Q8CBF3
Gene name |
Ephb1 |
Protein name |
Ephrin type-B receptor 1 |
Names |
|
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:270190 |
EC number |
2.7.10.1: Protein-tyrosine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
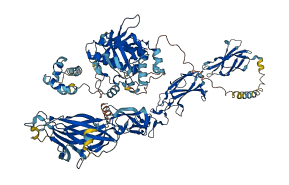
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
619-878 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
761-789 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
619-882 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q8CBF3
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q8CBF3-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
2 variants for Q8CBF3
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs33220099 | 305 | T>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs45773413 | 896 | A>T | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q8CBF3
11 regional properties for Q8CBF3
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Ephrin receptor ligand binding domain | 19 - 201 | IPR001090 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 620 - 878 | IPR001245 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class V, conserved site | 177 - 197 | IPR001426-1 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class V, conserved site | 240 - 260 | IPR001426-2 |
| domain | Sterile alpha motif domain | 908 - 975 | IPR001660 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 322 - 528 | IPR003961 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 740 - 752 | IPR008266 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 625 - 651 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 619 - 878 | IPR020635 |
| domain | Ephrin type-B receptor 1, ligand binding domain | 20 - 195 | IPR034231 |
| domain | EphB1, SAM domain | 908 - 975 | IPR042819 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.10.1 | Protein-tyrosine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
14 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon | The long process of a neuron that conducts nerve impulses, usually away from the cell body to the terminals and varicosities, which are sites of storage and release of neurotransmitter. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| dendrite | A neuron projection that has a short, tapering, morphology. Dendrites receive and integrate signals from other neurons or from sensory stimuli, and conduct nerve impulses towards the axon or the cell body. In most neurons, the impulse is conveyed from dendrites to axon via the cell body, but in some types of unipolar neuron, the impulse does not travel via the cell body. |
| early endosome membrane | The lipid bilayer surrounding an early endosome. |
| endoplasmic reticulum | The irregular network of unit membranes, visible only by electron microscopy, that occurs in the cytoplasm of many eukaryotic cells. The membranes form a complex meshwork of tubular channels, which are often expanded into slitlike cavities called cisternae. The ER takes two forms, rough (or granular), with ribosomes adhering to the outer surface, and smooth (with no ribosomes attached). |
| filopodium tip | The end of a filopodium distal to the body of the cell. |
| glutamatergic synapse | A synapse that uses glutamate as a neurotransmitter. |
| integral component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
| membrane raft | Any of the small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. Small rafts can sometimes be stabilized to form larger platforms through protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. |
| neuron projection | A prolongation or process extending from a nerve cell, e.g. an axon or dendrite. |
| plasma membrane | The membrane surrounding a cell that separates the cell from its external environment. It consists of a phospholipid bilayer and associated proteins. |
| receptor complex | Any protein complex that undergoes combination with a hormone, neurotransmitter, drug or intracellular messenger to initiate a change in cell function. |
7 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| axon guidance receptor activity | Combining with an extracellular messenger and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to results in a change in cellular activity involved in axon guidance. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
| protein-containing complex binding | Binding to a macromolecular complex. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase activity | Combining with a signal and transmitting the signal from one side of the membrane to the other to initiate a change in cell activity by catalysis of the reaction: ATP + a protein-L-tyrosine = ADP + a protein-L-tyrosine phosphate. |
| transmembrane-ephrin receptor activity | Combining with a transmembrane ephrin to initiate a change in cell activity. |
29 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| angiogenesis | Blood vessel formation when new vessels emerge from the proliferation of pre-existing blood vessels. |
| axon guidance | The chemotaxis process that directs the migration of an axon growth cone to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| camera-type eye morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of the eye are generated and organized. The camera-type eye is an organ of sight that receives light through an aperture and focuses it through a lens, projecting it on a photoreceptor field. |
| cell chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell guided by a specific chemical concentration gradient. Movement may be towards a higher concentration (positive chemotaxis) or towards a lower concentration (negative chemotaxis). |
| cell-substrate adhesion | The attachment of a cell to the underlying substrate via adhesion molecules. |
| central nervous system projection neuron axonogenesis | Generation of a long process of a CNS neuron, that carries efferent (outgoing) action potentials from the cell body towards target cells in a different central nervous system region. |
