Q8HXN7
Gene name |
CCNT1 |
Protein name |
Cyclin-T1 |
Names |
CycT1, Cyclin-T |
Species |
Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) |
KEGG Pathway |
ptr:450146 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
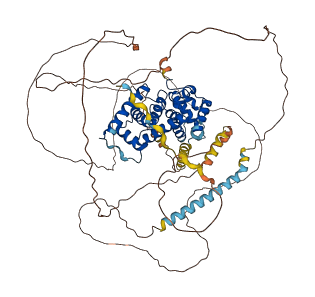
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
12-258 (N-terminal cyclin box) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM, Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q8HXN7
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q8HXN7-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q8HXN7
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q8HXN7 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q8HXN7
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cyclin/CDK positive transcription elongation factor complex | A transcription elongation factor complex that facilitates the transition from abortive to productive elongation by phosphorylating the CTD domain of the large subunit of DNA-directed RNA polymerase II, holoenzyme. Contains a cyclin and a cyclin-dependent protein kinase catalytic subunit. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| P-TEFb complex | A dimeric positive transcription elongation factor complex b that comprises a cyclin-dependent kinase containing the catalytic subunit, Cdk9, and a regulatory subunit, cyclin T. |
8 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| 7SK snRNA binding | Binding to a 7SK small nuclear RNA (7SK snRNA). |
| chromatin binding | Binding to chromatin, the network of fibers of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that make up the chromosomes of the eukaryotic nucleus during interphase. |
| cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of a cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase. |
| cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase regulator activity | Modulates the activity of a cyclin-dependent protein serine/threonine kinase, enzymes of the protein kinase family that are regulated through association with cyclins and other proteins. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor binding | Binding to a DNA-binding transcription factor, a protein that interacts with a specific DNA sequence (sometimes referred to as a motif) within the regulatory region of a gene to modulate transcription. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| RNA polymerase binding | Binding to an RNA polymerase molecule or complex. |
| transcription cis-regulatory region binding | Binding to a specific sequence of DNA that is part of a regulatory region that controls transcription of that section of the DNA. The transcribed region might be described as a gene, cistron, or operon. |
9 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell cycle | The progression of biochemical and morphological phases and events that occur in a cell during successive cell replication or nuclear replication events. Canonically, the cell cycle comprises the replication and segregation of genetic material followed by the division of the cell, but in endocycles or syncytial cells nuclear replication or nuclear division may not be followed by cell division. |
| cell division | The process resulting in division and partitioning of components of a cell to form more cells; may or may not be accompanied by the physical separation of a cell into distinct, individually membrane-bounded daughter cells. |
| negative regulation of mRNA polyadenylation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of mRNA polyadenylation. |
| phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain serine 2 residues involved in positive regulation of transcription elongation from RNA polymerase II promoter | Any phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain serine 2 residues that is involved in positive regulation of transcription elongation from RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain serine 5 residues involved in positive regulation of transcription elongation from RNA polymerase II promoter | Any phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II C-terminal domain serine 5 residues that is involved in positive regulation of transcription elongation from RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| positive regulation by host of viral transcription | Any process in which a host organism activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of viral transcription, the synthesis of either RNA on a template of DNA or DNA on a template of RNA. |
| positive regulation of DNA-templated transcription, elongation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription elongation, the extension of an RNA molecule after transcription initiation and promoter clearance by the addition of ribonucleotides catalyzed by a DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| transcription, DNA-templated | The synthesis of an RNA transcript from a DNA template. |
12 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q6T8E9 | CCNT1 | Cyclin-T1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q9XT26 | CCNT1 | Cyclin-T1 | Equus caballus (Horse) | SS |
| O75909 | CCNK | Cyclin-K | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8N1B3 | CCNQ | Cyclin-Q | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O60563 | CCNT1 | Cyclin-T1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O88874 | Ccnk | Cyclin-K | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9QWV9 | Ccnt1 | Cyclin-T1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q2QQS5 | CYCT1-1 | Cyclin-T1-4 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q6Z7H3 | CYCT1_2 | Cyclin-T1-2 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q2RAC5 | CYCT1-3 | Cyclin-T1-3 | Oryza sativa subsp japonica (Rice) | PR |
| Q8GYM6 | CYCT1-4 | Cyclin-T1-4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q503D6 | ccnq | Cyclin-Q | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEGERKNNKR | WYFTREQLEN | SPSRRFGVDP | DKELSYRQQA | ANLLQDMGQR | LNVSQLTINT |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| AIVYMHRFYM | IQSFTQFPGN | SVAPAALFLA | AKVEEQPKKL | EHVIKVAHTC | LHPQESLPDT |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RSEAYLQQVQ | DLVILESIIL | QTLGFELTID | HPHTHVVKCT | QLVRASKDLA | QTSYFMATNS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LHLTTFSLQY | TPPVVACVCI | HLACKWSNWE | IPVSTDGKHW | WEYVDATVTL | ELLDELTHEF |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LQILEKTPNR | LKRIWNWRAC | EAAKKTKADD | RGTDEKTSEQ | TILNMISQSS | SDTTIAGLMS |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| MSTSTTSAVP | SLPVSEESSS | NLTSVEMLPG | KRWLSSQPSF | KLEPTQGHRT | SENLALTGVD |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| HSLPQDGSNA | FISQKQNSKS | VPSAKVSLKE | YRAKHAEELA | AQKRQLENME | ANVKSQYAYA |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| AQNLLSHHDS | HSSVILKMPI | EGSENPERPF | LEKADKTALK | MRIPVAGGDK | AASSKPEEIK |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| MRIKVHAAAD | KHNSVEDSVT | KSREHKEKHK | THPSNHHHHH | NHHSHKHSHS | QLPVGTGNKR |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| PGDPKHSSQT | SNLAHKTYSL | SSSFSSSSST | RKRGPSEETG | GAVFDHPAKI | AKSTKSSSLN |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| FSFPSLPTMA | QMPGHSSDTS | GLSFSQPSCK | TRVPHSKLDK | GPTGANGHNT | TQTIDYQDTV |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| NMLHSLLSAQ | GVQPTQPTAF | EFVRPYSDYL | NPRAGGISSR | SGNTDKPRPP | PLPSEPPPPL |
| PPLPK |