Q9EPV5
Gene name |
Apaf1 |
Protein name |
Apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 |
Names |
APAF-1 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:78963 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
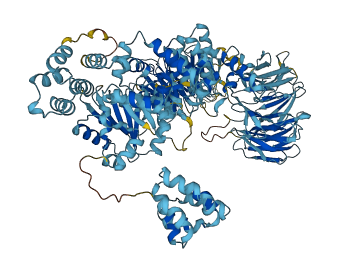
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
130-374 (NB-ARC domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Bao Q et al. (2005) "Structure of Apaf-1 in the auto-inhibited form: a critical role for ADP", Cell cycle (Georgetown, Tex.), 4, 1001-3
- Bao Q et al. (2007) "Calcium blocks formation of apoptosome by preventing nucleotide exchange in Apaf-1", Molecular cell, 25, 181-92
- Shakeri R et al. (2015) "Role of the salt bridge between glutamate 546 and arginine 907 in preservation of autoinhibited form of Apaf-1", International journal of biological macromolecules, 81, 370-4
- Reubold TF et al. (2011) "Crystal structure of full-length Apaf-1: how the death signal is relayed in the mitochondrial pathway of apoptosis", Structure (London, England : 1993), 19, 1074-83
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9EPV5
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9EPV5-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
3 variants for Q9EPV5
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs105117105 | 1073 | I>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs8155392 | 1190 | R>K | No | Ensembl | |
| rs8150686 | 1198 | G>R | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q9EPV5
17 regional properties for Q9EPV5
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | CARD domain | 1 - 90 | IPR001315 |
| repeat | WD40 repeat | 604 - 780 | IPR001680-1 |
| repeat | WD40 repeat | 780 - 825 | IPR001680-2 |
| repeat | WD40 repeat | 828 - 868 | IPR001680-3 |
| repeat | WD40 repeat | 871 - 912 | IPR001680-4 |
| repeat | WD40 repeat | 952 - 989 | IPR001680-5 |
| repeat | WD40 repeat | 992 - 1164 | IPR001680-6 |
| repeat | WD40 repeat | 1168 - 1204 | IPR001680-7 |
| domain | NB-ARC | 130 - 374 | IPR002182 |
| conserved_site | WD40 repeat, conserved site | 716 - 730 | IPR019775-1 |
| conserved_site | WD40 repeat, conserved site | 758 - 772 | IPR019775-2 |
| conserved_site | WD40 repeat, conserved site | 1142 - 1156 | IPR019775-3 |
| repeat | G-protein beta WD-40 repeat | 672 - 686 | IPR020472-1 |
| repeat | G-protein beta WD-40 repeat | 716 - 730 | IPR020472-2 |
| repeat | G-protein beta WD-40 repeat | 758 - 772 | IPR020472-3 |
| domain | Apoptotic Protease-Activating Factor 1, CARD domain | 7 - 92 | IPR037963 |
| domain | APAF-1 helical domain | 453 - 587 | IPR041452 |
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptosome | A multisubunit protein complex involved in the signaling phase of the apoptotic process. In mammals it is typically composed of seven Apaf-1 subunits bound to cytochrome c and caspase-9. A similar complex to promote apoptosis is formed from homologous gene products in other eukaryotic organisms. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| protein-containing complex | A stable assembly of two or more macromolecules, i.e. proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates or lipids, in which at least one component is a protein and the constituent parts function together. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ADP binding | Binding to ADP, adenosine 5'-diphosphate. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| cysteine-type endopeptidase activator activity involved in apoptotic process | Binds to and increases the rate of proteolysis catalyzed by a cysteine-type endopeptidase involved in the apoptotic process. |
| heat shock protein binding | Binding to a heat shock protein, a protein synthesized or activated in response to heat shock. |
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
17 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity | Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme cysteine-type endopeptidase. |
| activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process | Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme cysteine-type endopeptidase in the context of an apoptotic process. |
| activation of cysteine-type endopeptidase activity involved in apoptotic process by cytochrome c | Any process that initiates the activity of the inactive enzyme cysteine-type endopeptidase in the context of an apoptotic process and is mediated by cytochrome c. |
| aging | A developmental process that is a deterioration and loss of function over time. Aging includes loss of functions such as resistance to disease, homeostasis, and fertility, as well as wear and tear. Aging includes cellular senescence, but is more inclusive. May precede death and may succeed developmental maturation (GO:0021700). |
| brain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.). |
| cardiac muscle cell apoptotic process | A form of programmed cell death induced by external or internal signals that trigger the activity of proteolytic caspases, whose actions dismantle a cardiac muscle cell and result in its death. Cardiac muscle cells are striated muscle cells that are responsible for heart contraction. |
