Q9JI91
Gene name |
Actn2 |
Protein name |
Alpha-actinin-2 |
Names |
Alpha-actinin skeletal muscle isoform 2, F-actin cross-linking protein |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:11472 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
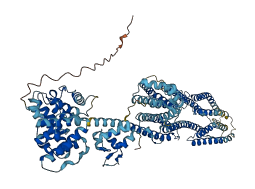
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
753-890 (EF-hand domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9JI91
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9JI91-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
5 variants for Q9JI91
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs13463802 | 70 | L>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs247407978 | 603 | T>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs13463807 | 803 | P>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs13463808 | 856 | P>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs13463806 | 859 | A>V | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q9JI91
12 regional properties for Q9JI91
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| conserved_site | Actinin-type actin-binding domain, conserved site | 40 - 49 | IPR001589-1 |
| conserved_site | Actinin-type actin-binding domain, conserved site | 114 - 138 | IPR001589-2 |
| domain | Calponin homology domain | 38 - 142 | IPR001715-1 |
| domain | Calponin homology domain | 151 - 257 | IPR001715-2 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 282 - 390 | IPR002017-1 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 401 - 505 | IPR002017-2 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 517 - 627 | IPR002017-3 |
| repeat | Spectrin repeat | 638 - 739 | IPR002017-4 |
| domain | EF-hand domain | 753 - 824 | IPR002048 |
| domain | EF-hand, Ca insensitive | 824 - 890 | IPR014837 |
| repeat | Spectrin/alpha-actinin | 402 - 629 | IPR018159-1 |
| repeat | Spectrin/alpha-actinin | 640 - 739 | IPR018159-2 |
12 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell junction | A cellular component that forms a specialized region of connection between two or more cells, or between a cell and the extracellular matrix, or between two membrane-bound components of a cell, such as flagella. |
| cell projection | A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon. |
| cortical actin cytoskeleton | The portion of the actin cytoskeleton, comprising filamentous actin and associated proteins, that lies just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| filopodium | Thin, stiff, actin-based protrusion extended by the leading edge of a motile cell such as a crawling fibroblast or amoeba, or an axonal or dendritic growth cone, or a dendritic shaft. |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| postsynaptic density membrane | The membrane component of the postsynaptic density. This is the region of the postsynaptic membrane in which the population of neurotransmitter receptors involved in synaptic transmission are concentrated. |
| postsynaptic density, intracellular component | A network of proteins adjacent to the postsynaptic membrane forming an electron dense disc. Its major components include neurotransmitter receptors and the proteins that spatially and functionally organize neurotransmitter receptors in the adjacent membrane, such as anchoring and scaffolding molecules, signaling enzymes and cytoskeletal components. |
| sarcomere | The repeating unit of a myofibril in a muscle cell, composed of an array of overlapping thick and thin filaments between two adjacent Z discs. |
| striated muscle thin filament | Filaments formed of actin and associated proteins; attached to Z discs at either end of sarcomeres in myofibrils. |
| Z disc | Platelike region of a muscle sarcomere to which the plus ends of actin filaments are attached. |
13 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament binding | Binding to an actin filament, also known as F-actin, a helical filamentous polymer of globular G-actin subunits. |
| calcium ion binding | Binding to a calcium ion (Ca2+). |
| cytoskeletal protein binding | Binding to a protein component of a cytoskeleton (actin, microtubule, or intermediate filament cytoskeleton). |
| FATZ binding | Binding to a member of the FATZ family of proteins, filamin-, actinin-, and telethonin-binding proteins of the Z-disc of striated muscle. FATZ proteins are located in the Z-disc of the sarcomere and are involved in a complex network of interactions with other Z-band components. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| LIM domain binding | Binding to a LIM domain (for Lin-11 Isl-1 Mec-3) of a protein, a domain with seven conserved cysteine residues and a histidine, that binds two zinc ions and acts as an interface for protein-protein interactions. |
| nuclear receptor coactivator activity | A transcription coactivator activity that activates or increases the transcription of specific gene sets via binding to a DNA-bound nuclear receptor, either on its own or as part of a complex. Coactivators often act by altering chromatin structure and modifications. For example, one class of transcription coregulators modifies chromatin structure through covalent modification of histones. A second class remodels the conformation of chromatin in an ATP-dependent fashion. A third class modulates interactions of DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factors with other transcription coregulators. A fourth class of coactivator activity is the bridging of a DNA-binding transcription factor to the general (basal) transcription machinery. The Mediator complex, which bridges sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factors and RNA polymerase, is also a transcription coactivator. |
| phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate binding | Binding to phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate, a derivative of phosphatidylinositol in which the inositol ring is phosphorylated at the 4' and 5' positions. |
| protein domain specific binding | Binding to a specific domain of a protein. |
| protein-macromolecule adaptor activity | The binding activity of a protein that brings together two or more macromolecules in contact, permitting those molecules to function in a coordinated way. The adaptor can bring together two proteins, or a protein and another macromolecule such as a lipid or a nucleic acid. |
| titin binding | Binding to titin, any of a family of giant proteins found in striated and smooth muscle. In striated muscle, single titin molecules span half the sarcomere, with their N- and C-termini in the Z-disc and M-line, respectively. |
| titin Z domain binding | Binding to a titin Z protein domain, which recognizes and binds to the C-terminal calmodulin-like domain of alpha-actinin-2 (Act-EF34), adopts a helical structure, and binds in a groove formed by the two planes between the helix pairs of Act-EF34. |
