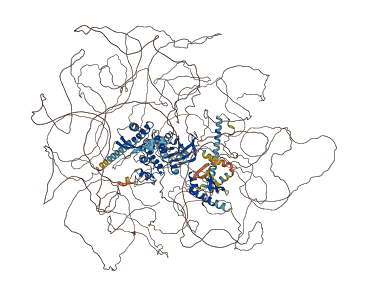
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure

8 structures for Q9JIH7
No variants for Q9JIH7
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9JIH7 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q9JIH7
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR13902 | SERINE/THREONINE-PROTEIN KINASE WNK WITH NO LYSINE -RELATED |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR13902:SF46 | SERINE_THREONINE-PROTEIN KINASE WNK1 |
| PANTHER Protein Class |
non-receptor serine/threonine protein kinase
protein modifying enzyme |
|
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
12 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| chloride channel inhibitor activity | Binds to and stops, prevents, or reduces the activity of a chloride channel. |
| magnesium ion binding | Binding to a magnesium (Mg) ion. |
| phosphatase binding | Binding to a phosphatase. |
| potassium channel inhibitor activity | Binds to and stops, prevents, or reduces the activity of a potassium channel. |
| protein kinase activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of a protein kinase, an enzyme which phosphorylates a protein. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase inhibitor activity | Binds to and stops, prevents or reduces the activity of a protein serine/threonine kinase. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
28 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cation homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of cations within an organism or cell. |
| cellular response to calcium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a calcium ion stimulus. |
| cellular response to chemokine | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a chemokine stimulus. |
| chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 21 signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the binding of the C-C chemokine CCL21 to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of ions within an organism or cell. |
| ion transport | The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| lymphocyte migration into lymph node | The movement of a lymphocyte within the lymphatic system into a lymph node, and its subsequent positioning within defined functional compartments such as sites of cell activation by antigen. |
| negative regulation of cell-cell adhesion mediated by integrin | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of cell-cell adhesion mediated by integrin. |
| negative regulation of GTPase activity | Any process that stops or reduces the rate of GTP hydrolysis by a GTPase. |
| negative regulation of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate, or extent of heterotypic cell-cell adhesion. |
| negative regulation of kinase activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| negative regulation of leukocyte cell-cell adhesion | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of leukocyte cell-cell adhesion. |
| negative regulation of pancreatic juice secretion | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of pancreatic juice secretion, the regulated release of pancreatic juice by the exocrine pancreas into the upper part of the intestine. |
| negative regulation of sodium ion transport | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| positive regulation of potassium ion import across plasma membrane | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of potassium ion import across the plasma membrane. |
| positive regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity. |
| positive regulation of systemic arterial blood pressure | The process that increases the force with which blood travels through the systemic arterial circulatory system. |
| positive regulation of T cell chemotaxis | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of T cell chemotaxis. T cell chemotaxis is the directed movement of a T cell in response to an external stimulus. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of cation transmembrane transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cation transmembrane transport. |
| regulation of sodium ion transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| T cell receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by the cross-linking of an antigen receptor on a T cell. |