| cranial nerve development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the cranial nerves over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The cranial nerves are composed of twelve pairs of nerves that emanate from the nervous tissue of the hindbrain. These nerves are sensory, motor, or mixed in nature, and provide the motor and general sensory innervation of the head, neck and viscera. They mediate vision, hearing, olfaction and taste and carry the parasympathetic innervation of the autonomic ganglia that control visceral functions. |
| dendritic spine development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the dendritic spine over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A dendritic spine is a protrusion from a dendrite and a specialized subcellular compartment involved in synaptic transmission. |
| dendritic spine morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a dendritic spine are generated and organized. A dendritic spine is a protrusion from a dendrite and a specialized subcellular compartment involved in synaptic transmission. |
| detection of temperature stimulus involved in sensory perception of pain | The series of events involved in the perception of pain in which a temperature stimulus is received and converted into a molecular signal. |
| ephrin receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by ephrin binding to its receptor, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| establishment of cell polarity | The specification and formation of anisotropic intracellular organization or cell growth patterns. |
| hindbrain tangential cell migration | The migration of a cell in the hindbrain in which cells move orthogonal to the direction of radial migration. |
| immunological synapse formation | The formation of an area of close contact between a lymphocyte (T-, B-, or natural killer cell) and a target cell through the clustering of particular signaling and adhesion molecules and their associated membrane rafts on both the lymphocyte and target cell, which facilitates activation of the lymphocyte, transfer of membrane from the target cell to the lymphocyte, and in some situations killing of the target cell through release of secretory granules and/or death-pathway ligand-receptor interaction. |
| modulation of chemical synaptic transmission | Any process that modulates the frequency or amplitude of synaptic transmission, the process of communication from a neuron to a target (neuron, muscle, or secretory cell) across a synapse. Amplitude, in this case, refers to the change in postsynaptic membrane potential due to a single instance of synaptic transmission. |
| negative regulation of satellite cell differentiation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of satellite cell differentiation. |
| negative regulation of skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of satellite cell proliferation. |
| neural precursor cell proliferation | The multiplication or reproduction of neural precursor cells, resulting in the expansion of a cell population. A neural precursor cell is either a nervous system stem cell or a nervous system progenitor cell. |
| neurogenesis | Generation of cells within the nervous system. |
| optic nerve morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structure of the optic nerve is generated and organized. The sensory optic nerve originates from the bipolar cells of the retina and conducts visual information to the brainstem. The optic nerve exits the back of the eye in the orbit, enters the optic canal, and enters the central nervous system at the optic chiasm (crossing) where the nerve fibers become the optic tract just prior to entering the hindbrain. |
| positive regulation of kinase activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of kinase activity, the catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group, usually from ATP, to a substrate molecule. |
| positive regulation of synapse assembly | Any process that activates, maintains or increases the frequency, rate or extent of synapse assembly, the aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form a synapse. |
| protein autophosphorylation | The phosphorylation by a protein of one or more of its own amino acid residues (cis-autophosphorylation), or residues on an identical protein (trans-autophosphorylation). |
| regulation of ERK1 and ERK2 cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the ERK1 and ERK2 cascade. |
| regulation of JNK cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the JNK cascade. |
| regulation of neuron death | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of neuron death. |
| retinal ganglion cell axon guidance | The process in which the migration of an axon growth cone of a retinal ganglion cell (RGC) is directed to its target in the brain in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| skeletal muscle satellite cell activation | The change of a skeletal muscle satellite cell from a mitotically quiescent to a mitotically active state following exposure to some activating factor such as a cellular or soluble ligand. In adult muscle, satellite cells become activated to divide and differentiate in response to muscle damage. |
| transmembrane receptor protein tyrosine kinase signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by an extracellular ligand binding to a receptor on the surface of the target cell where the receptor possesses tyrosine kinase activity, and ending with the regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
