Q9DBH0
Gene name |
Wwp2 |
Protein name |
NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP2 |
Names |
HECT-type E3 ubiquitin transferase WWP2, WW domain-containing protein 2 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:66894 |
EC number |
2.3.2.26: Aminoacyltransferases |
Protein Class |
|
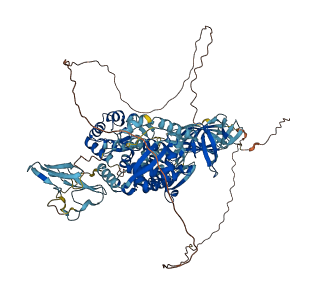
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
536-870 (HECT domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Mund T et al. (2009) "Control of the activity of WW-HECT domain E3 ubiquitin ligases by NDFIP proteins", EMBO reports, 10, 501-7
- Wiesner S et al. (2007) "Autoinhibition of the HECT-type ubiquitin ligase Smurf2 through its C2 domain", Cell, 130, 651-62
- Riling C et al. (2015) "Itch WW Domains Inhibit Its E3 Ubiquitin Ligase Activity by Blocking E2-E3 Ligase Trans-thiolation", The Journal of biological chemistry, 290, 23875-87
- Wang Z et al. (2019) "A multi-lock inhibitory mechanism for fine-tuning enzyme activities of the HECT family E3 ligases", Nature communications, 10, 3162
- Zhu K et al. (2017) "Allosteric auto-inhibition and activation of the Nedd4 family E3 ligase Itch", EMBO reports, 18, 1618-1630
- Tsunoda T et al. (2022) "ENTREP/FAM189A2 encodes a new ITCH ubiquitin ligase activator that is downregulated in breast cancer", EMBO reports, 23, e51182
- Chen Z et al. (2017) "A Tunable Brake for HECT Ubiquitin Ligases", Molecular cell, 66, 345-357.e6
- Lu K et al. (2011) "Pivotal role of the C2 domain of the Smurf1 ubiquitin ligase in substrate selection", The Journal of biological chemistry, 286, 16861-70
- Ogunjimi AA et al. (2005) "Regulation of Smurf2 ubiquitin ligase activity by anchoring the E2 to the HECT domain", Molecular cell, 19, 297-308
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9DBH0
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9DBH0-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
5 variants for Q9DBH0
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs215453015 | 33 | N>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs257437883 | 78 | Q>H | No | Ensembl | |
| rs37666062 | 225 | S>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs37582756 | 236 | N>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs13471728 | 438 | Q>H | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q9DBH0
4 regional properties for Q9DBH0
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | C2 domain | 1 - 117 | IPR000008 |
| domain | WW domain | 300 - 363 | IPR001202-1 |
| domain | WW domain | 405 - 437 | IPR001202-2 |
| domain | WW domain | 444 - 477 | IPR001202-3 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.3.2.26 | Aminoacyltransferases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| RNA polymerase II-specific DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a sequence-specific DNA binding RNA polymerase II transcription factor, any of the factors that interact selectively and non-covalently with a specific DNA sequence in order to modulate transcription. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of ubiquitin to a substrate protein via the reaction X-ubiquitin + S -> X + S-ubiquitin, where X is either an E2 or E3 enzyme, the X-ubiquitin linkage is a thioester bond, and the S-ubiquitin linkage is an amide bond: an isopeptide bond between the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin and the epsilon-amino group of lysine residues in the substrate or, in the linear extension of ubiquitin chains, a peptide bond the between the C-terminal glycine and N-terminal methionine of ubiquitin residues. |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of ubiquitin from one protein to another via the reaction X-Ub + Y --> Y-Ub + X, where both X-Ub and Y-Ub are covalent linkages. |
17 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| extracellular transport | The transport of substances that occurs outside cells. |
| negative regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the activity of a transcription factor, any factor involved in the initiation or regulation of transcription. |
| negative regulation of gene expression | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| negative regulation of protein transport | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of a protein into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| negative regulation of transcription, DNA-templated | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| negative regulation of transporter activity | Any process that stops or reduces the activity of a transporter. |
| positive regulation of protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein by the destruction of the native, active configuration, with or without the hydrolysis of peptide bonds. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| protein autoubiquitination | The ubiquitination by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues, or residues on an identical protein. Ubiquitination occurs on the lysine residue by formation of an isopeptide crosslink. |
| protein K63-linked ubiquitination | A protein ubiquitination process in which a polymer of ubiquitin, formed by linkages between lysine residues at position 63 of the ubiquitin monomers, is added to a protein. K63-linked ubiquitination does not target the substrate protein for degradation, but is involved in several pathways, notably as a signal to promote error-free DNA postreplication repair. |
