Q8VSC3
Gene name |
ipaH9.8 |
Protein name |
E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase ipaH9.8 |
Names |
IR, Invasion plasmid antigen ipaH9.8, RING-type E3 ubiquitin transferase ipaH9.8 |
Species |
Shigella flexneri |
KEGG Pathway |
sfl:CP0226 |
EC number |
2.3.2.27: Aminoacyltransferases |
Protein Class |
FAMILY NOT NAMED (PTHR47114) |
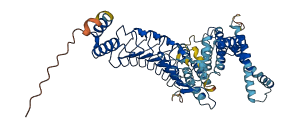
Descriptions
Shigellar flexneri IpaH9.8 E3 ligase inhibits MAPK kinase dependent signaling by targeting components of this pathway and disrupts both NF-κB-dependent gene expression and the activity of U2AF35 via the ubiquitination. The C-terminal region of IpaH9.8 can exist as a monomer that is able to catalyze the ubiquitination of U2AF35 and as a dimer that does not possess this activity. Under non-reducing conditions, the sole cysteine (Cys 337) of the C-terminal region of IpaH9.8 forms an intermolecular disulfide bridge resulting in the extension of an α-helix and formation of a domain-swapped dimer. Furthermore, the N-terminal domain (leucine-rich repeat) can autoinhibit the activity of full-length IpaH9.8, and substrate (human substrate U2AF35 and yeast substrate Ste7) binding releases this inhibition.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
251-545 (E3 ubiquitin-protein ligase catalytic domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
Mutagenesis experiment, Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Seyedarabi A et al. (2010) "A disulfide driven domain swap switches off the activity of Shigella IpaH9.8 E3 ligase", FEBS letters, 584, 4163-8
- Ye Y et al. (2020) "Substrate-binding destabilizes the hydrophobic cluster to relieve the autoinhibition of bacterial ubiquitin ligase IpaH9.8", Communications biology, 3, 752
Autoinhibited structure
Activated structure
4 variants for Q8VSC3
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 222 | P>Q | plasmid pWR100, plasmid pSF5 and plasmid pINV_F6_M1382 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 474 | Q>L | plasmid pINV_F6_M1382 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 536 | P>F | plasmid pWR100 [UniProt] | No | ||
| 536 | P>S | plasmid pSF5 [UniProt] | No |
No associated diseases with Q8VSC3
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.3.2.27 | Aminoacyltransferases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR47114 | FAMILY NOT NAMED |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR47114:SF2 | OLIGODENDROCYTE-MYELIN GLYCOPROTEIN |
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
| host cell cytosol | The part of the host cell cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| host cell nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle as it is found in the host cell in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. The host is defined as the larger of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction. |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| identical protein binding | Binding to an identical protein or proteins. |
| ubiquitin protein ligase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of ubiquitin to a substrate protein via the reaction X-ubiquitin + S -> X + S-ubiquitin, where X is either an E2 or E3 enzyme, the X-ubiquitin linkage is a thioester bond, and the S-ubiquitin linkage is an amide bond: an isopeptide bond between the C-terminal glycine of ubiquitin and the epsilon-amino group of lysine residues in the substrate or, in the linear extension of ubiquitin chains, a peptide bond the between the C-terminal glycine and N-terminal methionine of ubiquitin residues. |
| ubiquitin-protein transferase activity | Catalysis of the transfer of ubiquitin from one protein to another via the reaction X-Ub + Y --> Y-Ub + X, where both X-Ub and Y-Ub are covalent linkages. |
5 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| proteasome-mediated ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| protein autoubiquitination | The ubiquitination by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues, or residues on an identical protein. Ubiquitination occurs on the lysine residue by formation of an isopeptide crosslink. |
| protein K27-linked ubiquitination | A protein ubiquitination process in which a polymer of ubiquitin, formed by linkages between lysine residues at position 27 of the ubiquitin monomers, is added to a protein. |
| suppression by symbiont of host I-kappaB kinase/NF-kappaB cascade | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of host NF-kappaB-mediated signal transduction pathways during the host defense response. The host is defined as the larger of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction. |
| suppression by symbiont of host inflammatory response | Any process in which a symbiont stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response of the host organism; the inflammatory response is the immediate defensive reaction (by vertebrate tissue) to infection or injury caused by chemical or physical agents. The host is defined as the larger of the organisms involved in a symbiotic interaction. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MLPINNNFSL | PQNSFYNTIS | GTYADYFSAW | DKWEKQALPG | EERDEAVSRL | KECLINNSDE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LRLDRLNLSS | LPDNLPAQIT | LLNVSYNQLT | NLPELPVTLK | KLYSASNKLS | ELPVLPPALE |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| SLQVQHNELE | NLPALPDSLL | TMNISYNEIV | SLPSLPQALK | NLRATRNFLT | ELPAFSEGNN |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| PVVREYFFDR | NQISHIPESI | LNLRNECSIH | ISDNPLSSHA | LPALQRLTSS | PDYHGPRIYF |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| SMSDGQQNTL | HRPLADAVTA | WFPENKQSDV | SQIWHAFEHE | EHANTFSAFL | DRLSDTVSAR |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| NTSGFREQVA | AWLEKLSASA | ELRQQSFAVA | ADATESCEDR | VALTWNNLRK | TLLVHQASEG |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| LFDNDTGALL | SLGREMFRLE | ILEDIARDKV | RTLHFVDEIE | VYLAFQTMLA | EKLQLSTAVK |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| EMRFYGVSGV | TANDLRTAEA | MVRSREENEF | TDWFSLWGPW | HAVLKRTEAD | RWAQAEEQKY |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| EMLENEYPQR | VADRLKASGL | SGDADAEREA | GAQVMRETEQ | QIYRQLTDEV | LALRLPENGS |
| QLHHS |