Q9JHW5
Gene name |
Vamp7 (Sybl1) |
Protein name |
Vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 |
Names |
VAMP-7 , Synaptobrevin-like protein 1 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:85491 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
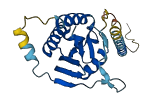
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
125-185 (v-SNARE coiled-coil homology) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Martinez-Arca S et al. (2003) "A dual mechanism controlling the localization and function of exocytic v-SNAREs", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 9011-6
- Gonzalez LC Jr et al. (2001) "A novel snare N-terminal domain revealed by the crystal structure of Sec22b", The Journal of biological chemistry, 276, 24203-11
- Mancias JD et al. (2007) "The transport signal on Sec22 for packaging into COPII-coated vesicles is a conformational epitope", Molecular cell, 26, 403-14
- Wen W et al. (2010) "Lipid-Induced conformational switch controls fusion activity of longin domain SNARE Ykt6", Molecular cell, 37, 383-95
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9JHW5
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9JHW5-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q9JHW5
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9JHW5 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q9JHW5
4 regional properties for Q9JHW5
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 14 - 272 | IPR000719 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 132 - 144 | IPR008271 |
| domain | Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, association-domain | 410 - 537 | IPR013543 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 20 - 43 | IPR017441 |
Functions
26 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical part of cell | The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue. |
| azurophil granule membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an azurophil granule, a primary lysosomal granule found in neutrophil granulocytes that contains a wide range of hydrolytic enzymes and is released into the extracellular fluid. |
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| endoplasmic reticulum membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the endoplasmic reticulum. |
| filopodium | Thin, stiff, actin-based protrusion extended by the leading edge of a motile cell such as a crawling fibroblast or amoeba, or an axonal or dendritic growth cone, or a dendritic shaft. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| hippocampal mossy fiber to CA3 synapse | One of the giant synapses that form between the mossy fiber axons of dentate gyrus granule cells and the large complex spines of CA3 pyramidal cells. It consists of a giant bouton known as the mossy fiber expansion, synapsed to the complex, multiheaded spine (thorny excresence) of a CA3 pyramidal cell. |
| lamellipodium | A thin sheetlike process extended by the leading edge of a migrating cell or extending cell process; contains a dense meshwork of actin filaments. |
| late endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a late endosome. |
| lysosomal membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the lysosome and separating its contents from the cell cytoplasm. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it and attached to it. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| phagocytic vesicle | A membrane-bounded intracellular vesicle that arises from the ingestion of particulate material by phagocytosis. |
| phagocytic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a phagocytic vesicle. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| platelet alpha granule | A secretory organelle found in blood platelets, which is unique in that it exhibits further compartmentalization and acquires its protein content via two distinct mechanisms |
| pseudopodium | A temporary protrusion or retractile process of a cell, associated with flowing movements of the protoplasm, and serving for locomotion and feeding. |
| secretory granule | A small subcellular vesicle, surrounded by a membrane, that is formed from the Golgi apparatus and contains a highly concentrated protein destined for secretion. Secretory granules move towards the periphery of the cell and upon stimulation, their membranes fuse with the cell membrane, and their protein load is exteriorized. Processing of the contained protein may take place in secretory granules. |
| secretory granule membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a secretory granule. |
| SNARE complex | A protein complex involved in membrane fusion; a stable ternary complex consisting of a four-helix bundle, usually formed from one R-SNARE and three Q-SNAREs with an ionic layer sandwiched between hydrophobic layers. One well-characterized example is the neuronal SNARE complex formed of synaptobrevin 2, syntaxin 1a, and SNAP-25. |
| synaptic vesicle | A secretory organelle, typically 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and secretes these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane. |
| synaptic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a synaptic vesicle. |
| trans-Golgi network | The network of interconnected tubular and cisternal structures located within the Golgi apparatus on the side distal to the endoplasmic reticulum, from which secretory vesicles emerge. The trans-Golgi network is important in the later stages of protein secretion where it is thought to play a key role in the sorting and targeting of secreted proteins to the correct destination. |
| transport vesicle | Any of the vesicles of the constitutive secretory pathway, which carry cargo from the endoplasmic reticulum to the Golgi, between Golgi cisternae, from the Golgi to the ER (retrograde transport) or to destinations within or outside the cell. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| SNAP receptor activity | Acting as a marker to identify a membrane and interacting selectively with one or more SNAREs on another membrane to mediate membrane fusion. |
