Q9ES74
Gene name |
Nek7 |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase Nek7 |
Names |
Never in mitosis A-related kinase 7, NimA-related protein kinase 7 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:59125 |
EC number |
2.7.11.34: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
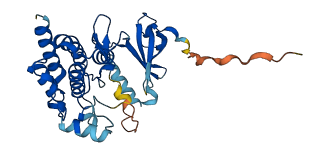
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
20-30 (N-terminal extension of kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
178-201 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
34-299 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9ES74
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9ES74-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q9ES74
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9ES74 | |||||
2 associated diseases with Q9ES74
[MIM: 613780]: Aortic aneurysm, familial thoracic 7 (AAT7)
A disease characterized by permanent dilation of the thoracic aorta usually due to degenerative changes in the aortic wall. It is primarily associated with a characteristic histologic appearance known as 'medial necrosis' or 'Erdheim cystic medial necrosis' in which there is degeneration and fragmentation of elastic fibers, loss of smooth muscle cells, and an accumulation of basophilic ground substance. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 249210]: Megacystis-microcolon-intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome (MMIHS)
A form of megacystis-microcolon-intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome, a congenital visceral myopathy primarily affecting females, and characterized by loss of smooth muscle contraction in the bladder and intestine. Affected individuals present at birth with functional obstruction of intestine, microcolon, dilation of bladder, and secondary hydronephrosis. The majority of cases have a fatal outcome due to malnutrition and sepsis, followed by multiorgan failure. MMIHS inheritance is autosomal recessive. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Without disease ID
- A disease characterized by permanent dilation of the thoracic aorta usually due to degenerative changes in the aortic wall. It is primarily associated with a characteristic histologic appearance known as 'medial necrosis' or 'Erdheim cystic medial necrosis' in which there is degeneration and fragmentation of elastic fibers, loss of smooth muscle cells, and an accumulation of basophilic ground substance. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- A form of megacystis-microcolon-intestinal hypoperistalsis syndrome, a congenital visceral myopathy primarily affecting females, and characterized by loss of smooth muscle contraction in the bladder and intestine. Affected individuals present at birth with functional obstruction of intestine, microcolon, dilation of bladder, and secondary hydronephrosis. The majority of cases have a fatal outcome due to malnutrition and sepsis, followed by multiorgan failure. MMIHS inheritance is autosomal recessive. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
41 regional properties for Q9ES74
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 1464 - 1719 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 45 - 113 | IPR003598-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 173 - 240 | IPR003598-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 426 - 494 | IPR003598-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 526 - 590 | IPR003598-4 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 635 - 702 | IPR003598-5 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 733 - 801 | IPR003598-6 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 1110 - 1177 | IPR003598-7 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 1250 - 1317 | IPR003598-8 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype 2 | 1821 - 1889 | IPR003598-9 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 39 - 124 | IPR003599-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 167 - 251 | IPR003599-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 420 - 505 | IPR003599-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 520 - 601 | IPR003599-4 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 629 - 713 | IPR003599-5 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 727 - 812 | IPR003599-6 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 1104 - 1188 | IPR003599-7 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 1244 - 1328 | IPR003599-8 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin subtype | 1815 - 1900 | IPR003599-9 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 1331 - 1426 | IPR003961 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 33 - 122 | IPR007110-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 161 - 249 | IPR007110-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 414 - 503 | IPR007110-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 514 - 599 | IPR007110-4 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 620 - 711 | IPR007110-5 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 721 - 808 | IPR007110-6 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 1098 - 1186 | IPR007110-7 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 1238 - 1326 | IPR007110-8 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin-like domain | 1809 - 1898 | IPR007110-9 |
| active_site | Serine/threonine-protein kinase, active site | 1581 - 1593 | IPR008271 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 33 - 123 | IPR013098-1 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 161 - 250 | IPR013098-2 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 414 - 504 | IPR013098-3 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 514 - 600 | IPR013098-4 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 624 - 712 | IPR013098-5 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 722 - 809 | IPR013098-6 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 1098 - 1187 | IPR013098-7 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 1238 - 1327 | IPR013098-8 |
| domain | Immunoglobulin I-set | 1809 - 1899 | IPR013098-9 |
| domain | Myosin Light Chain Kinase 1, Kinase domain | 1461 - 1719 | IPR015725 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 1470 - 1493 | IPR017441 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.34 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| microtubule organizing center | An intracellular structure that can catalyze gamma-tubulin-dependent microtubule nucleation and that can anchor microtubules by interacting with their minus ends, plus ends or sides. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| spindle pole | Either of the ends of a spindle, where spindle microtubules are organized; usually contains a microtubule organizing center and accessory molecules, spindle microtubules and astral microtubules. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
6 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to potassium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a potassium ion stimulus. |
| positive regulation of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of NLRP3 inflammasome complex assembly. |
| positive regulation of telomerase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of telomerase activity, the catalysis of the reaction: deoxynucleoside triphosphate + DNA(n) = diphosphate + DNA(n+1). |
| positive regulation of telomere capping | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of telomere capping. |
| positive regulation of telomere maintenance via telomerase | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the addition of telomeric repeats by telomerase. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
7 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9HC98 | NEK6 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Nek6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8TDX7 | NEK7 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Nek7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9ES70 | Nek6 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Nek6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| A2BD05 | NEK6 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Nek6 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| P59895 | Nek6 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Nek6 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| D3ZBE5 | Nek7 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Nek7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| G5EFM9 | nekl-3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase nekl-3 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MDEQSQGMQG | PPVTQFQPQK | ALRPDMGYNT | LANFRIEKKI | GRGQFSEVYR | ASCLLDGVPV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| ALKKVQIFDL | MDAKARADCI | KEIDLLKQLN | HPNVIKYYAS | FIEDNELNIV | LELADAGDLS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RMIKHFKKQK | RLIPERTVWK | YFVQLCSALD | HMHSRRVMHR | DIKPANVFIT | ATGVVKLGDL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GLGRFFSSKT | TAAHSLVGTP | YYMSPERIHE | NGYNFKSDIW | SLGCLLYEMA | ALQSPFYGDK |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| MNLYSLCKKI | EQCDYPPLPS | DHYSEELRQL | VNICINPDPE | KRPDIAYVYD | VAKRMHACTA |
| ST |