Q99MJ6
Gene name |
Pdzd3 (Nherf4, Pdzk2) |
Protein name |
Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF4 |
Names |
NHERF-4, Natrium-phosphate cotransporter IIa C-terminal-associated protein 2, Na/Pi cotransporter C-terminal-associated protein 2, NaPi-Cap2, PDZ domain-containing protein 2, PDZ domain-containing protein 3, Sodium-hydrogen exchanger regulatory factor 4 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:170761 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
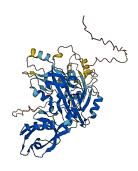
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q99MJ6
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q99MJ6-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q99MJ6
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q99MJ6 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q99MJ6
6 regional properties for Q99MJ6
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | PDZ domain | 49 - 130 | IPR001478-1 |
| domain | PDZ domain | 157 - 235 | IPR001478-2 |
| domain | PDZ domain | 263 - 346 | IPR001478-3 |
| domain | PDZ domain | 394 - 475 | IPR001478-4 |
| domain | PDZ domain 6 | 74 - 126 | IPR041489-1 |
| domain | PDZ domain 6 | 419 - 459 | IPR041489-2 |
Functions
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical junction complex | A functional unit located near the cell apex at the points of contact between epithelial cells, which in vertebrates is composed of the tight junction, the zonula adherens, and desmosomes and in some invertebrates, such as Drosophila, is composed of the subapical complex (SAC), the zonula adherens and the septate junction. Functions in the regulation of cell polarity, tissue integrity and intercellular adhesion and permeability. |
| apical part of cell | The region of a polarized cell that forms a tip or is distal to a base. For example, in a polarized epithelial cell, the apical region has an exposed surface and lies opposite to the basal lamina that separates the epithelium from other tissue. |
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| brush border | The dense covering of microvilli on the apical surface of an epithelial cell in tissues such as the intestine, kidney, and choroid plexus; the microvilli aid absorption by increasing the surface area of the cell. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| guanylate cyclase inhibitor activity | Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of guanylate cyclase. |
| protein C-terminus binding | Binding to a protein C-terminus, the end of a peptide chain at which the 1-carboxyl function of a constituent amino acid is not attached in peptide linkage to another amino-acid residue. |
| protein-membrane adaptor activity | The binding activity of a molecule that brings together a protein or a protein complex with a membrane, or bringing together two membranes, either via membrane lipid binding or by interacting with a membrane protein, to establish or maintain the localization of the protein, protein complex or organelle. |
| ubiquitin-specific protease binding | Binding to a ubiquitin-specific protease. |
4 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ion transport | The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| negative regulation of cGMP-mediated signaling | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of cGMP-mediated signaling. |
| protein localization to plasma membrane | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location in the plasma membrane. |
| receptor guanylyl cyclase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses guanylyl cyclase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
11 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q3SZK8 | NHERF1 | Na | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q5ZM14 | NHERF1 | Na | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q24008 | inaD | Inactivation-no-after-potential D protein | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q9Y6N9 | USH1C | Harmonin | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O14745 | SLC9A3R1 | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q86UT5 | PDZD3 | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q0QWG9 | Grid2ip | Delphilin | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9JIL4 | Pdzk1 | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P70441 | Slc9a3r1 | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9JJ40 | Pdzk1 | Na(+)/H(+) exchange regulatory cofactor NHE-RF3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9JJ19 | Nherf1 | Na | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEAAADLRDT | ALLTLKFKFN | PRLGIDNPVL | SLAEDQDQSD | PWNLHRPRFC | LLSKEEEKTF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| GFHLQQHLGK | ADHVVCRVDP | GTSAQRQGLR | EGDRILAVNN | NIVAHEDHAV | VVRYIRASGP |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RVLLTVLAQH | VHDVARVLQG | SDAFLCPTLP | SGVRPRLCHV | VKDEGGFGFS | VTHGSRGPFW |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LVLSAGGAAE | RAGVPPGARL | LEVNGASVEK | LTYNQLNRKL | WQSGDQVTLL | VAGLEVEEQC |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| HQLGMPLAAP | LAEGWALPAK | PRCLNIEKGP | EGFGFLLREE | KGLDGRLGQF | LWDVDPGLPA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DKAGMKAGDR | LVAVAGESVD | GLGHEETVSR | IRAQGSCVSL | IVVDPEADRF | FSMVRLSPLL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| FLENTEIAAP | PLAETKDLPV | EDTVEPSGLA | GSCQCFLYPG | PGGGYGFRLC | CVASGPCLFI |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SQVTPGGSTA | RAGLQVGDTV | LEVNGYPVGG | DSELDRLQQL | TEAEPPLCLK | LGARNPQGLE |
| 490 | |||||
| AWISLESGED | WTLASELL |