Q94392
Gene name |
nsf-1 |
Protein name |
Vesicle-fusing ATPase |
Names |
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein, NEM-sensitive fusion protein, Vesicular-fusion protein NSF |
Species |
Caenorhabditis elegans |
KEGG Pathway |
cel:CELE_H15N14.2 |
EC number |
3.6.4.6: Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
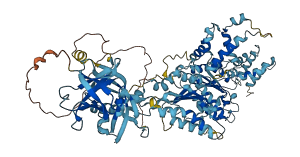
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
329-476 (D1 domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q94392
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q94392-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q94392
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q94392 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q94392
6 regional properties for Q94392
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | CDC48, N-terminal subdomain | 67 - 150 | IPR003338 |
| domain | ATPase, AAA-type, core | 333 - 473 | IPR003959-1 |
| domain | ATPase, AAA-type, core | 616 - 741 | IPR003959-2 |
| conserved_site | ATPase, AAA-type, conserved site | 444 - 462 | IPR003960 |
| domain | CDC48, domain 2 | 174 - 248 | IPR004201 |
| domain | AAA ATPase, AAA+ lid domain | 500 - 535 | IPR041569 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.4.6 | Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
1 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Golgi stack | The set of thin, flattened membrane-bounded compartments, called cisternae, that form the central portion of the Golgi complex. The stack usually comprises cis, medial, and trans cisternae; the cis- and trans-Golgi networks are not considered part of the stack. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + H+ phosphate. ATP hydrolysis is used in some reactions as an energy source, for example to catalyze a reaction or drive transport against a concentration gradient. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
4 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| Golgi to plasma membrane protein transport | The directed movement of proteins from the Golgi to the plasma membrane in transport vesicles that move from the trans-Golgi network to the plasma membrane. |
| Golgi vesicle docking | The initial attachment of a Golgi transport vesicle membrane to a target membrane, mediated by proteins protruding from the membrane of the Golgi vesicle and the target membrane. |
| intra-Golgi vesicle-mediated transport | The directed movement of substances within the Golgi, mediated by small transport vesicles. These either fuse with the cis-Golgi or with each other to form the membrane stacks known as the cis-Golgi reticulum (network). |
| SNARE complex disassembly | The disaggregation of the SNARE protein complex into its constituent components. The SNARE complex is a protein complex involved in membrane fusion; a stable ternary complex consisting of a four-helix bundle, usually formed from one R-SNARE and three Q-SNAREs with an ionic layer sandwiched between hydrophobic layers. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P46461 | comt | Vesicle-fusing ATPase 1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P54351 | Nsf2 | Vesicle-fusing ATPase 2 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| P46459 | NSF | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P46460 | Nsf | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9QUL6 | Nsf | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9M0Y8 | NSF | Vesicle-fusing ATPase | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSPVPCLSTC | CCFRKIVEYS | TMSWFRKSAN | DSLLETNHDR | IPVAPPREVR | APSPRLPPSY |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| QTSNEKMFRV | RKAPSEEHTL | ANYAYVNRSD | FDDKQIKHVR | VNPGPAHHYI | FSIRNDGSIK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PGEIAFGVPH | RKWAALSLDQ | EVRVTPFTFQ | QSEYVGSMIL | TADFNAKKNV | TSEPLNADLM |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| AREFSIQFGG | QAFSKGMQMA | FRFEDKEKNK | THTLSLVVKS | IEGFDIGKAA | AAASGASNTD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SSATKPKQIE | AGELLPNSVI | VFDKEEGSML | NLIGKSKGKS | AYRSIINPDW | DFQQMGIGGL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DTEFSHIFRR | AFASRVFPPE | FIEQLGMKHV | RGILLFGPPG | TGKTLMARQI | GKMLNAREPK |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| IVNGPQILDK | YVGESESNVR | KLFADAEEEW | RRCGANSGLH | IIIFDEIDAI | CKQRGSMAGS |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| SSVHDTVVNQ | LLSKMDGVEQ | LNNILVIGMT | NRRDMIDEAL | LRPGRLEVQM | EVSLPDETGR |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| LQILKIHTAR | MREYNKMDPN | VDLEDISKRT | KNFSGAELEG | LVRAAQSSAM | NRLVKAGGKA |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| QADPDAIEKL | AINSGDFDYA | LENDIKPAFG | RSDESLNRFL | SRGMIVWGPE | VTKILDEGSL |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| LAATVKNPEN | SGFRTVVLAG | AAKTGKTSLA | AQMAKSSDFP | FVKVISPEDT | VGFSESAKCM |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| ALKKAFEDAK | RSKLSVLLID | NLERLIDYHP | VGPRYSNLVI | QALLVLLNAP | PPAGHRLFVI |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| ATSSDRMFLR | DMGLMDVFGD | VIDIPKLTTA | GQMMNVIQES | NIYSDDQLPM | IEQKLASICR |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | ||
| GEGFHGVGIK | HLLELIESAR | QCEADYRVPT | LLNMMEGLAL | NLYR |