Q99PQ1
Gene name |
Trim12a (Trim12) |
Protein name |
Tripartite motif-containing protein 12A |
Names |
|
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:76681 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
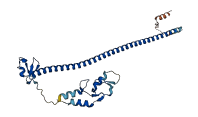
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q99PQ1
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q99PQ1-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
36 variants for Q99PQ1
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs584141544 | 7 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs1133020227 | 26 | V>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388917068 | 31 | G>D | No | EVA | |
| rs258708070 | 41 | L>V | No | EVA | |
| rs248236284 | 43 | F>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388931948 | 46 | I>V | No | EVA | |
| rs578550520 | 54 | I>F | No | EVA | |
| rs584667743 | 54 | I>S | No | EVA | |
| rs212876991 | 61 | S>R | No | EVA | |
| rs581326916 | 79 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs583989381 | 82 | M>K | No | EVA | |
| rs587438234 | 82 | M>V | No | EVA | |
| rs581761600 | 87 | P>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388938897 | 101 | K>M | No | EVA | |
| rs231948652 | 123 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs31924865 | 156 | K>E | No | EVA | |
| rs586409398 | 169 | T>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3388935787 | 175 | I>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3412695451 | 177 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs31928753 | 183 | R>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs1132977043 | 188 | R>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388927901 | 188 | R>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388938910 | 192 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388938841 | 193 | M>V | No | EVA | |
| rs31928751 | 194 | D>N | No | EVA | |
| rs31928749 | 210 | D>N | No | EVA | |
| rs31928747 | 212 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs31928744 | 220 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs1131745115 | 231 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388932199 | 237 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3388933527 | 245 | I>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388933530 | 260 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs31927838 | 264 | W>* | No | EVA | |
| rs31927835 | 272 | A>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3388938824 | 278 | V>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388936932 | 284 | S>F | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q99PQ1
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| omegasome | Omega-shaped (as in the Greek capital letter) intracellular membrane-bounded organelle enriched in phosphatidylinositol 3-phosphate and dynamically connected to the endoplasmic reticulum. Omegasomes are the first step of the formation of autophagosomes via the phagophore assembly sites. |
| P-body | A focus in the cytoplasm where mRNAs may become inactivated by decapping or some other mechanism. Protein and RNA localized to these foci are involved in mRNA degradation, nonsense-mediated mRNA decay (NMD), translational repression, and RNA-mediated gene silencing. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| pattern recognition receptor activity | Combining with a pathogen-associated molecular pattern (PAMP), a structure conserved among microbial species to initiate an innate immune response. |
| protein homodimerization activity | Binding to an identical protein to form a homodimer. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| protein-macromolecule adaptor activity | The binding activity of a protein that brings together two or more macromolecules in contact, permitting those molecules to function in a coordinated way. The adaptor can bring together two proteins, or a protein and another macromolecule such as a lipid or a nucleic acid. |
| transcription coactivator activity | A transcription coregulator activity that activates or increases the transcription of specific gene sets via binding to a DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factor, either on its own or as part of a complex. Coactivators often act by altering chromatin structure and modifications. For example, one class of transcription coactivators modifies chromatin structure through covalent modification of histones. A second class remodels the conformation of chromatin in an ATP-dependent fashion. A third class modulates interactions of DNA-bound DNA-binding transcription factors with other transcription coregulators. A fourth class of coactivator activity is the bridging of a DNA-binding transcription factor to the general (basal) transcription machinery. The Mediator complex, which bridges sequence-specific DNA binding transcription factors and RNA polymerase, is also a transcription coactivator. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of ubiquitin to a substrate protein via the reaction X-ubiquitin + S -> X + S-ubiquitin, where X is either an E2 or E3 enzyme, the X-ubiquitin linkage is a thioester bond, and the S-ubiquitin linkage is an amide bond: an isopeptide bond between the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin and the epsilon-amino group of lysine residues in the substrate or, in the linear extension of ubiquitin chains, a peptide bond the between the C-terminal glycine and N-terminal methionine of ubiquitin residues. |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of ubiquitin from one protein to another via the reaction X-Ub + Y --> Y-Ub + X, where both X-Ub and Y-Ub are covalent linkages. |
| zinc ion binding | Binding to a zinc ion (Zn). |
17 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| activation of innate immune response | Any process that initiates an innate immune response. Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. Examples of this process include activation of the hypersensitive response of Arabidopsis thaliana and activation of any NOD or TLR signaling pathway in vertebrate species. |
| autophagy | The cellular catabolic process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm; allows for both recycling of macromolecular constituents under conditions of cellular stress and remodeling the intracellular structure for cell differentiation. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| negative regulation of viral entry into host cell | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the entry of viral entry into a host cell. |
| positive regulation of autophagy | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the rate of autophagy. Autophagy is the process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm. |
| positive regulation of DNA-binding transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of a transcription factor, any factor involved in the initiation or regulation of transcription. |
| positive regulation of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB signaling. |
| positive regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAPK cascade. |
| positive regulation of NF-kappaB transcription factor activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of activity of the transcription factor NF-kappaB. |
