Q9D7F7
Gene name |
Chmp4c |
Protein name |
Charged multivesicular body protein 4c |
Names |
Chromatin-modifying protein 4c, CHMP4c |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:66371 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
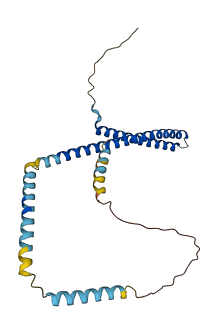
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
1-144 (N-terminal α1-α4 domains) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q9D7F7
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q9D7F7-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
5 variants for Q9D7F7
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs1134848785 | 18 | A>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs29707553 | 21 | S>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs29709942 | 121 | D>E | No | Ensembl | |
| rs244653197 | 122 | N>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs253408595 | 219 | E>D | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q9D7F7
No regional properties for Q9D7F7
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for Q9D7F7 | |||
Functions
12 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| amphisome membrane | Any membrane that is part of an amphisome. |
| cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The leaflet the plasma membrane that faces the cytoplasm and any proteins embedded or anchored in it or attached to its surface. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| ESCRT III complex | A complex with membrane scission activity that plays a major role in many processes where membranes are remodelled - including endosomal transport (vesicle budding), nuclear envelope organisation (membrane closure, mitotic bridge cleavage), and cytokinesis (abscission). |
| Flemming body | A cell part that is the central region of the midbody characterized by a gap in alpha-tubulin staining. It is a dense structure of antiparallel microtubules from the central spindle in the middle of the intercellular bridge. |
| kinetochore | A multisubunit complex that is located at the centromeric region of DNA and provides an attachment point for the spindle microtubules. |
| kinetochore microtubule | Any of the spindle microtubules that attach to the kinetochores of chromosomes by their plus ends, and maneuver the chromosomes during mitotic or meiotic chromosome segregation. |
| lysosomal membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding the lysosome and separating its contents from the cell cytoplasm. |
| midbody | A thin cytoplasmic bridge formed between daughter cells at the end of cytokinesis. The midbody forms where the contractile ring constricts, and may persist for some time before finally breaking to complete cytokinesis. |
| multivesicular body | A type of endosome in which regions of the limiting endosomal membrane invaginate to form internal vesicles; membrane proteins that enter the internal vesicles are sequestered from the cytoplasm. |
| multivesicular body membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a multivesicular body. |
| nuclear pore | A protein complex providing a discrete opening in the nuclear envelope of a eukaryotic cell, where the inner and outer nuclear membranes are joined. |
1 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| protein homodimerization activity | Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
20 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| abscission | The controlled shedding of a body part. |
| autophagosome maturation | Removal of PI3P and Atg8/LC3 after the closure of the phagophore and before the fusion with the endosome/lysosome (e.g. mammals and insects) or vacuole (yeast), and that very likely destabilizes other Atg proteins and thus enables their efficient dissociation and recycling. |
| late endosome to lysosome transport | The directed movement of substances from late endosome to lysosome. |
| late endosome to vacuole transport via multivesicular body sorting pathway | The directed movement of substances from endosomes to vacuoles by a pathway in which molecules are sorted into multivesicular bodies, which then fuse with the vacuole. |
| midbody abscission | The process by which the midbody, the cytoplasmic bridge that connects the two prospective daughter cells, is severed at the end of mitotic cytokinesis, resulting in two separate daughter cells. |
| mitotic cytokinesis checkpoint signaling | A signaling process that contributes to a mitotic cell cycle checkpoint that detects a defect in cytokinesis and prevents further rounds of nuclear division until cytokinesis is completed. |
| mitotic metaphase plate congression | The cell cycle process in which chromosomes are aligned at the metaphase plate, a plane halfway between the poles of the mitotic spindle, during mitosis. |
| negative regulation of cell death | Any process that decreases the rate or frequency of cell death. Cell death is the specific activation or halting of processes within a cell so that its vital functions markedly cease, rather than simply deteriorating gradually over time, which culminates in cell death. |
| negative regulation of cytokinesis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the division of the cytoplasm of a cell, and its separation into two daughter cells. |
| nuclear membrane reassembly | The reformation of the nuclear membranes following their breakdown in the context of a normal process. |
| nucleus organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of the nucleus. |
| plasma membrane repair | The resealing of a cell plasma membrane after cellular wounding due to, for instance, mechanical stress. |
| protein transport | The directed movement of proteins into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| regulation of centrosome duplication | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of centrosome duplication. Centrosome duplication is the replication of a centrosome, a structure comprised of a pair of centrioles and peri-centriolar material from which a microtubule spindle apparatus is organized. |
| regulation of mitotic spindle assembly | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of mitotic spindle assembly. |
| ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide covalently tagged with ubiquitin, via the multivesicular body (MVB) sorting pathway; ubiquitin-tagged proteins are sorted into MVBs, and delivered to a lysosome/vacuole for degradation. |
| ubiquitin-independent protein catabolic process via the multivesicular body sorting pathway | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide, via the multivesicular body (MVB) sorting pathway; proteins are sorted into MVBs, and delivered to a lysosome/vacuole for degradation. This process is independent of ubiquitination. |
| vesicle budding from membrane | The evagination of a membrane, resulting in formation of a vesicle. |
| viral budding from plasma membrane | A viral budding that starts with formation of a membrane curvature in the host plasma membrane. |
| viral budding via host ESCRT complex | Viral budding which uses a host ESCRT protein complex, or complexes, to mediate the budding process. |
3 homologous proteins in AiPD
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSKLGKFFKG | TRSSRARAAP | SAQEALARLR | ETEEMLAKKQ | EYLENRIQRE | LALAKKHGSQ |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NKRAALQALK | RKKRFEKQLT | QVDGTLSTIE | FQREALENSH | TNTEVLRNMG | FAAKAMKAVH |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DNMDLNKIDD | LMQDITEQQD | IAQEISEAFS | QRVQFADGFD | EAELLAELEE | LEQEELNKKM |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | |
| TSLELPNVPS | SSLPAQPSRK | ASMPSSVHRS | RAASSRRAEE | DDDFKQLAAW | AT |