Q8K120
Gene name |
Nfatc4 |
Protein name |
Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 4 |
Names |
NF-ATc4, NFATc4, T-cell transcription factor NFAT3, NF-AT3 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:73181 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
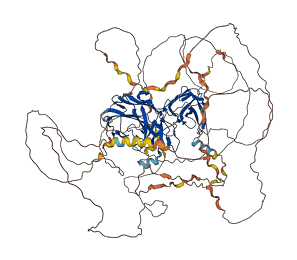
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q8K120
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q8K120-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
50 variants for Q8K120
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs226706809 | 25 | P>A | No | EVA | |
| rs3405238350 | 26 | L>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3389287293 | 64 | P>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389333407 | 66 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389343060 | 73 | S>L | No | EVA | |
| rs233610183 | 104 | G>S | No | EVA | |
| rs50342063 | 135 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389332104 | 136 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389333397 | 140 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389295663 | 182 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389287325 | 190 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389343029 | 195 | C>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3389322545 | 260 | P>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3389343085 | 276 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389343063 | 313 | G>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389327252 | 318 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs241055119 | 348 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs220133490 | 367 | A>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389333367 | 378 | L>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389304763 | 393 | G>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389295690 | 427 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389343018 | 433 | Y>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3389304841 | 450 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389329238 | 479 | H>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389332020 | 480 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389254281 | 481 | F>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389333386 | 481 | F>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3389314539 | 508 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs31144482 | 562 | G>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389331665 | 580 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389322616 | 603 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3404372874 | 616 | K>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3405239930 | 640 | Q>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3405034415 | 640 | Q>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3404692338 | 641 | S>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3389314564 | 652 | E>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389347724 | 682 | K>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389343103 | 683 | F>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389327215 | 708 | P>L | No | EVA | |
| rs1135100991 | 712 | D>G | No | EVA | |
| rs1131743291 | 713 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3389343046 | 732 | Y>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3389329283 | 744 | S>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3389304843 | 761 | G>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3389333455 | 790 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389347654 | 792 | Y>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389287371 | 806 | S>P | No | EVA | |
| rs3389329138 | 827 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs1132018834 | 883 | I>V | No | EVA | |
| rs46055583 | 885 | G>A | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q8K120
Functions
5 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| nuclear speck | A discrete extra-nucleolar subnuclear domain, 20-50 in number, in which splicing factors are seen to be localized by immunofluorescence microscopy. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| transcription regulator complex | A protein complex that is capable of associating with DNA by direct binding, or via other DNA-binding proteins or complexes, and regulating transcription. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity | A transcription regulator activity that modulates transcription of gene sets via selective and non-covalent binding to a specific double-stranded genomic DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within a cis-regulatory region. Regulatory regions include promoters (proximal and distal) and enhancers. Genes are transcriptional units, and include bacterial operons. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription repressor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that represses or decreases the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| peroxisome proliferator activated receptor binding | Binding to a peroxisome proliferator activated receptor, alpha, beta or gamma. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA, e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
32 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| brain-derived neurotrophic factor receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals generated as a consequence of a brain-derived neurotrophic factor receptor binding to one of its physiological ligands. |
| branching involved in blood vessel morphogenesis | The process of coordinated growth and sprouting of blood vessels giving rise to the organized vascular system. |
| calcineurin-NFAT signaling cascade | Any intracellular signal transduction in which the signal is passed on within the cell by activation of a member of the NFAT protein family as a consequence of NFAT dephosphorylation by Ca(2+)-activated calcineurin. The cascade begins with calcium-dependent activation of the phosphatase calcineurin. Calcineurin dephosphorylates multiple phosphoserine residues on NFAT, resulting in the translocation of NFAT to the nucleus. The cascade ends with regulation of transcription by NFAT. The calcineurin-NFAT cascade lies downstream of many cell surface receptors, including G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs) and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) that signal to mobilize calcium ions (Ca2+). |
| cellular respiration | The enzymatic release of energy from inorganic and organic compounds (especially carbohydrates and fats) which either requires oxygen (aerobic respiration) or does not (anaerobic respiration). |
| cellular response to ionomycin | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ionomycin stimulus. |
| cellular response to lithium ion | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a lithium (Li+) ion stimulus. |