| transmembrane transporter binding | Binding to a transmembrane transporter, a protein or protein complex that enables the transfer of a substance, usually a specific substance or a group of related substances, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
18 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| actin filament uncapping | The removal of capping protein from the end of actin filaments to free the ends for addition, exchange or removal of further actin subunits. |
| cardiac muscle cell development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a cardiac muscle cell over time, from its formation to the mature state. |
| focal adhesion assembly | The aggregation and bonding together of a set of components to form a focal adhesion, a complex of intracellular signaling and structural proteins that provides a structural link between the internal actin cytoskeleton and the ECM, and also function as a locus of signal transduction activity. |
| microspike assembly | Formation of a microspike, a dynamic, actin-rich projection extending from the surface of a migrating animal cell. |
| muscle cell development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a muscle cell over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Muscle cell development does not include the steps involved in committing an unspecified cell to the muscle cell fate. |
| muscle contraction | A process in which force is generated within muscle tissue, resulting in a change in muscle geometry. Force generation involves a chemo-mechanical energy conversion step that is carried out by the actin/myosin complex activity, which generates force through ATP hydrolysis. |
| negative regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity. |
| negative regulation of potassium ion transport | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| negative regulation of protein localization to cell surface | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to the cell surface. |
| phospholipase C-activating angiotensin-activated signaling pathway | A phospholipase C-activating G protein-coupled receptor signaling pathway initiated by angiotensin binding to its receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| positive regulation of cation channel activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cation channel activity. |
| positive regulation of endocytic recycling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of endocytic recycling. |
| positive regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity. |
| positive regulation of potassium ion transport | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of potassium ions (K+) into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| protein localization to plasma membrane | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location in the plasma membrane. |
| regulation of membrane potential | Any process that modulates the establishment or extent of a membrane potential, the electric potential existing across any membrane arising from charges in the membrane itself and from the charges present in the media on either side of the membrane. |
| sarcomere organization | The myofibril assembly process that results in the organization of muscle actomyosin into sarcomeres. The sarcomere is the repeating unit of a myofibril in a muscle cell, composed of an array of overlapping thick and thin filaments between two adjacent Z discs. |
19 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| A5D7D1 | ACTN4 | Alpha-actinin-4 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q0III9 | ACTN3 | Alpha-actinin-3 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3B7N2 | ACTN1 | Alpha-actinin-1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3ZC55 | ACTN2 | Alpha-actinin-2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q90734 | ACTN4 | Alpha-actinin-4 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P05094 | ACTN1 | Alpha-actinin-1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P20111 | ACTN2 | Alpha-actinin-2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P18091 | Actn | Alpha-actinin, sarcomeric | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q08043 | ACTN3 | Alpha-actinin-3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O43707 | ACTN4 | Alpha-actinin-4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P12814 | ACTN1 | Alpha-actinin-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P35609 | ACTN2 | Alpha-actinin-2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O88990 | Actn3 | Alpha-actinin-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P57780 | Actn4 | Alpha-actinin-4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q7TPR4 | Actn1 | Alpha-actinin-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62261 | Sptbn1 | Spectrin beta chain, non-erythrocytic 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P15508 | Sptb | Spectrin beta chain, erythrocytic | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9Z1P2 | Actn1 | Alpha-actinin-1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9QXQ0 | Actn4 | Alpha-actinin-4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MNQIEPGVQY | NYVYDEDEYM | IQEEEWDRDL | LLDPAWEKQQ | RKTFTAWCNS | HLRKAGTQIE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NIEEDFRNGL | KLMLLLEVIS | GERLPKPDRG | KMRFHKIANV | NKALDYIASK | GVKLVSIGAE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| EIVDGNVKMT | LGMIWTIILR | FAIQDISVEE | TSAKEGLLLW | CQRKTAPYRN | VNIQNFHTSW |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| KDGLGLCALI | HRHRPDLIDY | SKLNKDDPIG | NINLAMEIAE | KHLDIPKMLD | AEDIVNTPKP |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| DERAIMTYVS | CFYHAFAGAE | QAETAANRIC | KVLAVNQENE | RLMEEYERLA | SELLEWIRRT |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| IPWLENRTPE | KTMQAMQKKL | EDFRDYRRKH | KPPKVQEKCQ | LEINFNTLQT | KLRISNRPAF |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| MPSEGKMVSD | IAGAWQRLEQ | AEKGYEEWLL | NEIRRLERLE | HLAEKFRQKA | STHETWAYGK |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| EQILLQKDYE | SASLTEVRAL | LRKHEAFESD | LAAHQDRVEQ | IAAIAQELNE | LDYHDAVNVN |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| DRCQKICDQW | DRLGTLTQKR | REALERTEKL | LETIDQLHLE | FAKRAAPFNN | WMEGAMEDLQ |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| DMFIVHSIEE | IQSLITAHEQ | FKATLPEADG | ERQSILAIQN | EVEKVIQSYS | IRISSSNPYS |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| TVTMDELRNK | WDKVKQLVPV | RDQSLQEELA | RQHANERLRR | QFAAQANAIG | PWIQNKMEEI |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| ARSSIQITGA | LEDQMNQLKQ | YEHNIINYKN | NIDKLEGDHQ | LIQEALVFDN | KHTNYTMEHI |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| RVGWELLLTT | IARTINEVET | QILTRDAKGI | TQEQMNEFRA | SFNHFDRRKN | GLMDHEDFRA |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| CLISMGYDLG | EAEFARIMTL | VDPNGQGTVT | FQSFIDFMTR | ETADTDTAEQ | VIASFRILAS |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | |
| DKPYILAEEL | RRELPPDQAQ | YCIKRMPPYS | GPGSVPGALD | YTAFSSALYG | ESDL |