Q8CG09
Gene name |
Abcc1 |
Protein name |
Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 |
Names |
ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 1, Glutathione-S-conjugate-translocating ATPase ABCC1, Leukotriene C(4) transporter, LTC4 transporter |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:24565 |
EC number |
7.6.2.2: Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate |
Protein Class |
|
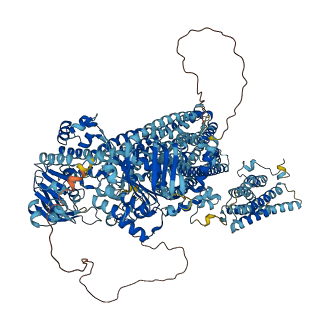
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q8CG09
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q8CG09-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
2 variants for Q8CG09
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3321469054 | 471 | V>G | No | EVA | |
| rs3321745752 | 624 | E>D | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q8CG09
5 regional properties for Q8CG09
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | 3'5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase, catalytic domain | 481 - 814 | IPR002073 |
| domain | GAF domain | 71 - 230 | IPR003018-1 |
| domain | GAF domain | 252 - 439 | IPR003018-2 |
| domain | HD/PDEase domain | 554 - 741 | IPR003607 |
| conserved_site | 3'5'-cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase, conserved site | 597 - 608 | IPR023174 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 7.6.2.2 | Linked to the hydrolysis of a nucleoside triphosphate |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
8 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apical plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the apical end of the cell. |
| basal plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane located at the basal end of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis. |
| basolateral plasma membrane | The region of the plasma membrane that includes the basal end and sides of the cell. Often used in reference to animal polarized epithelial membranes, where the basal membrane is the part attached to the extracellular matrix, or in plant cells, where the basal membrane is defined with respect to the zygotic axis. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| lateral plasma membrane | The portion of the plasma membrane at the lateral side of the cell. In epithelial cells, lateral plasma membranes are on the sides of cells which lie at the interface of adjacent cells. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
15 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ABC-type glutathione S-conjugate transporter activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + glutathione S-conjugate(in) -> ADP + phosphate + glutathione S-conjugate(out). |
| ABC-type transporter activity | Primary active transporter characterized by two nucleotide-binding domains and two transmembrane domains. Uses the energy generated from ATP hydrolysis to drive the transport of a substance across a membrane. |
| ABC-type vitamin B12 transporter activity | Enables the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: vitamin B12(out) + ATP + H2O = ADP + an vitamin B12(in) + H+ + phosphate. Vitamin B12 is alkylcob(III)alamin. |
| ABC-type xenobiotic transporter activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + H2O + xenobiotic(in) = ADP + phosphate + xenobiotic(out). |
| amide transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the transfer of an amide, any compound containing one, two, or three acyl groups attached to a nitrogen atom, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| ATPase-coupled lipid transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the transfer of a solute or solutes from one side of a membrane to the other according to the reaction: ATP + H2O + lipid(in) = ADP + phosphate + lipid(out). |
| ATPase-coupled transmembrane transporter activity | Primary active transporter of a solute across a membrane, via the reaction: ATP + H2O = ADP + phosphate, to directly drive the transport of a substance across a membrane. The transport protein may be transiently phosphorylated (P-type transporters), or not (ABC-type transporters and other families of transporters). Primary active transport occurs up the solute's concentration gradient and is driven by a primary energy source. |
| carboxylic acid transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the transfer of carboxylic acids from one side of a membrane to the other. Carboxylic acids are organic acids containing one or more carboxyl (COOH) groups or anions (COO-). |
| efflux transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the transfer of a specific substance or related group of substances from the inside of the cell to the outside of the cell across a membrane. |
| glutathione transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the transfer of glutathione, the tripeptide glutamylcysteinylglycine, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| hydrolase activity | Catalysis of the hydrolysis of various bonds, e.g. C-O, C-N, C-C, phosphoric anhydride bonds, etc. |
