Q9DC28
Gene name |
Csnk1d (Hckid) |
Protein name |
Casein kinase I isoform delta |
Names |
CKI-delta, CKId, Tau-protein kinase CSNK1D |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:104318 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
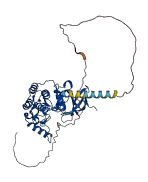
Descriptions
(Annotation based on sequence homology with P49674)
Casein kinase I epsilon (CSNK1E) is a member of CKI family and is involved in signaling, circadian clock, DNA repair, and metabolism. The tail of autophosphorylated CKIε interacts with the kinase domain and blocks the active site. Proteolytic lysis of the C-terminal region relieves autoinhibition.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
148-178 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
9-287 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

3 structures for Q9DC28
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 4JJR | X-ray | 241 A | A/B | 1-299 | PDB |
| 5X17 | X-ray | 200 A | A/B | 1-294 | PDB |
| AF-Q9DC28-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
18 variants for Q9DC28
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3389214289 | 26 | G>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3389201215 | 82 | M>SDG* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389201237 | 84 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389214281 | 84 | L>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3389219575 | 89 | L>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389224523 | 104 | T>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3389189116 | 105 | V>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389214320 | 115 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3389214283 | 164 | H>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3389214324 | 250 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389161164 | 253 | N>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389236857 | 259 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389201189 | 273 | F>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389228168 | 298 | S>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389236803 | 300 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389214291 | 300 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389189100 | 375 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389223590 | 376 | G>W | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q9DC28
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
12 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| centrosome | A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle. |
| ciliary basal body | A membrane-tethered, short cylindrical array of microtubules and associated proteins found at the base of a eukaryotic cilium (also called flagellum) that is similar in structure to a centriole and derives from it. The cilium basal body is the site of assembly and remodelling of the cilium and serves as a nucleation site for axoneme growth. As well as anchoring the cilium, it is thought to provide a selective gateway regulating the entry of ciliary proteins and vesicles by intraflagellar transport. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| spindle | The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart. |
| spindle microtubule | Any microtubule that is part of a mitotic or meiotic spindle; anchored at one spindle pole. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| kinase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction: a protein + ATP = a phosphoprotein + ADP. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| tau-protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + tau-protein = ADP + O-phospho-tau-protein. |
19 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| circadian regulation of gene expression | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression such that an expression pattern recurs with a regularity of approximately 24 hours. |
| Golgi organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the Golgi apparatus. |
| microtubule nucleation | The process in which tubulin alpha-beta heterodimers begin aggregation to form an oligomeric tubulin structure (a microtubule seed). Microtubule nucleation is the initiating step in the formation of a microtubule in the absence of any existing microtubules ('de novo' microtubule formation). |
| non-motile cilium assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a non-motile cilium. |
| peptidyl-serine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-serine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-serine. |
| positive regulation of canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway through beta-catenin, the series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell, followed by propagation of the signal via beta-catenin, and ending with a change in transcription of target genes. |
| positive regulation of non-canonical Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of non-canonical Wnt-activated signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| positive regulation of protein phosphorylation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of addition of phosphate groups to amino acids within a protein. |
| positive regulation of Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of Wnt signal transduction. |
| positive regulation of Wnt-mediated midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of Wnt signaling pathway involved in midbrain dopaminergic neuron differentiation. |
| protein localization to centrosome | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained at, the centrosome. |
| protein localization to cilium | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a location within a cilium. |
| protein localization to Golgi apparatus | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a location within the Golgi apparatus. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of circadian rhythm | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of a circadian rhythm. A circadian rhythm is a biological process in an organism that recurs with a regularity of approximately 24 hours. |
| signal transduction | The cellular process in which a signal is conveyed to trigger a change in the activity or state of a cell. Signal transduction begins with reception of a signal (e.g. a ligand binding to a receptor or receptor activation by a stimulus such as light), or for signal transduction in the absence of ligand, signal-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. Signal transduction ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. regulation of transcription or regulation of a metabolic process. Signal transduction covers signaling from receptors located on the surface of the cell and signaling via molecules located within the cell. For signaling between cells, signal transduction is restricted to events at and within the receiving cell. |
| spindle assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that serves to move duplicated chromosomes apart. |
| Wnt signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell and ending with a change in cell state. |
15 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P29295 | HRR25 | Casein kinase I homolog HRR25 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P35508 | CSNK1D | Casein kinase I isoform delta | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q5ZLL1 | CSNK1E | Casein kinase I isoform epsilon | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q86Y07 | VRK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase VRK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P49674 | CSNK1E | Casein kinase I isoform epsilon | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P48730 | CSNK1D | Casein kinase I isoform delta | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9JMK2 | Csnk1e | Casein kinase I isoform epsilon | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8BN21 | Vrk2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase VRK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q06486 | Csnk1d | Casein kinase I isoform delta | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| P42169 | C03C10.2 | Putative casein kinase I C03C10.2 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| P34516 | K06H7.8 | Putative serine/threonine-protein kinase K06H7.1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q6P647 | csnk1d | Casein kinase I isoform delta | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| Q7T2E3 | csnk1da | Casein kinase I isoform delta-A | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q7ZUS1 | vrk1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase VRK1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| Q6P3K7 | csnk1db | Casein kinase I isoform delta-B | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MELRVGNRYR | LGRKIGSGSF | GDIYLGTDIA | AGEEVAIKLE | CVKTKHPQLH | IESKIYKMMQ |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GGVGIPTIRW | CGAEGDYNVM | VMELLGPSLE | DLFNFCSRKF | SLKTVLLLAD | QMISRIEYIH |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| SKNFIHRDVK | PDNFLMGLGK | KGNLVYIIDF | GLAKKYRDAR | THQHIPYREN | KNLTGTARYA |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SINTHLGIEQ | SRRDDLESLG | YVLMYFNLGS | LPWQGLKAAT | KRQKYERISE | KKMSTPIEVL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| CKGYPSEFAT | YLNFCRSLRF | DDKPDYSYLR | QLFRNLFHRQ | GFSYDYVFDW | NMLKFGASRA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| ADDAERERRD | REERLRHSRN | PATRGLPSTA | SGRLRGTQEV | APPTPLTPTS | HTANTSPRPV |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | |
| SGMERERKVS | MRLHRGAPVN | VSSSDLTGRQ | DTSRMSTSQI | PGRVASSGLQ | SVVHR |