Q99M15
Gene name |
Pstpip2 (Mayp) |
Protein name |
Proline-serine-threonine phosphatase-interacting protein 2 |
Names |
PEST phosphatase-interacting protein 2, Macrophage actin-associated tyrosine-phosphorylated protein, pp37 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:19201 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
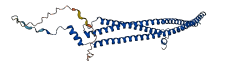
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q99M15
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q99M15-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
16 variants for Q99M15
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3389511920 | 2 | T>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3389506807 | 11 | W>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3408984610 | 46 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389504882 | 72 | T>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3389419481 | 101 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389515514 | 120 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389477891 | 125 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389510647 | 184 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389523454 | 190 | A>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3408984562 | 202 | R>L | No | EVA | |
| rs45693329 | 237 | Q>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389504838 | 244 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389510611 | 266 | Q>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3389490579 | 275 | G>* | No | EVA | |
| rs260834348 | 301 | T>I | No | EVA | |
| rs222083330 | 334 | Q>Q* | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q99M15
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament | A filamentous structure formed of a two-stranded helical polymer of the protein actin and associated proteins. Actin filaments are a major component of the contractile apparatus of skeletal muscle and the microfilaments of the cytoskeleton of eukaryotic cells. The filaments, comprising polymerized globular actin molecules, appear as flexible structures with a diameter of 5-9 nm. They are organized into a variety of linear bundles, two-dimensional networks, and three dimensional gels. In the cytoskeleton they are most highly concentrated in the cortex of the cell just beneath the plasma membrane. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoskeleton | A cellular structure that forms the internal framework of eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. The cytoskeleton includes intermediate filaments, microfilaments, microtubules, the microtrabecular lattice, and other structures characterized by a polymeric filamentous nature and long-range order within the cell. The various elements of the cytoskeleton not only serve in the maintenance of cellular shape but also have roles in other cellular functions, including cellular movement, cell division, endocytosis, and movement of organelles. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin binding | Binding to monomeric or multimeric forms of actin, including actin filaments. |
| actin filament binding | Binding to an actin filament, also known as F-actin, a helical filamentous polymer of globular G-actin subunits. |
3 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament polymerization | Assembly of actin filaments by the addition of actin monomers to a filament. |
| cell migration | The controlled self-propelled movement of a cell from one site to a destination guided by molecular cues. Cell migration is a central process in the development and maintenance of multicellular organisms. |
| cytoskeleton organization | A process that is carried out at the cellular level which results in the assembly, arrangement of constituent parts, or disassembly of cytoskeletal structures. |
15 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q05080 | HOF1 | Cytokinesis protein 2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| A7MBI0 | PACSIN1 | Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q9BQI5 | SGIP1 | SH3-containing GRB2-like protein 3-interacting protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O60861 | GAS7 | Growth arrest-specific protein 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9H939 | PSTPIP2 | Proline-serine-threonine phosphatase-interacting protein 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UNF0 | PACSIN2 | Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9UKS6 | PACSIN3 | Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9BY11 | PACSIN1 | Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8VD37 | Sgip1 | SH3-containing GRB2-like protein 3-interacting protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q99JB8 | Pacsin3 | Protein kinase C and casein kinase II substrate protein 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q61644 | Pacsin1 | Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q9WVE8 | Pacsin2 | Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| P97814 | Pstpip1 | Proline-serine-threonine phosphatase-interacting protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60780 | Gas7 | Growth arrest-specific protein 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q4V920 | pacsin1b | Protein kinase C and casein kinase substrate in neurons protein 1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MTGSLFKGNF | WSTDILSTIG | YDSIIQHLNN | GRKNCKEFED | FLKERASIEE | KYGKDLLNLS |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| RKKPCGQSEI | NTLKRALEVF | KQQVDNVAQC | HIQLAQTLRE | EARKMEEFRE | KQKLQRKKTE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| TIMDAAHKQR | NAQFKKAMDA | KKNYEQKCRD | KDEAEQAVHR | SANVANQRQQ | EKLFVKLATS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| KTAVEDSDKA | YMLHINMLEK | VREDWQSEHI | KACEVFEAQE | CERINFFRNA | LWLHLNQLSQ |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| QCVANDEMYE | QVRKSLETCS | IEKDIQYFVN | QRKTGQTPPA | PIMYENFYSP | QRNAAPPGKT |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | |||
| TGPNPARRGP | LPVPKRIPDD | PDYSVVEDYS | LLYQ |