| protein K63-linked ubiquitination | A protein ubiquitination process in which a polymer of ubiquitin, formed by linkages between lysine residues at position 63 of the ubiquitin monomers, is added to a protein. K63-linked ubiquitination does not target the substrate protein for degradation, but is involved in several pathways, notably as a signal to promote error-free DNA postreplication repair. |
| protein polyubiquitination | Addition of multiple ubiquitin groups to a protein, forming a ubiquitin chain. |
| protein ubiquitination | The process in which one or more ubiquitin groups are added to a protein. |
| regulation of gene expression | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of gene expression. Gene expression is the process in which a gene's coding sequence is converted into a mature gene product (protein or RNA). |
| regulation of lipopolysaccharide-mediated signaling pathway | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signaling in response to detection of lipopolysaccharide. |
| regulation of protein localization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| regulation of viral entry into host cell | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the viral entry into the host cell. |
| suppression of viral release by host | A process in which a host organism stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the release of a virus with which it is infected, from its cells. |
46 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q5E9G4 | TRIM10 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 10 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q2T9Z0 | TRIM17 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM17 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| E1BJS7 | TRIM71 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM71 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q7YRV4 | TRIM21 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM21 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q1PRL4 | TRIM71 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM71 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q7YR32 | TRIM10 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 10 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | PR |
| O15553 | MEFV | Pyrin | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9BTV5 | FSD1 | Fibronectin type III and SPRY domain-containing protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9H2S5 | RNF39 | RING finger protein 39 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P19474 | TRIM21 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM21 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UJV3 | MID2 | Probable E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase MID2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P29590 | PML | Protein PML | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9C029 | TRIM7 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9NQ86 | TRIM36 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM36 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q86UV6 | TRIM74 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 74 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UPQ4 | TRIM35 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM35 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q6ZMU5 | TRIM72 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 72 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q86UV7 | TRIM73 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 73 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8N9V2 | TRIML1 | Probable E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIML1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q86XT4 | TRIM50 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM50 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q5EBN2 | TRIM61 | Putative tripartite motif-containing protein 61 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9BZY9 | TRIM31 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM31 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q2Q1W2 | TRIM71 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM71 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9BXM9 | FSD1L | FSD1-like protein | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9WUH5 | Trim10 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 10 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BZT2 | Sh3rf2 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase SH3RF2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q7TPM3 | Trim17 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM17 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q1XH17 | Trim72 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 72 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60953 | Pml | Protein PML | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9JJ26 | Mefv | Pyrin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61510 | Trim25 | E3 ubiquitin/ISG15 ligase TRIM25 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q810I2 | Trim50 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM50 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q1PSW8 | Trim71 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM71 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q3TL54 | Trim43a | Tripartite motif-containing protein 43A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P86449 | Trim43c | Tripartite motif-containing protein 43C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O77666 | TRIM26 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 26 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| O19085 | TRIM10 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 10 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| Q865W2 | TRIM50 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM50 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| Q920M2 | Rnf39 | RING finger protein 39 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9JJ25 | Mefv | Pyrin | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| A0JPQ4 | Trim72 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 72 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q810I1 | Trim50 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM50 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| D3ZVM4 | Trim71 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM71 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| F6QEU4 | trim71 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM71 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| Q640S6 | trim72 | Tripartite motif-containing protein 72 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| E7FAM5 | trim71 | E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase TRIM71 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MASQFMKNLK | EEVTCPVCLN | LMVKPVSADC | GHTFCQGCIT | LYFESIKCDK | KVFICPVCRI |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| SYQFSNLRPN | RNVANIVERL | KMFKPSPEEE | QKVFNCARHG | KKLQLFCRKD | MMAICWLCER |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| SQEHRGHKTA | LIEEVAQEYK | EQLQVVLQRL | MADKKKFENW | KDDLQKDRTY | WENQIQKDVQ |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| NVRSEFKRMR | DIMDSEEKKE | LQKLRQEKED | ILNNLAESES | EHAQQSKLLE | DFISDVEHQL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | ||
| QCSDIEILQV | RLQDVPGSES | QKAWKPLPFL | SAAVVFLVMT | VSSS |