49 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P28693 | EPHB2 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q07496 | EPHA4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07497 | EPHB5 | Ephrin type-B receptor 5 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| P29318 | EPHA3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| O42422 | EPHA7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P54755 | EPHA5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07498 | EPHB3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q07494 | EPHB1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| P0C0K6 | EPHB6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Pan troglodytes (Chimpanzee) | SS |
| P29322 | EPHA8 | Ephrin type-A receptor 8 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P21709 | EPHA1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54764 | EPHA4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54753 | EPHB3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29320 | EPHA3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| P54760 | EPHB4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29317 | EPHA2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q15375 | EPHA7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q5JZY3 | EPHA10 | Ephrin type-A receptor 10 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P29323 | EPHB2 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q9UF33 | EPHA6 | Ephrin type-A receptor 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54756 | EPHA5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| O15197 | EPHB6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| P54762 | EPHB1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q03145 | Epha2 | Ephrin type-A receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q60629 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q60750 | Epha1 | Ephrin type-A receptor 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54761 | Ephb4 | Ephrin type-B receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q61772 | Epha7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O09127 | Epha8 | Ephrin type-A receptor 8 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q03137 | Epha4 | Ephrin type-A receptor 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54754 | Ephb3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8BYG9 | Epha10 | Ephrin type-A receptor 10 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| O08644 | Ephb6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P54763 | Ephb2 | Ephrin type-B receptor 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q62413 | Epha6 | Ephrin type-A receptor 6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P29319 | Epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P54757 | Epha5 | Ephrin type-A receptor 5 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P54759 | Epha7 | Ephrin type-A receptor 7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P0C0K7 | Ephb6 | Ephrin type-B receptor 6 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O08680 | Epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| P09759 | Ephb1 | Ephrin type-B receptor 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| O61460 | vab-1 | Ephrin receptor 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q8VZJ9 | CRCK2 | Calmodulin-binding receptor-like cytoplasmic kinase 2 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LMN7 | WAK5 | Wall-associated receptor kinase 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LSV3 | WAKL16 | Putative wall-associated receptor kinase-like 16 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9M342 | WAKL15 | Wall-associated receptor kinase-like 15 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| O13147 | ephb3 | Ephrin type-B receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O73878 | ephb4b | Ephrin type-B receptor 4b | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| O13146 | epha3 | Ephrin type-A receptor 3 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MALDCLLLFL | LASAVAAMEE | TLMDTRTATA | ELGWTANPAS | GWEEVSGYDE | NLNTIRTYQV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| CNVFEPNQNN | WLLTTFINRR | GAHRIYTEMR | FTVRDCSSLP | NVPGSCKETF | NLYYYETDSV |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| IATKKSAFWS | EAPYLKVDTI | AADESFSQVD | FGGRLMKVNT | EVRSFGPLTR | NGFYLAFQDY |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| GACMSLLSVR | VFFKKCPSIV | QNFAVFPETM | TGAESTSLVI | ARGTCIPNAE | EVDVPIKLYC |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| NGDGEWMVPI | GRCTCKPGYE | PENSVACKAC | PAGTFKASQE | AEGCSHCPSN | SRSPSEASPI |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| CTCRTGYYRA | DFDPPEVACT | SVPSGPRNVI | SIVNETSIIL | EWHPPRETGG | RDDVTYNIIC |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| KKCRADRRSC | SRCDDNVEFV | PRQLGLTECR | VSISSLWAHT | PYTFDIQAIN | GVSSKSPFPP |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| QHVSVNITTN | QAAPSTVPIM | HQVSATMRSI | TLSWPQPEQP | NGIILDYEIR | YYEKEHNEFN |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| SSMARSQTNT | ARIDGLRPGM | VYVVQVRART | VAGYGKFSGK | MCFQTLTDDD | YKSELREQLP |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| LIAGSAAAGV | VFVVSLVAIS | IVCSRKRAYS | KEAAYSDKLQ | HYSTGRGSPG | MKIYIDPFTY |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| EDPNEAVREF | AKEIDVSFVK | IEEVIGAGEF | GEVYKGRLKL | PGKREIYVAI | KTLKAGYSEK |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| QRRDFLSEAS | IMGQFDHPNI | IRLEGVVTKS | RPVMIITEFM | ENGALDSFLR | QNDGQFTVIQ |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| LVGMLRGIAA | GMKYLSEMNY | VHRDLAARNI | LVNSNLVCKV | SDFGLSRYLQ | DDTSDPTYTS |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| SLGGKIPVRW | TAPEAIAYRK | FTSASDVWSY | GIVMWEVMSF | GERPYWDMSN | QDVINAIEQD |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| YRLPPPMDCP | AALHQLMLDC | WQKDRNSRPR | FAEIVNTLDK | MIRNPASLKT | VATITAVPSQ |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| PLLDRSIPDF | TAFTTVDDWL | SAIKMVQYRD | SFLTAGFTSL | QLVTQMTSED | LLRIGVTLAG |
| 970 | 980 | ||||
| HQKKILSSIH | SMRVQMNQSP | SVMA |