| cellular response to UV | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of an ultraviolet radiation (UV light) stimulus. Ultraviolet radiation is electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength in the range of 10 to 380 nanometers. |
| dendrite morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a dendrite are generated and organized. |
| heart development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the heart over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The heart is a hollow, muscular organ, which, by contracting rhythmically, keeps up the circulation of the blood. |
| intrinsic apoptotic signaling pathway in response to DNA damage | The series of molecular signals in which an intracellular signal is conveyed to trigger the apoptotic death of a cell. The pathway is induced by the detection of DNA damage, and ends when the execution phase of apoptosis is triggered. |
| long-term memory | The memory process that deals with the storage, retrieval and modification of information a long time (typically weeks, months or years) after receiving that information. This type of memory is typically dependent on gene transcription regulated by second messenger activation. |
| long-term synaptic potentiation | A process that modulates synaptic plasticity such that synapses are changed resulting in the increase in the rate, or frequency of synaptic transmission at the synapse. |
| negative regulation of chromatin binding | Any process that stops or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of chromatin binding. Chromatin binding is the selective interaction with chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| negative regulation of dendrite morphogenesis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of dendrite morphogenesis. |
| negative regulation of miRNA transcription | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of microRNA (miRNA) gene transcription. |
| negative regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of cell death by apoptotic process in neurons. |
| negative regulation of protein binding | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein binding. |
| negative regulation of synapse maturation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of synapse maturation. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| negative regulation of Wnt signaling pathway | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of the Wnt signaling pathway. |
| neuron apoptotic process | Any apoptotic process in a neuron, the basic cellular unit of nervous tissue. Each neuron consists of a body, an axon, and dendrites. Their purpose is to receive, conduct, and transmit impulses in the nervous system. |
| positive regulation of apoptotic signaling pathway | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of apoptotic signaling pathway. |
| positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell death of neurons by apoptotic process. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation of tumor necrosis factor production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of tumor necrosis factor production. |
| regulation of DNA-templated transcription | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of cellular DNA-templated transcription. |
| regulation of synaptic plasticity | A process that modulates synaptic plasticity, the ability of synapses to change as circumstances require. They may alter function, such as increasing or decreasing their sensitivity, or they may increase or decrease in actual numbers. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| synapse maturation | The process that organizes a synapse so that it attains its fully functional state. Synaptic maturation plays a critical role in the establishment of effective synaptic connections in early development. |
| transcription by RNA polymerase II | The synthesis of RNA from a DNA template by RNA polymerase II (RNAP II), originating at an RNA polymerase II promoter. Includes transcription of messenger RNA (mRNA) and certain small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). |
| vascular associated smooth muscle cell development | The process aimed at the progression of a vascular smooth muscle cell over time, from initial commitment of the cell to a specific fate, to the fully functional differentiated cell. A vascular smooth muscle cell is a non-striated, elongated, spindle-shaped cell found lining the blood vessels. |
| vascular associated smooth muscle cell differentiation | The process in which a relatively unspecialized cell acquires specialized features of a vascular smooth muscle cell. |
5 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q14934 | NFATC4 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O95644 | NFATC1 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q60591 | Nfatc2 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P97305 | Nfatc3 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O88942 | Nfatc1 | Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGAASCEDEE | LEFKLVFGEE | KEPPPLGPGG | PGEELDSEDT | PPCCRLALGE | PLPYGAAPIG |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| IPRPPPPRPG | MHSPPPRPAP | SPGTWESQPA | RSVRLGGPGG | NAGGAGGGRV | LECPSIRITS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| ISPTPDPPTS | LEDTSETWGD | GSPRDYPPPE | GFGGYREAGG | QGGGAFFSPS | PGSSSLSSWS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| FFSDASDEAA | LYAACDEVES | ELNEAASRFG | LSSPLPSPRA | SPRPWTPEDP | WSLYGPSSGG |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| RAPEDSWLLL | SAPGPVPASP | RPASPCGKRR | YSSSGTPSSA | SPALSRRGSL | GEEGPEPPPP |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| PPLPLVRDPS | SPGPFDYVGA | PPTESIPQKT | RRTSSEQAVA | LPRSEEPPSC | NGKLPSGTED |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| SVAAPGALRK | EVAGMDYLAV | PSPLAWSKAR | IGGHSPIFRT | SALPPLDWPL | PSQYEQLELR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| IEVQPRAHHR | AHYETEGSRG | AVKAAPGGHP | VVKLLGYSEK | PLTLQMFIGT | ADERSLRPHA |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| FYQVHRITGK | MVATASYEAV | VSGTKVLEMT | LLPENNMAAN | IDCAGILKLR | NSDIELRKGE |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| TDIGRKNTRV | RLVFRVHVPQ | GGGKVVSVQA | ASVPIECSQR | SAQELPQVET | YSPSACSVRG |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| GEELVLTGSN | FLPDSKVVFI | ERGPDGKLQW | EEEAAVNRLQ | SSEVTLTLTI | PEYSNKRVSR |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| PVQVYFYVSN | GRRKRSPTQS | FKFLPVVFKE | EPLPDSSLRG | FPSTSGPPFG | PDVDFSPPRP |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| PYPSYPHEDP | AYETPYLSEG | FGYSTPALYP | QTGPPPSYRS | GLRMFPETGG | TTGCARLPSV |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| SFLPRPFPGD | QYGGQGSSFA | LGLPFSPPAP | FRPPLPSSPP | LEDPFHPQSA | IHPLPPEGYN |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| EVGPGYTPGE | GASEQEKARG | GYSSGFRDSV | PIQGITLEEV | SEIIGRDLSG | FPARPGEEPP |
| A |