Q8CIB5
Gene name |
Fermt2 (Plekhc1) |
Protein name |
Fermitin family homolog 2 |
Names |
Kindlin-2 , Pleckstrin homology domain-containing family C member 1 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:218952 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
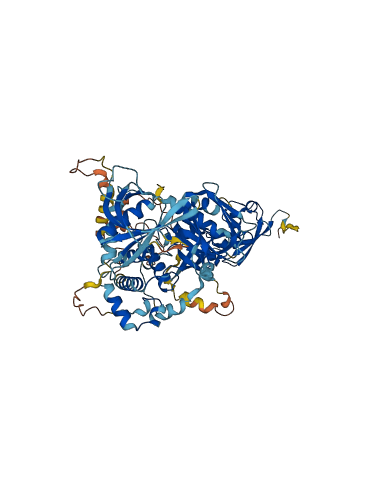
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
584-680 (F3 subdomain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

5 structures for Q8CIB5
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5XPY | X-ray | 210 A | A | 15-680 | PDB |
| 5XPZ | X-ray | 260 A | A/B | 1-680 | PDB |
| 5XQ0 | X-ray | 275 A | A/B | 1-680 | PDB |
| 5XQ1 | X-ray | 295 A | A/B | 1-680 | PDB |
| AF-Q8CIB5-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
27 variants for Q8CIB5
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3389321367 | 55 | K>I | No | EVA | |
| rs223111582 | 66 | E>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3389323844 | 86 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389321725 | 93 | T>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389276321 | 138 | L>H | No | EVA | |
| rs224979399 | 163 | A>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389246928 | 177 | S>R | No | EVA | |
| rs3389323817 | 189 | M>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3405063880 | 276 | Y>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389322529 | 287 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3405180464 | 290 | R>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389321746 | 323 | H>L | No | EVA | |
| rs3389319065 | 344 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389319057 | 369 | I>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389332881 | 386 | K>Q | No | EVA | |
| rs3389338124 | 491 | N>K | No | EVA | |
| rs251291020 | 516 | V>I | No | EVA | |
| rs3389295461 | 557 | R>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389304888 | 582 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389314967 | 583 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389276263 | 586 | I>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3389276316 | 594 | I>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389318828 | 611 | N>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389321764 | 618 | N>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3389338172 | 643 | C>Y | No | EVA | |
| rs3389322532 | 665 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389323818 | 672 | F>L | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q8CIB5
Functions
13 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adherens junction | A cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex. The epithelial cadherins, or E-cadherins, of each interacting cell extend through the plasma membrane into the extracellular space and bind to each other. The E-cadherins bind to catenins on the cytoplasmic side of the membrane, where the E-cadherin-catenin complex binds to cytoskeletal components and regulatory and signaling molecules. |
| cell cortex | The region of a cell that lies just beneath the plasma membrane and often, but not always, contains a network of actin filaments and associated proteins. |
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The leaflet the plasma membrane that faces the cytoplasm and any proteins embedded or anchored in it or attached to its surface. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| extrinsic component of cytoplasmic side of plasma membrane | The component of a plasma membrane consisting of gene products and protein complexes that are loosely bound to its cytoplasmic surface, but not integrated into the hydrophobic region. |
| focal adhesion | A cell-substrate junction that anchors the cell to the extracellular matrix and that forms a point of termination of actin filaments. In insects focal adhesion has also been referred to as hemi-adherens junction (HAJ). |
| I band | A region of a sarcomere that appears as a light band on each side of the Z disc, comprising a region of the sarcomere where thin (actin) filaments are not overlapped by thick (myosin) filaments; contains actin, troponin, and tropomyosin; each sarcomere includes half of an I band at each end. |
| lamellipodium membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane surrounding a lamellipodium. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| stress fiber | A contractile actin filament bundle that consists of short actin filaments with alternating polarity, cross-linked by alpha-actinin and possibly other actin bundling proteins, and with myosin present in a periodic distribution along the fiber. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| actin filament binding | Binding to an actin filament, also known as F-actin, a helical filamentous polymer of globular G-actin subunits. |
| integrin binding | Binding to an integrin. |
| phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate binding | Binding to phosphatidylinositol-3,4,5-trisphosphate, a derivative of phosphatidylinositol in which the inositol ring is phosphorylated at the 3', 4' and 5' positions. |
| protein kinase binding | Binding to a protein kinase, any enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a protein substrate. |
| SMAD binding | Binding to a SMAD signaling protein. |
| type I transforming growth factor beta receptor binding | Binding to a type I transforming growth factor beta receptor. |
25 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| adherens junction maintenance | The maintenance of an adherens junction. An adherens junction is a cell-cell junction composed of the epithelial cadherin-catenin complex at which the cytoplasmic face of the plasma membrane is attached to actin filaments. |
| cell-matrix adhesion | The binding of a cell to the extracellular matrix via adhesion molecules. |
| focal adhesion assembly | The aggregation and bonding together of a set of components to form a focal adhesion, a complex of intracellular signaling and structural proteins that provides a structural link between the internal actin cytoskeleton and the ECM, and also function as a locus of signal transduction activity. |