16 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q96J92 | WNK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9Y3S1 | WNK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9BYP7 | WNK3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9H4A3 | WNK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q3UH66 | Wnk2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q80UE6 | Wnk4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q80XP9 | Wnk3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P83741 | Wnk1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6R2V0 | WNK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK1 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q7TPK6 | Wnk4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| X5M5N0 | wnk-1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q8RXE5 | WNK10 | Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK10 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q944Q0 | WNK8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LVL5 | WNK4 | Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9STK6 | WNK3 | Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8LST2 | WNK7 | Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK7 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSDGTAEKQS | GTPGFLSPPA | PVPKNGSSSD | SSVGEKLGAA | VADSGIGRTE | EYRRRRHTMD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| KDSRGAAATT | TPTEHRFFRR | SVICDSNATA | LELPGLPLSI | PQPSVPAVVP | QSAPPEPHRE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| ETLTATVASQ | VSQQPSAAAS | PGEQAVVGSA | TATVPSSTSK | DRPVSQPSLV | GSKEEPPPSR |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SGSGSGGASA | KEPQEERNQQ | QDDIEELETK | AVGMSNDGRF | LKFDIEIGRG | SFKTVYKGLD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| TETTVEVAWC | ELQDRKLTKS | ERQRFKEEAE | MLKGLQHPNI | VRFYDSWEST | VKGKKCIVLV |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| TELMTSGTLK | TYLKRFKVMK | IKVLRSWCRQ | ILKGLQFLHT | RTPPIIHRDL | KCDNIFITGP |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| TGSVKIGDLG | LATLKRASFA | KSVIGTPEFM | APEMYEEKYD | ESVDVYAFGM | CMLEMATSEY |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| PYSECQNAAQ | IYRRVTSGVK | PASFDKVAIP | EVKEIIEGCI | RQNKDERYSI | KDLLNHAFFQ |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| EETGVRVELA | EEDDGEKIAI | KLWLRIEDIK | KLKGKYKDNE | AIEFSFDLER | DVPEDVAQEM |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| VESGYVCEGD | HKTMAKAIKD | RVSLIKRKRE | QRQLVREEQE | KRKQEESSFK | QQNEQQASVS |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| QAGIQPLSVA | STGIPTAPTT | SASVSTQVEP | EEPEADQHQQ | LQYQQPSISV | LSDGTVDSGQ |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| GSSVFTESRV | SSQQTVSYGS | QHEQAHSIGT | APGHTVSSIQ | AQSQPHGVYP | PSSMAQGQNQ |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| GQPSSSLAGV | LSSQPVQHPQ | QQGIQPTVPP | QQAVQYSLPQ | AASSSEGTVQ | PVSQPQVSAG |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| TQSSTQGVSQ | AAPPEQTPIT | QSQPTQPVPL | VSSVDSAHSD | VASGMSDGNE | NAPSSSGRHE |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| GRTTKRHYRK | SVRSRSRHEK | TSRPKLRILN | VSNKGDRVVE | CQLETHNRKM | VTFKFDLDGD |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| NPEEIATIMV | NNDFILAIER | ESFVAQVREI | IEKADEMLSE | DVSVEPEGDQ | GLESLQGKDD |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| YGFPGSQKLE | GEFKQPIAVS | SMPQQIGVPT | SSLTQVVHSA | GRRFIVSPVP | ESRLRESKIF |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| TSEIPDPVAA | STSQGPGMNL | SHSASSLSLQ | QAFSELKHGQ | MTEGPNTAPP | NFNHPGPTFS |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| PFLTSIAGVQ | TVAASTPSVS | VPITSSPLND | ISTSVMQSEG | ALPTDKGIGG | VTTSTGVVAS |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| GGLTTLSVSE | TPTLSSAVSS | STAPAVVTVS | TTSQPVQAST | SGSIASSTGS | FPSGTFSTTT |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| GTTVSSVAVP | NAKPPTVLLQ | QVAGNTAGVA | IVTSVSTTTP | FPAMASQPSL | PLGSSTSAPT |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| LAETVVVSAH | SLDKASHSST | AGLGLSFCAP | SSSSSSGTAV | SSSVSQPGIV | HPLVISSAIA |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 | 1380 |
| STPVLPQPAV | PTSTPLLPQV | PNIPPLVQPV | ANVPAVQQTL | IHSQPQPALL | PNQPHTHCPE |
| 1390 | 1400 | 1410 | 1420 | 1430 | 1440 |
| MDADTQSKAP | GIDDIKTLEE | KLRSLFSEHS | SSGTQHASVS | LETPLVVETV | TPGIPTTAVA |
| 1450 | 1460 | 1470 | 1480 | 1490 | 1500 |
| PSKLMTSTTS | TCLPPTNLPL | GTAGMPVMPV | GTPGQVSTPG | THASAPASTA | TGAKPGTTPP |
| 1510 | 1520 | 1530 | 1540 | 1550 | 1560 |
| KPSLTKTVVP | PVGTELSAGT | VPCEQLPPFP | GPSLIQTQQP | LEDLDAQLRR | TLSPETIPVT |
| 1570 | 1580 | 1590 | 1600 | 1610 | 1620 |
| PAVGPLSTMS | STAVTEAGSQ | PQKDGTEVHV | TASSSGAGVV | KMGRFQVSVT | MDDAQKERKN |
| 1630 | 1640 | 1650 | 1660 | 1670 | 1680 |
| RSEDTKSVHF | ESSTSESSVL | SSSSPESTLV | KPEPNGITVS | GISLDVPDST | HRTPTPEAKS |
| 1690 | 1700 | 1710 | 1720 | 1730 | 1740 |
| ETGQPTKVGR | FQVTTTANKV | GRFSVSRTED | KVTELKKEGP | VTSPFRDSEQ | TVIPAAIPKK |
| 1750 | 1760 | 1770 | 1780 | 1790 | 1800 |
| EKPELAEPSH | LNGPSSDLEA | AFLSRGGEDG | SGSPHSPPHL | CSKSLPIQTL | SQSLSNSFNS |
| 1810 | 1820 | 1830 | 1840 | 1850 | 1860 |
| SYMSSDNESD | IEDEDLRLEL | RRLREKHLKE | IQDLQSRQKH | EIESLYTKLG | KVPPAVIIPP |
| 1870 | 1880 | 1890 | 1900 | 1910 | 1920 |
| AAPLSGRRRR | PTKSKGSKSS | RSSSLGNKSP | QLSGNLSGQS | GTSVLNPQQT | LHPPGNTPET |
| 1930 | 1940 | 1950 | 1960 | 1970 | 1980 |
| GHNQLLQPLK | PSPSSDNLYS | AFTSDGAISV | PSLSAPGQGT | SSTNTVGGTV | SSQAAQAQPP |
| 1990 | 2000 | 2010 | 2020 | 2030 | 2040 |
| AMTSSRKGTF | TDDLHKLVDN | WARDAMNLSG | RRGSKGHMNY | EGPGMARKFS | APGQLCISMT |
| 2050 | 2060 | 2070 | 2080 | 2090 | 2100 |
| SNMGGSTPIS | AASATSLGHF | TKSMCPPQQY | GFPAAPFGTQ | WSGTGGPAPQ | PLGQFQPVGT |
| 2110 | 2120 | ||||
| TSLQNFNISN | LQKSISNPPG | SNLRTT |