Q99P74
Gene name |
Rab27b |
Protein name |
Ras-related protein Rab-27B |
Names |
|
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:84590 |
EC number |
3.6.5.2: Acting on GTP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
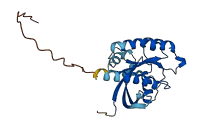
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q99P74
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q99P74-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
1 variants for Q99P74
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3323385162 | 88 | F>L | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q99P74
1 regional properties for Q99P74
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Small GTP-binding protein domain | 8 - 176 | IPR005225 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.5.2 | Acting on GTP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
13 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anchored component of synaptic vesicle membrane | The component of the synaptic vesicle membrane consisting of the gene products that are tethered to the membrane only by a covalently attached anchor, such as a lipid group that is embedded in the membrane. Gene products with peptide sequences that are embedded in the membrane are excluded from this grouping. |
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| axon cytoplasm | Any cytoplasm that is part of a axon. |
| exocytic vesicle | A transport vesicle that mediates transport from an intracellular compartment to the plasma membrane, and fuses with the plasma membrane to release various cargo molecules, such as proteins or hormones, by exocytosis. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| Golgi stack | The set of thin, flattened membrane-bounded compartments, called cisternae, that form the central portion of the Golgi complex. The stack usually comprises cis, medial, and trans cisternae; the cis- and trans-Golgi networks are not considered part of the stack. |
| late endosome | A prelysosomal endocytic organelle differentiated from early endosomes by lower lumenal pH and different protein composition. Late endosomes are more spherical than early endosomes and are mostly juxtanuclear, being concentrated near the microtubule organizing center. |
| melanosome | A tissue-specific, membrane-bounded cytoplasmic organelle within which melanin pigments are synthesized and stored. Melanosomes are synthesized in melanocyte cells. |
| multivesicular body membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a multivesicular body. |
| secretory granule | A small subcellular vesicle, surrounded by a membrane, that is formed from the Golgi apparatus and contains a highly concentrated protein destined for secretion. Secretory granules move towards the periphery of the cell and upon stimulation, their membranes fuse with the cell membrane, and their protein load is exteriorized. Processing of the contained protein may take place in secretory granules. |
| secretory granule membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a secretory granule. |
| trans-Golgi network transport vesicle | A vesicle that mediates transport between the trans-Golgi network and other parts of the cell. |
| zymogen granule membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding a zymogen granule. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| G protein activity | A molecular function regulator that cycles between active GTP-bound and inactive GDP-bound states. In its active state, binds to a variety of effector proteins to regulate cellular processes. Intrinsic GTPase activity returns the G protein to its GDP-bound state. The return to the GDP-bound state can be accelerated by the action of a GTPase-activating protein (GAP). |
| GDP binding | Binding to GDP, guanosine 5'-diphosphate. |
| GTP binding | Binding to GTP, guanosine triphosphate. |
| GTPase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: GTP + H2O = GDP + H+ + phosphate. |
| myosin V binding | Binding to a class V myosin; myosin V is a dimeric molecule involved in intracellular transport. |
| protein domain specific binding | Binding to a specific domain of a protein. |
7 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anterograde axonal protein transport | The directed movement of proteins along microtubules from the cell body toward the cell periphery in nerve cell axons. |
| exocytosis | A process of secretion by a cell that results in the release of intracellular molecules (e.g. hormones, matrix proteins) contained within a membrane-bounded vesicle. Exocytosis can occur either by full fusion, when the vesicle collapses into the plasma membrane, or by a kiss-and-run mechanism that involves the formation of a transient contact, a pore, between a granule (for exemple of chromaffin cells) and the plasma membrane. The latter process most of the time leads to only partial secretion of the granule content. Exocytosis begins with steps that prepare vesicles for fusion with the membrane (tethering and docking) and ends when molecules are secreted from the cell. |
| multivesicular body sorting pathway | A vesicle-mediated transport process in which transmembrane proteins are ubiquitylated to facilitate their entry into luminal vesicles of multivesicular bodies (MVBs); upon subsequent fusion of MVBs with lysosomes or vacuoles, the cargo proteins are degraded. |
| positive regulation of exocytosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of exocytosis. |
| regulation of exocytosis | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of exocytosis. |
| synaptic vesicle endocytosis | A vesicle-mediated transport process, in which the synaptic vesicle membrane constituents are retrieved from the presynaptic membrane on the axon terminal after neurotransmitter secretion by exocytosis. Synaptic vesicle endocytosis can occur via clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent mechanisms. |
| vesicle-mediated transport | A cellular transport process in which transported substances are moved in membrane-bounded vesicles; transported substances are enclosed in the vesicle lumen or located in the vesicle membrane. The process begins with a step that directs a substance to the forming vesicle, and includes vesicle budding and coating. Vesicles are then targeted to, and fuse with, an acceptor membrane. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q8HZJ5 | RAB27B | Ras-related protein Rab-27B | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q1HE58 | RAB27A | Ras-related protein Rab-27A | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| P51159 | RAB27A | Ras-related protein Rab-27A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O00194 | RAB27B | Ras-related protein Rab-27B | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9ERI2 | Rab27a | Ras-related protein Rab-27A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q99P58 | Rab27b | Ras-related protein Rab-27B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q4LE85 | RAB27A | Ras-related protein Rab-27A | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| P23640 | Rab27a | Ras-related protein Rab-27A | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MTDGDYDYLI | KLLALGDSGV | GKTTFLYRYT | DNKFNPKFIT | TVGIDFREKR | VVYDTQGADG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| SSGKAFKVHL | QLWDTAGQER | FRSLTTAFFR | DAMGFLLMFD | LTSQQSFLNV | RNWMSQLQAN |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| AYCENPDIVL | IGNKADLLDQ | REVNERQARE | LAEKYGIPYF | ETSAATGQNV | EKSVETLLDL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | |||
| IMKRMEKCVE | KTQVPDTVNG | VNSGKVDGEK | PAEKKCAC |