| cell differentiation | The process in which relatively unspecialized cells, e.g. embryonic or regenerative cells, acquire specialized structural and/or functional features that characterize the cells, tissues, or organs of the mature organism or some other relatively stable phase of the organism's life history. Differentiation includes the processes involved in commitment of a cell to a specific fate and its subsequent development to the mature state. |
| cellular response to transforming growth factor beta stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a transforming growth factor beta stimulus. |
| forebrain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the forebrain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The forebrain is the anterior of the three primary divisions of the developing chordate brain or the corresponding part of the adult brain (in vertebrates, includes especially the cerebral hemispheres, the thalamus, and the hypothalamus and especially in higher vertebrates is the main control center for sensory and associative information processing, visceral functions, and voluntary motor functions). |
| intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to endoplasmic reticulum stress | The series of molecular signals in which an intracellular signal is conveyed to trigger the apoptotic death of a cell. The pathway is induced in response to a stimulus indicating endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress, and ends when the execution phase of apoptosis is triggered. ER stress usually results from the accumulation of unfolded or misfolded proteins in the ER lumen. |
| kidney development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the kidney over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The kidney is an organ that filters the blood and/or excretes the end products of body metabolism in the form of urine. |
| neural tube closure | The last step in the formation of the neural tube, where the paired neural folds are brought together and fuse at the dorsal midline. |
| neuron apoptotic process | Any apoptotic process in a neuron, the basic cellular unit of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| regulation of apoptotic DNA fragmentation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of apoptotic DNA fragmentation. |
| response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| response to nutrient | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a nutrient stimulus. |
4 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q3MJ13 | WDR72 | WD repeat-containing protein 72 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O14727 | APAF1 | Apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O88879 | Apaf1 | Apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9I9H8 | apaf1 | Apoptotic protease-activating factor 1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MDAKARNCLL | QHKEALEKDI | KTSYIMDHMI | SNGVLTVVEE | EKVKSQATQY | QRAAALIKMI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LNKDNYAYIS | FYNALLHEGY | KDLAGLLHSG | LPLVSSSSGK | DTDGGNTSFV | RTVLCEGGVP |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QRPVIFVTRK | KLVSAIQQKL | WKLNGEPGWV | TIYGMAGCGK | SVLAAEAVRD | HALLEGCFSG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GVHWVSIGKQ | DKSGLLMKLQ | NLCTRLGQEE | SFSQRLPLNI | EEAKDRLRVL | MLRKHPRSLL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| ILDDVWDPWV | LKAFDNQCQI | LLTTRDKSVT | DSVMGPKYVI | PVESGLGKEK | GLEILSLFVN |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| MKKEDLPVEA | HSIIKECKGS | PLVVSLVGAL | LRDFPNRWAY | YLRQLQNKQF | KRIRKSSSYD |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| YEALDEAMSI | SVEMLREDIK | DYYTDLSILQ | KDVKVPTKVL | CVLWDLETEE | VEDILQEFVN |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| KSLLFCNRNG | KSFCYYLHDL | QVDFLTEKNR | SQLQDLHRKM | VTQFQRYHQP | HTLSPGQEDC |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| MYWYNFLAYH | MASAGMHKEL | CALMFSLDWI | KAKTELVGPA | HLIHEFVEYR | HILDEKDCAV |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| CENFQEFLSL | NGHLLGRQPF | PNIVQLGLCE | PETSEVYQQA | KLQAKQEVDT | GRLYLEWINK |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| KTIKNLSRLV | VRPHTDAVYH | ACFSQDGQRI | ASCGADKTLQ | VFKAETGEKL | LDIKAHEDEV |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| LCCAFSSDDS | YIATCSVDKK | VKIWDSGTGK | LVHTYEEHSE | QVNCCHFTNK | SNHLLLATGS |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| NDSFLKLWDL | NQKECRNTMF | GHTNSVTHCR | FSPDDELLAS | CSADGTLKLW | DVRSANEKKS |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| INVKRFFLSS | EDPPEDVEVI | VKCCSWSADG | DRIIVAAKNK | VLLLDIHTSG | LLTEIHTGHH |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| STIQYCDFSP | YDHLAVIALS | QYCVELWNID | SRVKVADCRG | HLSWVHGVMF | SPDGSSFLTA |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| SDDQTIRVWE | TRKVCKNSAI | VLKQEIDVVF | QENEMMVLAV | DNIRGLQLIA | GKTGQIDYLP |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| EAQVSCCCLS | PHLEYVAFGD | EEGAIKIIEL | PNNRVFSSGI | GHKKAVRHIQ | FTADGKTLIS |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| SSEDSVIQVW | NWQTEEYVFL | QAHQETVKDF | RLLRDSRLLS | WSFDGTVKVW | NVITGRIERD |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| FTCHQGTVLS | CAISSDATKF | SSTSADKTAK | IWSFELPSPL | HELKGHNSCV | RCSAFSLDGI |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| LLATGDDNGE | IRIWNVSDGQ | LLHLCAPISI | EEGTATHGGW | VTDVCFSPDR | KMLVSAGGYL |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | ||
| KWWNVVTGES | SQTFYTNGTN | LKKIHVSPDF | RTYVTVDNLG | ILYILQVLE |