| protein polyubiquitination | Addition of multiple ubiquitin groups to a protein, forming a ubiquitin chain. |
| protein ubiquitination | The process in which one or more ubiquitin groups are added to a protein. |
| regulation of ion transmembrane transport | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of ions from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| regulation of membrane potential | Any process that modulates the establishment or extent of a membrane potential, the electric potential existing across any membrane arising from charges in the membrane itself and from the charges present in the media on either side of the membrane. |
| regulation of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of potassium ion transmembrane transporter activity. |
23 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P39940 | RSP5 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase RSP5 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q9V853 | Smurf | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Smurf1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9Y0H4 | Su(dx) | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Su | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9HAU4 | SMURF2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9HCE7 | SMURF1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O95817 | BAG3 | BAG family molecular chaperone regulator 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96PU5 | NEDD4L | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4-like | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O60861 | GAS7 | Growth arrest-specific protein 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P46934 | NEDD4 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9H0M0 | WWP1 | NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q96J02 | ITCH | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Itchy homolog | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O00308 | WWP2 | NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q60780 | Gas7 | Growth arrest-specific protein 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P46935 | Nedd4 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BZZ3 | Wwp1 | NEDD4-like E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase WWP1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9CUN6 | Smurf1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| A2A5Z6 | Smurf2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8C863 | Itch | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase Itchy | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q3U0D9 | Hace1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase HACE1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8CFI0 | Nedd4l | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4-like | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q62940 | Nedd4 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase NEDD4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9N2Z7 | wwp-1 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase wwp-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| A9JRZ0 | smurf2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SMURF2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MASASSSRAG | VALPFEKSQL | TLKVVSAKPK | VHNRQPRINS | YVEVAVDGLP | SETKKTGKRI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GSSELLWNEI | IVLNVTAQSH | LDLKVWSCHT | LRNELLGTAS | VNLSNVLKNN | GGKMENTQLT |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LNLQTENKGS | VVSGGELTIF | LDGPTVDLGS | VPNGSAVTDG | SQPPSRESSG | TAIAPETRHQ |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| PPSTNCFGGR | SRTHRHSGGS | ARTATAASEQ | SPGARNRHRQ | PVKNSSSSGL | ANGTVNEEPT |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| PASEPEESSV | VGVTSLPAAA | LSVSSNPNTT | SLPAQSTPAE | GEEASTSGTQ | QLPAAAQAPD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| ALPAGWEQRE | LPNGRVYYVD | HNTKTTTWER | PLPPGWEKRT | DPRGRFYYVD | HNTRTTTWQR |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| PTAEYVRNYE | QWQSQRNQLQ | GAMQHFSQRF | LYQSSSASTD | HDPLGPLPPG | WEKRQDNGRV |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| YYVNHNTRTT | QWEDPRTQGM | IQEPALPPGW | EMKYTSEGVR | YFVDHNTRTT | TFKDPRPGFE |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| SGTKQGSPGA | YDRSFRWKYH | QFRFLCHSNA | LPSHVKISVS | RQTLFEDSFQ | QIMNMKPYDL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| RRRLYIIMRG | EEGLDYGGIA | REWFFLLSHE | VLNPMYCLFE | YAGKNNYCLQ | INPASSINPD |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| HLTYFRFIGR | FIAMALYHGK | FIDTGFTLPF | YKRMLNKRPT | LKDLESIDPE | FYNSIVWIKE |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| NNLEECGLEL | FFIQDMEILG | KVTTHELKEG | GENIRVTEEN | KEEYIMLLTD | WRFTRGVEEQ |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| TKAFLDGFNE | VAPLEWLRYF | DEKELELMLC | GMQEIDMSDW | QKNAIYRHYT | KSSKQIQWFW |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| QVVKEMDNEK | RIRLLQFVTG | TCRLPVGGFA | ELIGSNGPQK | FCIDRVGKET | WLPRSHTCFN |
| 850 | 860 | ||||
| RLDLPPYKSY | EQLKEKLLYA | IEETEGFGQE |