Q9DDA9
Gene name |
pacsin2 |
Protein name |
Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 2 |
Names |
x-PACSIN2 |
Species |
Xenopus laevis (African clawed frog) |
KEGG Pathway |
xla:398138 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
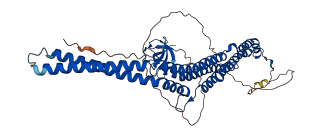
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
11-282 (F-BAR domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9DDA9
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9DDA9-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q9DDA9
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q9DDA9 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q9DDA9
Functions
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| caveola | A membrane raft that forms small pit, depression, or invagination that communicates with the outside of a cell and extends inward, indenting the cytoplasm and the cell membrane. Examples include flask-shaped invaginations of the plasma membrane in adipocytes associated with caveolin proteins, and minute pits or incuppings of the cell membrane formed during pinocytosis. Caveolae may be pinched off to form free vesicles within the cytoplasm. |
| cytoskeleton | A cellular structure that forms the internal framework of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton includes intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| recycling endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a recycling endosome. |
| ruffle membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a ruffle. |
1 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| phosphatidic acid binding | Binding to phosphatidic acid, any of a class of glycerol phosphate in which both the remaining hydroxyl groups of the glycerol moiety are esterified with fatty acids. |
4 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures comprising actin filaments and their associated proteins. |
| caveola assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a caveola. A caveola is a plasma membrane raft that forms a small pit, depression, or invagination that communicates with the outside of a cell and extends inward, indenting the cytoplasm and the cell membrane. |
| endocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process in which cells take up external materials or membrane constituents by the invagination of a small region of the plasma membrane to form a new membrane-bounded vesicle. |
| plasma membrane tubulation | A membrane tubulation process occurring in a plasma membrane. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSGTYDDSVG | VEVSSDSFWE | VGNYKRTVKR | IDDGHRLCND | LMNCIHERAR | IEKVYAQQLT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| EWAKRWKQLV | ERGPQYGTVE | KAWHNLMTEA | EKVSELHLEV | KNALMNEDFE | KIKNWQKEAF |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| HKQMMGGFKE | TKEADDGFRK | AQKPWAKKLK | EVEAAKKSYH | AACKEEKLAT | SRETNSKADP |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| AMNPEQLKKL | QDKVEKSKQD | SQKTKEKYEK | SLKDLDGTTP | QYMENMEQVF | EQCQQFEDKR |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LSFFREVLLE | VEKHLDLSNV | ESYASIYREL | EYAIKSADAM | EDLKWFRNNH | GPGMSMNWPQ |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| FEDWSADLNR | TLSRREKKKP | TDGVTLTGIS | QSGEQSSIQN | QHSSHLSVQS | AQSTNNPFED |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| EEETVSINET | ENKKIENVGS | YEKTHPAEWS | DDESNNPFNP | SDTNGDNNPF | DEDALTTLEV |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | |
| RVRALYDYDG | QELDELSFKA | GEELTKIEDE | DEQGWCKGRL | EGGQVGLYPA | NYVESVQ |