| SNARE binding | Binding to a SNARE (soluble N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor attached protein receptor) protein. |
| syntaxin binding | Binding to a syntaxin, a SNAP receptor involved in the docking of synaptic vesicles at the presynaptic zone of a synapse. |
18 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| calcium-ion regulated exocytosis | The release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle by fusion of the vesicle with the plasma membrane of a cell, induced by a rise in cytosolic calcium-ion levels. |
| endoplasmic reticulum to Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | The directed movement of substances from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) to the Golgi, mediated by COP II vesicles. Small COP II coated vesicles form from the ER and then fuse directly with the cis-Golgi. Larger structures are transported along microtubules to the cis-Golgi. |
| endosome to lysosome transport | The directed movement of substances from endosomes to lysosomes. |
| eosinophil degranulation | The regulated exocytosis of secretory granules containing preformed mediators such as major basic protein, eosinophil peroxidase, and eosinophil cationic protein by an eosinophil. |
| exocytosis | A process of secretion by a cell that results in the release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle. Exocytosis can occur either by full fusion, when the vesicle collapses into the plasma membrane, or by a kiss-and-run mechanism that involves the formation of a transient contact, a pore, between a granule (for exemple of chromaffin cells) and the plasma membrane. The latter process most of the time leads to only partial secretion of the granule content. Exocytosis begins with steps that prepare vesicles for fusion with the membrane (tethering and docking) and ends when molecules are secreted from the cell. |
| Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport | The directed movement of proteins from the Golgi to the plasma membrane in transport vesicles that move from the trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane. |
| natural killer cell degranulation | The regulated exocytosis of secretory granules containing preformed mediators such as perforin and granzymes by a natural killer cell. |
| neutrophil degranulation | The regulated exocytosis of secretory granules containing preformed mediators such as proteases, lipases, and inflammatory mediators by a neutrophil. |
| phagocytosis, engulfment | The internalization of bacteria, immune complexes and other particulate matter or of an apoptotic cell by phagocytosis, including the membrane and cytoskeletal processes required, which involves one of three mechanisms |
| positive regulation of dendrite morphogenesis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of dendrite morphogenesis. |
| positive regulation of histamine secretion by mast cell | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of histamine secretion by mast cell. |
| regulation of protein targeting to vacuolar membrane | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of protein targeting to vacuolar membrane. |
| SNARE complex assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a SNARE complex, a protein complex involved in membrane fusion; a stable ternary complex consisting of a four-helix bundle, usually formed from one R-SNARE and three Q-SNAREs with an ionic layer sandwiched between hydrophobic layers. |
| triglyceride transport | The directed movement of triglyceride into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. Triglycerides are important components of plant oils, animal fats and animal plasma lipoproteins. |
| vesicle fusion | Fusion of the membrane of a transport vesicle with its target membrane. |
| vesicle fusion with Golgi apparatus | The joining of the lipid bilayer membrane around a vesicle to the lipid bilayer membrane around the Golgi. |
| vesicle transport along microtubule | The directed movement of a vesicle along a microtubule, mediated by motor proteins. This process begins with the attachment of a vesicle to a microtubule, and ends when the vesicle reaches its final destination. |
| vesicle-mediated transport | A cellular transport process in which transported substances are moved in membrane-bounded vesicles; transported substances are enclosed in the vesicle lumen or located in the vesicle membrane. The process begins with a step that directs a substance to the forming vesicle, and includes vesicle budding and coating. Vesicles are then targeted to, and fuse with, an acceptor membrane. |
10 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q12255 | NYV1 | Vacuolar v-SNARE NYV1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q17QI5 | VAMP7 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q5ZL74 | VAMP7 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P51809 | VAMP7 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P70280 | Vamp7 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O49377 | VAMP711 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 711 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9FMR5 | VAMP714 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 714 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LFP1 | VAMP713 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 713 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9M376 | VAMP727 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 727 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q9SIQ9 | VAMP712 | Vesicle-associated membrane protein 712 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAILFAVVAR | GTTILAKHAW | CGGNFLEVTE | QILAKIPSEN | NKLTYSHGNY | LFHYICQDRI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| VYLCITDDDF | ERSRAFGFLN | EVKKRFQTTY | GSRAQTALPY | AMNSEFSSVL | AAQLKHHSEN |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QSLDRVTETQ | AQVDELKGIM | VRNIDLVAQR | GERLELLIDK | TENLVDSSVT | FKTTSRNLAR |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | |||
| AMCVKNVKLT | AIIVVVSIVF | IYIIVSPLCG | GFTWPSCVKK |