Q91ZW3
Gene name |
Smarca5 (Snf2h) |
Protein name |
SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 5 |
Names |
EC 3.6.4.- , Sucrose nonfermenting protein 2 homolog , mSnf2h |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:93762 |
EC number |
3.6.4.-: Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
Protein Class |
|
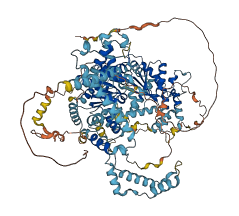
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
182-637 (Helicase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q91ZW3
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q91ZW3-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
15 variants for Q91ZW3
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs254241703 | 63 | H>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388987082 | 69 | Q>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3399510546 | 236 | P>T | No | EVA | |
| rs232544563 | 249 | K>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3388997884 | 427 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388993048 | 443 | M>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3388987109 | 452 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388998759 | 549 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388995521 | 556 | L>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3388990276 | 562 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3388980733 | 591 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3388975197 | 721 | K>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3388990531 | 750 | A>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3388990525 | 751 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388990263 | 752 | R>H | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q91ZW3
8 regional properties for Q91ZW3
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 242 - 493 | IPR000719 |
| domain | SH2 domain | 125 - 217 | IPR000980 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 242 - 492 | IPR001245 |
| domain | SH3 domain | 61 - 121 | IPR001452 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 359 - 371 | IPR008266 |
| domain | F-actin binding | 997 - 1123 | IPR015015 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 248 - 271 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 242 - 493 | IPR020635 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.6.4.- | Acting on ATP; involved in cellular and subcellular movement |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
17 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ACF complex | An ISWI complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family (SNF2H in mammals, Isw2 in S. cerevisiae), an ACF1 homolog, and generally no other subunits, though Xenopus is an exception with a third non-conserved subunit. ACF plays roles in regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription and in DNA replication and repair. |
| B-WICH complex | A chromatin remodeling complex that positively regulates histone H3 acetylation, in particular H3K9, by recruiting histone acetyltransferases to rDNA gene regions. Located in the nucleolus where it assembles on RNA Polymerase I (Pol I) and possibly on RNA Polymerase III (Pol III) promoter and coding regions during early G1 phase and activates the post-initiation phases of Pol I transcription. May also activate RNA Polymerase II (Pol II) gene transcription. In mammals, B-WICH contains the WICH complex core of BAZ1B and SMARCA5, additional protein subunits and possibly rRNAs. Although it contains several catalytic subunits it is not clear which functions are carried out by the complex itself. |
| CHRAC | An ISWI complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family (SNF2H in mammals, Isw2 in S. cerevisiae), an ACF1 homolog, and additional small histone fold subunits (generally two of these, but Xenopus has only one and some additional non-conserved subunits). CHRAC plays roles in the regulation of RNA polymerase II transcription and in DNA replication and repair. |
| chromatin silencing complex | Any protein complex that mediates changes in chromatin structure that result in transcriptional silencing. |
| condensed chromosome | A highly compacted molecule of DNA and associated proteins resulting in a cytologically distinct structure. |
| fibrillar center | A structure found most metazoan nucleoli, but not usually found in lower eukaryotes; surrounded by the dense fibrillar component; the zone of transcription from multiple copies of the pre-rRNA genes is in the border region between these two structures. |
| ISWI-type complex | Any nuclear protein complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the imitation switch (ISWI) family. ISWI ATPases are involved in assembling chromatin and in sliding and spacing nucleosomes to regulate transcription of nuclear RNA polymerases I, II, and III and also DNA replication, recombination and repair. |
| NoRC complex | An ISWI complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family (specifically SNF2H in mammals, which contain two ISWI homologs) and a Tip5 homolog. In mammals, NoRC is involved in regulation of transcription from RNAP I and RNA polymerase III promoters. |