| long-chain fatty acid transporter activity | Enables the transfer of long-chain fatty acids from one side of a membrane to the other. A long-chain fatty acid is a fatty acid with a chain length between C13 and C22. |
| oxidoreductase activity | Catalysis of an oxidation-reduction (redox) reaction, a reversible chemical reaction in which the oxidation state of an atom or atoms within a molecule is altered. One substrate acts as a hydrogen or electron donor and becomes oxidized, while the other acts as hydrogen or electron acceptor and becomes reduced. |
| xenobiotic transmembrane transporter activity | Enables the directed movement of a xenobiotic from one side of a membrane to the other. A xenobiotic is a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
22 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| carboxylic acid transmembrane transport | The process in which carboxylic acid is transported across a membrane. |
| cell chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
| cellular response to amyloid-beta | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a amyloid-beta stimulus. |
| cobalamin metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving cobalamin (vitamin B12), a water-soluble vitamin characterized by possession of a corrin nucleus containing a cobalt atom. |
| export across plasma membrane | The directed movement of some substance from inside of a cell, across the plasma membrane and into the extracellular region. |
| glutathione transmembrane transport | A process in which glutathione is transported across a membrane. |
| leukotriene transport | The directed movement of leukotrienes into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. Leukotrienes are linear C20 endogenous metabolites of arachidonic acid (icosa-5,8,11,14-tetraenoic acid) containing a terminal carboxy function and four or more double bonds (three or more of which are conjugated) as well as other functional groups. |
| long-chain fatty acid import across plasma membrane | The directed movement of long-chain fatty acids from outside of a cell, across the plasma membrane and into the cytosol. A long-chain fatty acid is a fatty acid with a chain length between C13 and C22. |
| negative regulation of cell death | Any process that decreases the rate or frequency of cell death. Cell death is the specific activation or halting of processes within a cell so that its vital functions markedly cease, rather than simply deteriorating gradually over time, which culminates in cell death. |
| negative regulation of neuron death | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of neuron death. |
| phospholipid efflux | The directed movement of a phospholipid out of a cell or organelle. |
| phospholipid translocation | The movement of a phospholipid molecule from one leaflet of a membrane bilayer to the opposite leaflet. |
| positive regulation of cell migration | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of cell migration. |
| positive regulation of inflammatory response | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the inflammatory response. |
| response to oxidative stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of oxidative stress, a state often resulting from exposure to high levels of reactive oxygen species, e.g. superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals. |
| response to xenobiotic stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a xenobiotic, a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| sphingolipid translocation | The movement of a sphingolipid molecule from one leaflet of a membrane bilayer to the opposite leaflet. |
| transepithelial transport | The directed movement of a substance from one side of an epithelium to the other. |
| transmembrane transport | The process in which a solute is transported across a lipid bilayer, from one side of a membrane to the other. |
| xenobiotic detoxification by transmembrane export across the plasma membrane | A process that reduces or removes the toxicity of a xenobiotic by exporting it outside the cell. |
| xenobiotic transport | The directed movement of a xenobiotic into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. A xenobiotic is a compound foreign to the organim exposed to it. It may be synthesized by another organism (like ampicilin) or it can be a synthetic chemical. |
| xenobiotic transport across blood-brain barrier | The directed movement of a xenobiotic through the blood-brain barrier. |
26 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P14772 | BPT1 | Bile pigment transporter 1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| Q8HXQ5 | ABCC1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q2QLE5 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | PR |
| Q6UR05 | ABCC1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Canis lupus familiaris (Dog) (Canis familiaris) | PR |
