Q9DD03
Gene name |
Rab13 |
Protein name |
Ras-related protein Rab-13 |
Names |
|
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:68328 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
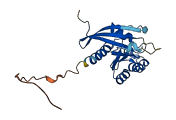
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9DD03
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9DD03-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
5 variants for Q9DD03
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388640806 | 29 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388646875 | 89 | D>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388647730 | 102 | W>R | No | EVA | |
| rs216840527 | 188 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3674470 | 196 | K>N | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q9DD03
Functions
20 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| bicellular tight junction | An occluding cell-cell junction that is composed of a branching network of sealing strands that completely encircles the apical end of each cell in an epithelial sheet; the outer leaflets of the two interacting plasma membranes are seen to be tightly apposed where sealing strands are present. Each sealing strand is composed of a long row of transmembrane adhesion proteins embedded in each of the two interacting plasma membranes. |
| cell-cell junction | A cell junction that forms a connection between two or more cells of an organism; excludes direct cytoplasmic intercellular bridges, such as ring canals in insects. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle | A vesicle found in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| cytoplasmic vesicle membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a cytoplasmic vesicle. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| endocytic vesicle | A membrane-bounded intracellular vesicle formed by invagination of the plasma membrane around an extracellular substance. Endocytic vesicles fuse with early endosomes to deliver the cargo for further sorting. |
| endosome | A vacuole to which materials ingested by endocytosis are delivered. |
| extrinsic component of plasma membrane | The component of a plasma membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to one of its surfaces, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| insulin-responsive compartment | A small membrane-bounded vesicle that releases its contents by exocytosis in response to insulin stimulation; the contents are enriched in GLUT4, IRAP and VAMP2. |
| intracellular membrane-bounded organelle | Organized structure of distinctive morphology and function, bounded by a single or double lipid bilayer membrane and occurring within the cell. Includes the nucleus, mitochondria, plastids, vacuoles, and vesicles. Excludes the plasma membrane. |
| lamellipodium | A thin sheetlike process extended by the leading edge of a migrating cell or extending cell process; contains a dense meshwork of actin filaments. |
| lateral plasma membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane at the lateral side of the cell. In epithelial cells, lateral plasma membranes are on the sides of cells which lie at the interface of adjacent cells. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| recycling endosome | An organelle consisting of a network of tubules that functions in targeting molecules, such as receptors transporters and lipids, to the plasma membrane. |
| recycling endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a recycling endosome. |
| synaptic vesicle | A secretory organelle, typically 50 nm in diameter, of presynaptic nerve terminals; accumulates in high concentrations of neurotransmitters and secretes these into the synaptic cleft by fusion with the 'active zone' of the presynaptic plasma membrane. |
| trans-Golgi network | The network of interconnected tubular and cisternal structures located within the Golgi apparatus on the side distal to the endoplasmic reticulum, from which secretory vesicles emerge. The trans-Golgi network is important in the later stages of protein secretion where it is thought to play a key role in the sorting and targeting of secreted proteins to the correct destination. |
| trans-Golgi network transport vesicle | A vesicle that mediates transport between the trans-Golgi network and other parts of the cell. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
| protein kinase A catalytic subunit binding | Binding to one or both of the catalytic subunits of protein kinase A. |
17 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| bicellular tight junction assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a tight junction, an occluding cell-cell junction that is composed of a branching network of sealing strands that completely encircles the apical end of each cell in an epithelial sheet. |
| cellular response to insulin stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an insulin stimulus. Insulin is a polypeptide hormone produced by the islets of Langerhans of the pancreas in mammals, and by the homologous organs of other organisms. |
| cortical actin cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of actin-based cytoskeletal structures in the cell cortex, i.e. just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| endocytic recycling | The directed movement of membrane-bounded vesicles from endosomes back to the plasma membrane, a trafficking pathway that promotes the recycling of internalized transmembrane proteins. |
| endosomal transport | The directed movement of substances mediated by an endosome, a membrane-bounded organelle that carries materials enclosed in the lumen or located in the endosomal membrane. |
| endothelial cell chemotaxis | The directed movement of an endothelial cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
| establishment of Sertoli cell barrier | Establishment of a structure near the basement membrane in adjacent Sertoli cells of the seminiferous epithelium for maintaining spermatogenesis. The structure consists of tight junctions, basal ectoplasmic specializations, and desmosome-like junctions. |
| Golgi vesicle fusion to target membrane | The joining of the lipid bilayer membrane around a Golgi transport vesicle to the target lipid bilayer membrane. |
| intracellular protein transport | The directed movement of proteins in a cell, including the movement of proteins between specific compartments or structures within a cell, such as organelles of a eukaryotic cell. |
| neuron projection development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
| protein kinase A signaling | A series of reactions, mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase A, which occurs as a result of a single trigger reaction or compound. |
| protein localization to cell leading edge | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a location within a cell leading edge. |
| protein localization to plasma membrane | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location in the plasma membrane. |
| protein secretion | The controlled release of proteins from a cell. |
| regulation of exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of exocytosis. |
| trans-Golgi network to recycling endosome transport | The directed movement of substances, in membrane-bounded vesicles, from the trans-Golgi network to the recycling endosomes. |
| vesicle docking involved in exocytosis | The initial attachment of a vesicle membrane to a target membrane, mediated by proteins protruding from the membrane of the vesicle and the target membrane, that contributes to exocytosis. |
27 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P07560 | SEC4 | Ras-related protein SEC4 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q2HJI8 | RAB8B | Ras-related protein Rab-8B | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| A4FV54 | RAB8A | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q1RMR4 | RAB15 | Ras-related protein Rab-15 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q5F470 | RAB8A | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P0C0E4 | RAB40AL | Ras-related protein Rab-40A-like | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P61006 | RAB8A | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q92930 | RAB8B | Ras-related protein Rab-8B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6IQ22 | RAB12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8WXH6 | RAB40A | Ras-related protein Rab-40A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96S21 | RAB40C | Ras-related protein Rab-40C | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q12829 | RAB40B | Ras-related protein Rab-40B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8CB87 | Rab44 | Ras-related protein Rab-44 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35283 | Rab12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P55258 | Rab8a | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P61028 | Rab8b | Ras-related protein Rab-8B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VHQ4 | Rab40c | Ras-related protein Rab-40C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VHP8 | Rab40b | Ras-related protein Rab-40B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8K386 | Rab15 | Ras-related protein Rab-15 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P35289 | Rab15 | Ras-related protein Rab-15 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P35280 | Rab8a | Ras-related protein Rab-8A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P70550 | Rab8b | Ras-related protein Rab-8B | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P35284 | Rab12 | Ras-related protein Rab-12 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P35281 | Rab10 | Ras-related protein Rab-10 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| O24466 | RABE1A | Ras-related protein RABE1a | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9SF91 | RABE1E | Ras-related protein RABE1e | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LZD4 | RABE1D | Ras-related protein RABE1d | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAKAYDHLFK | LLLIGDSGVG | KTCLIIRFAE | DNFNSTYIST | IGIDFKIRTV | DIEGKRIKLQ |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| VWDTAGQERF | KTITTAYYRG | AMGIILVYDI | TDEKSFENIQ | NWMKSIKENA | SAGVERLLLG |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| NKCDMEAKRQ | VQREQAEKLA | REHRIRFFET | SAKSSVNVDE | AFSSLARDIL | LKTGGRRSGT |
| 190 | 200 | ||||
| NSKPSSTGLK | TSDKKKNKCL | LG |