| nuclear replication fork | The Y-shaped region of a nuclear replicating DNA molecule, resulting from the separation of the DNA strands and in which the synthesis of new strands takes place. Also includes associated protein complexes. |
| nucleolus | A small, dense body one or more of which are present in the nucleus of eukaryotic cells. It is rich in RNA and protein, is not bounded by a limiting membrane, and is not seen during mitosis. Its prime function is the transcription of the nucleolar DNA into 45S ribosomal-precursor RNA, the processing of this RNA into 5.8S, 18S, and 28S components of ribosomal RNA, and the association of these components with 5S RNA and proteins synthesized outside the nucleolus. This association results in the formation of ribonucleoprotein precursors; these pass into the cytoplasm and mature into the 40S and 60S subunits of the ribosome. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| NURF complex | An ISWI complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family (SNF2L in mammals), a NURF301 homolog (BPTF in humans), and additional subunits, though the composition of these additional subunits varies slightly with species. NURF is involved in regulation of transcription from TRNA polymerase II promoters. |
| pericentric heterochromatin | Heterochromatin that is located adjacent to the CENP-A rich centromere 'central core' and characterized by methylated H3 histone at lysine 9 (H3K9me2/H3K9me3). |
| RSF complex | An ISWI complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family (SNF2H in mammals) and an RSF1 homolog. It mediates nucleosome deposition and generates regularly spaced nucleosome arrays. In mammals, RSF is involved in regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoters). |
| site of double-strand break | A region of a chromosome at which a DNA double-strand break has occurred. DNA damage signaling and repair proteins accumulate at the lesion to respond to the damage and repair the DNA to form a continuous DNA helix. |
| WICH complex | An ISWI complex that contains an ATPase subunit of the ISWI family (specifically SNF2H in mammals, which contain two ISWI homologs) and WSTF (Williams Syndrome Transcription Factor). WICH plays roles in regulation of RNAP I and III transcription and in DNA replication and repair. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATP hydrolysis activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| ATP-dependent activity, acting on DNA | Catalytic activity that acts to modify DNA, driven by ATP hydrolysis. |
| ATP-dependent chromatin remodeler activity | An activity, driven by ATP hydrolysis, that modulates the contacts between histones and DNA, resulting in a change in chromosome architecture within the nucleosomal array, leading to chromatin remodeling. |
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| helicase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| histone binding | Binding to a histone, any of a group of water-soluble proteins found in association with the DNA of eukaryotic or archaeal chromosomes. They are involved in the condensation and coiling of chromosomes during cell division and have also been implicated in gene regulation and DNA replication. They may be chemically modified (methylated, acetlyated and others) to regulate gene transcription. |
| histone octamer slider activity | A chromatin remodeler activity that slides core histone octamers along chromosomal DNA. |
| nucleosome binding | Binding to a nucleosome, a complex comprised of DNA wound around a multisubunit core and associated proteins, which forms the primary packing unit of DNA into higher order structures. |
19 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to leukemia inhibitory factor | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a leukemia inhibitory factor stimulus. |
| chromatin organization | The assembly or remodeling of chromatin composed of DNA complexed with histones, other associated proteins, and sometimes RNA. |
| chromatin remodeling | A dynamic process of chromatin reorganization resulting in changes to chromatin structure. These changes allow DNA metabolic processes such as transcriptional regulation, DNA recombination, DNA repair, and DNA replication. |
| DNA damage response | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism. |
| DNA repair | The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway. |
| DNA-templated transcription initiation | The initial step of transcription, consisting of the assembly of the RNA polymerase preinitiation complex (PIC) at a gene promoter, as well as the formation of the first few bonds of the RNA transcript. Transcription initiation includes abortive initiation events, which occur when the first few nucleotides are repeatedly synthesized and then released, and ends when promoter clearance takes place. |
| heterochromatin formation | An epigenetic gene silencing mechanism in which chromatin is compacted into heterochromatin, resulting in a chromatin conformation refractory to transcription. This process starts with heterochromatin nucleation, its spreading, and ends with heterochromatin boundary formation. |
| negative regulation of mitotic chromosome condensation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of mitotic chromosome condensation. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase I. |