| integrin activation | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of an integrin, a heterodimeric adhesion receptor formed by the non-covalent association of particular alpha and beta subunits, that lead to the increased affinity of the integrin for its extracellular ligands. |
| integrin-mediated signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to an integrin on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| limb development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of a limb over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A limb is an appendage of an animal used for locomotion or grasping. Examples include legs, arms or some types of fin. |
| negative regulation of fat cell differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of adipocyte differentiation. |
| negative regulation of vascular permeability | Any process that reduces the extent to which blood vessels can be pervaded by fluid. |
| positive regulation of epithelial to mesenchymal transition | Any process that increases the rate, frequency, or extent of epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is where an epithelial cell loses apical/basolateral polarity, severs intercellular adhesive junctions, degrades basement membrane components and becomes a migratory mesenchymal cell. |
| positive regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| positive regulation of focal adhesion assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of focal adhesion assembly, the establishment and maturation of focal adhesions. |
| positive regulation of integrin activation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of integrin activation. |
| positive regulation of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of mesenchymal stem cell proliferation. |
| positive regulation of osteoblast differentiation | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of osteoblast differentiation. |
| positive regulation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B signal transduction | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein kinase B signaling, a series of reactions mediated by the intracellular serine/threonine kinase protein kinase B. |
| positive regulation of protein localization to nucleus | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of protein localization to nucleus. |
| positive regulation of stress fiber assembly | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the assembly of a stress fiber, a bundle of microfilaments and other proteins found in fibroblasts. |
| positive regulation of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading. |
| positive regulation of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of wound healing, spreading of epidermal cells. |
| protein localization to cell junction | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a location within a cell junction. |
| protein localization to membrane | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location in a membrane. |
| regulation of cell shape | Any process that modulates the surface configuration of a cell. |
| substrate adhesion-dependent cell spreading | The morphogenetic process that results in flattening of a cell as a consequence of its adhesion to a substrate. |
| transforming growth factor beta receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a transforming growth factor beta receptor on the surface of a target cell, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| Wnt signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by binding of a Wnt protein to a frizzled family receptor on the surface of the target cell and ending with a change in cell state. |
12 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q32LP0 | FERMT3 | Fermitin family homolog 3 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q9VZI3 | Fit1 | Unc-112-related protein | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q86UX7 | FERMT3 | Fermitin family homolog 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9BQL6 | FERMT1 | Fermitin family homolog 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q96AC1 | FERMT2 | Fermitin family homolog 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9Y4G6 | TLN2 | Talin-2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9Y490 | TLN1 | Talin-1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| P59113 | Fermt1 | Fermitin family homolog 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8K1B8 | Fermt3 | Fermitin family homolog 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26039 | Tln1 | Talin-1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | EV |
| Q18685 | unc-112 | Protein unc-112 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| F1Q8X5 | fermt2 | Fermitin family homolog 2 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MALDGIRMPD | GCYADGTWEL | SVHVTDLNRD | VTLRVTGEVH | IGGVMLKLVE | KLDVKKDWSD |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| HALWWEKKRT | WLLKTHWTLD | KCGIQADAKL | QFTPQHKLLR | LQLPNMKYVK | VKVNFSDRVF |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| KAVSDICKTF | NIRHPEELSL | LKKPRDPTKK | KKKKLDDQSE | DEALELEGPL | IMPGSGSIYS |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SPGLYSKTMT | PTYDAHDGSP | LSPTSAWFGD | SALSEGNPGI | LAVSQPVTSP | EILAKMFKPQ |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| ALLDKAKTNQ | GWLDSSRSLM | EQDVKENEAL | LLRFKYYSFF | DLNPKYDAIR | INQLYEQAKW |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| ALLLEEIECT | EEEMMMFAAL | QYHINKLSIM | TSENHLNNSD | KEVDEVDAAL | SDLEITLEGG |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KTSTILGDIT | SIPELADYIK | VFKPKKLTLK | GYKQYWCTFK | DTSISCYKSR | EESSGTPAHQ |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| LNLRGCEVTP | DVNISGQKFN | IKLLIPVAEG | MNEIWLRCDN | EKQYAHWMAA | CRLASKGKTM |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| ADSSYNLEVQ | NILSFLKMQH | LNPDPQLIPD | QITTDVNPEC | LVSPRYLKKY | KSKQITARIL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| EAHQNVAQMS | LIEAKMRFIQ | AWQSLPEFGI | THFIARFQGG | KREELIGIAY | NRLIRMDAST |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| GDAIKTWRFS | NMKQWNVNWE | IKMVTVEFAD | EVRLSFICTE | VDCKVVHEFI | GGYIFLSTRA |
| 670 | |||||
| KDQNESLDEE | MFYKLTSGWV |