| P91660 | Rh5 | Probable multidrug resistance-associated protein lethal(2)03659 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| P13569 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O95255 | ABCC6 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O15438 | ABCC3 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q92887 | ABCC2 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O15439 | ABCC4 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96J66 | ABCC11 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 11 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P33527 | ABCC1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| B2RX12 | Abcc3 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8VI47 | Abcc2 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P26361 | Cftr | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q80WJ6 | Abcc12 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 12 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O35379 | Abcc1 | Multidrug resistance-associated protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q6PQZ2 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Sus scrofa (Pig) | PR |
| Q63120 | Abcc2 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | EV |
| Q6Y306 | Abcc12 | ATP-binding cassette sub-family C member 12 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q00553 | CFTR | Cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator | Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque) | PR |
| Q9SKX0 | ABCC13 | ABC transporter C family member 13 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8VZZ4 | ABCC6 | ABC transporter C family member 6 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9M1C7 | ABCC9 | ABC transporter C family member 9 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9C8G9 | ABCC1 | ABC transporter C family member 1 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9C8H0 | ABCC12 | ABC transporter C family member 12 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MALSSFCSSD | GSDPLWDWNV | TWHTSNPDFT | KCFQNTVLTW | VPCFYLWSCF | PLYFLYLSRH |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| DRGYIQMTHL | NKAKTALGFF | LWIICWADLF | YSFWERSQGM | LLAPVLLVSP | TLLGITMLLA |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| TFLIQFERRK | GVQSSGIMLT | FWLVALLCAL | AILRSKIISA | LKKDAQVDMF | RDSAFYLYFT |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LVFIQLVLSC | FSDSSPLFSE | TVRDPNPCPE | SSASFLSRIT | FWWITGMMVQ | GYRQPLKSSD |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LWSLNKEDTS | EEVVPVLVNN | WKKECVKSRK | QPVRIVYAPP | KDPTKPKGSS | QLDVNEEVEA |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| LIVKSSHKDR | DPSLFKVLYK | TFGPYFLMSF | LYKALHDLMM | FAGPEILELI | INFVNDREAP |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| DWQGYLYTAL | LFVSACLQTL | ALHQYFHICF | VTGMRIKTAV | VGAVYRKALV | ITNSARKSST |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| VGEIVNLMSV | DAQRFMDLAT | YINMIWSAPL | QVTLALYFLW | LNLGPSVLAG | VAVMILMVPF |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| NAVMAMKTKT | YQVAHMKSKD | NRIKLMNEIL | NGIKVLKLYA | WELAFQDKVM | NIRQEELKVL |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| KKSAYLAAVG | TFTWVCTPFL | VALSTFAVFV | TVDEKNILDA | KKAFVSLALF | NILRFPLNIL |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| PMVISSIVQA | SVSLKRLRIF | LSHEELEPDS | IERWSIKDGG | GMNSITVKNA | TFTWARDEPP |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| TLNGITFAIP | DGALVAVVGQ | VGCGKSSLLS | ALLAEMDKVE | GHVTLKGSVA | YVPQQAWIQN |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| DSLRENILFG | RPLQEHCYKA | VMEACALLPD | LEILPSGDLT | EIGEKGVNLS | GGQKQRVSLA |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| RAVYCNSDIY | LLDDPLSAVD | AHVGKHIFEK | VVGPMGLLKN | KTRILVTHGI | SYLPQVDVII |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| VMSGGKISEM | GSYQELLDRD | GAFAEFVRTY | ANTEQDLASE | DDSKNGVSGL | GKESKPVENG |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| ILVTDAVGKP | LQRHLSNSSS | HSVVTNQQHS | STAELQKSGV | KEETWKLMEA | DKAQTGQVKL |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| SVYWNYMKAI | GLCISFLSIF | LFLCNHVSAL | ASNYWLSLWT | DDRPAVNGTQ | ENRNFRLSVY |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| GALGILQGVA | VFGYSMAVSI | GGIFASRRLH | LDLLQNVLRS | PMSFFERTPS | GNLVNRFSKE |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| LDTVDSMIPQ | VIKMFMGSLF | SVIGAVIIIL | LATPIAAVII | PPLGLVYFFV | QRFYVASSRQ |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| LKRLESVSRS | PVYSHFNETL | LGVSVIRAFE | EQERFIRQSD | LKVDENQKAY | YPSIVANRWL |
| 1210 | 1220 | 1230 | 1240 | 1250 | 1260 |
| AVRLECVGNC | IVLFAALFAV | ISRHSLSAGL | VGLSVSYSLQ | ITAYLNWLVR | MSSEMETNIV |
| 1270 | 1280 | 1290 | 1300 | 1310 | 1320 |
| AVERLKEYSE | TEKEASWQIQ | ETAPPSTWPH | SGRVEFRDYC | LRYREDLDLV | LKHINVTIEG |
| 1330 | 1340 | 1350 | 1360 | 1370 | 1380 |
| GEKVGIVGRT | GAGKSSLTLG | LFRINESAEG | EIIIDGINIA | KIGLHNLRFK | ITIIPQDPVL |
| 1390 | 1400 | 1410 | 1420 | 1430 | 1440 |
| FSGSLRMNLD | PFSQYSDEEV | WMALELAHLK | GFVSALPDKL | NHECAEGGEN | LSVGQRQLVC |
| 1450 | 1460 | 1470 | 1480 | 1490 | 1500 |
| LARALLRKTK | ILVLDEATAA | VDLETDDLIQ | STIRTQFEDS | TVLTIAHRLN | TIMDYTRVIV |
| 1510 | 1520 | 1530 | |||
| LDKGEIRECG | APSELLQQRG | VFYSMAKDAG | LV |