| nucleosome assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a nucleosome, the beadlike structural units of eukaryotic chromatin composed of histones and DNA. |
| positive regulation of DNA replication | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication. |
| positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase I | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase I. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase III | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase III. |
| rDNA heterochromatin formation | The formation of heterochromatin at ribosomal DNA, characterized by the modified histone H3K9me3. |
| regulation of DNA methylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the covalent transfer of a methyl group to either N-6 of adenine or C-5 or N-4 of cytosine. |
| regulation of DNA replication | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of DNA replication. |
| regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
16 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P38144 | ISW1 | ISWI chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase ISW1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q3B7N1 | CHD1L | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1-like | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q24368 | Iswi | Chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase chain Iswi | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q86WJ1 | CHD1L | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1-like | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9NRZ9 | HELLS | Lymphoid-specific helicase | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P28370 | SMARCA1 | Probable global transcription activator SNF2L1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O60264 | SMARCA5 | SWI/SNF-related matrix-associated actin-dependent regulator of chromatin subfamily A member 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q60848 | Hells | Lymphocyte-specific helicase | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9CXF7 | Chd1l | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1-like | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P40201 | Chd1 | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q6PGB8 | Smarca1 | Probable global transcription activator SNF2L1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q7G8Y3 | Os01g0367900 | Probable chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase chain | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| P41877 | isw-1 | Chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase chain isw-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q22516 | chd-3 | Chromodomain-helicase-DNA-binding protein 3 homolog | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9XFH4 | DDM1 | ATP-dependent DNA helicase DDM1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8RWY3 | CHR11 | ISWI chromatin-remodeling complex ATPase CHR11 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSSAVEPPPP | PPPESAPSKP | SAAGAGGSSS | GNKGGPEGGA | APAAPCAAGS | GPADTEMEEV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| FDHGSPGKQK | EIQEPDPTYE | EKMQTDRANR | FEYLLKQTEL | FAHFIQPAAQ | KTPTSPLKMK |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| PGRPRVKKDE | KQNLLSVGDY | RHRRTEQEED | EELLTESSKA | TNVCTRFEDS | PSYVKWGKLR |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| DYQVRGLNWL | ISLYENGING | ILADEMGLGK | TLQTISLLGY | MKHYRNIPGP | HMVLVPKSTL |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| HNWMSEFKKW | VPTLRSVCLI | GDKEQRAAFV | RDVLLPGEWD | VCVTSYEMLI | KEKSVFKKFN |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| WRYLVIDEAH | RIKNEKSKLS | EIVREFKTTN | RLLLTGTPLQ | NNLHELWSLL | NFLLPDVFNS |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| ADDFDSWFDT | NNCLGDQKLV | ERLHMVLRPF | LLRRIKADVE | KSLPPKKEVK | IYVGLSKMQR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| EWYTRILMKD | IDILNSAGKM | DKMRLLNILM | QLRKCCNHPY | LFDGAEPGPP | YTTDMHLVTN |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| SGKMVVLDKL | LPKLKEQGSR | VLIFSQMTRV | LDILEDYCMW | RNYEYCRLDG | QTPHDERQDS |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| INAYNEPNST | KFVFMLSTRA | GGLGINLATA | DVVILYDSDW | NPQVDLQAMD | RAHRIGQTKT |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| VRVFRFITDN | TVEERIVERA | EMKLRLDSIV | IQQGRLVDQN | LNKIGKDEML | QMIRHGATHV |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| FASKESEITD | EDIDGILERG | AKKTAEMNEK | LSKMGESSLR | NFTMDTESSV | YNFEGEDYRE |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| KQKIAFTEWI | EPPKRERKAN | YAVDAYFREA | LRVSEPKAPK | APRPPKQPNV | QDFQFFPPRL |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| FELLEKEILY | YRKTIGYKVP | RSPDLPNAAQ | AQKEEQLKID | EAEPLNDEEL | EEKEKLLTQG |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| FTNWNKRDFN | QFIKANEKWG | RDDIENIARE | VEGKTPEEVI | EYSAVFWERC | NELQDIEKIM |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| AQIERGEARI | QRRISIKKAL | DTKIGRYKAP | FHQLRISYGT | NKGKNYTEEE | DRFLICMLHK |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| LGFDKENVYD | ELRQCIRNSP | QFRFDWFLKS | RTAMELQRRC | NTLITLIERE | NMELEEKEKA |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | |||
| EKKKRGPKPS | TQKRKMDGAP | DGRGRKKKLK | L |