Q8C7G5
Gene name |
Apoa5 (Rap3) |
Protein name |
Apolipoprotein A-V |
Names |
Apo-AV, ApoA-V, Apolipoprotein A5, Regeneration-associated protein 3 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:66113 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
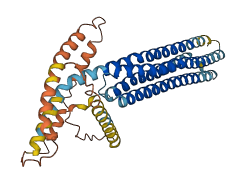
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q8C7G5
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q8C7G5-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
19 variants for Q8C7G5
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3388990401 | 5 | I>T | No | EVA | |
| rs48268831 | 8 | A>V | No | EVA | |
| rs218792858 | 13 | A>S | No | EVA | |
| rs263353150 | 31 | N>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389049098 | 36 | G>C | No | EVA | |
| rs227075004 | 37 | V>M | No | EVA | |
| rs3400189930 | 39 | G>C | No | EVA | |
| rs3389037341 | 71 | R>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389041616 | 87 | I>T | No | EVA | |
| rs3389036506 | 96 | G>R | No | EVA | |
| rs1132135101 | 101 | R>H | No | EVA | |
| rs3389037345 | 116 | N>I | No | EVA | |
| rs258253931 | 162 | D>E | No | EVA | |
| rs3389047072 | 163 | E>* | No | EVA | |
| rs3389045505 | 243 | R>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389036494 | 267 | D>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3388990406 | 276 | E>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389015565 | 331 | N>D | No | EVA | |
| rs3389040887 | 333 | A>T | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q8C7G5
No regional properties for Q8C7G5
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| No domain, repeats, and functional sites for Q8C7G5 | |||
Functions
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chylomicron | A large lipoprotein particle (diameter 75-1200 nm) composed of a central core of triglycerides and cholesterol surrounded by a protein-phospholipid coating. The proteins include one molecule of apolipoprotein B-48 and may include a variety of apolipoproteins, including APOAs, APOCs and APOE. Chylomicrons are found in blood or lymph and carry lipids from the intestines into other body tissues. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| early endosome | A membrane-bounded organelle that receives incoming material from primary endocytic vesicles that have been generated by clathrin-dependent and clathrin-independent endocytosis; vesicles fuse with the early endosome to deliver cargo for sorting into recycling or degradation pathways. |
| extracellular region | The space external to the outermost structure of a cell. For cells without external protective or external encapsulating structures this refers to space outside of the plasma membrane. This term covers the host cell environment outside an intracellular parasite. |
| extracellular space | That part of a multicellular organism outside the cells proper, usually taken to be outside the plasma membranes, and occupied by fluid. |
| Golgi apparatus | A membrane-bound cytoplasmic organelle of the endomembrane system that further processes the core oligosaccharides (e.g. N-glycans) added to proteins in the endoplasmic reticulum and packages them into membrane-bound vesicles. The Golgi apparatus operates at the intersection of the secretory, lysosomal, and endocytic pathways. |
| high-density lipoprotein particle | A lipoprotein particle with a high density (typically 1.063-1.21 g/ml) and a diameter of 5-10 nm that contains APOAs and may contain APOCs and APOE; found in blood and carries lipids from body tissues to the liver as part of the reverse cholesterol transport process. |
| late endosome | A prelysosomal endocytic organelle differentiated from early endosomes by lower lumenal pH and different protein composition. Late endosomes are more spherical than early endosomes and are mostly juxtanuclear, being concentrated near the microtubule organizing center. |
| very-low-density lipoprotein particle | A triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle that is typically composed of APOB100, APOE and APOCs and has a density of about 1.006 g/ml and a diameter of between 20-80 nm. It is found in blood and transports endogenous products (newly synthesized cholesterol and triglycerides) from the liver. |
13 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cholesterol binding | Binding to cholesterol (cholest-5-en-3-beta-ol); the principal sterol of vertebrates and the precursor of many steroids, including bile acids and steroid hormones. |
| enzyme activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of an enzyme. |
| enzyme binding | Binding to an enzyme, a protein with catalytic activity. |
| heparin binding | Binding to heparin, a member of a group of glycosaminoglycans found mainly as an intracellular component of mast cells and which consist predominantly of alternating alpha-(1->4)-linked D-galactose and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-6-sulfate residues. |
| lipase activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of a lipase, an enzyme that catalyzes of the hydrolysis of a lipid. |
| lipase binding | Binding to a lipase. |
| lipid binding | Binding to a lipid. |
| lipoprotein lipase activator activity | Binds to and increases the activity of a lipoprotein lipase, an enzyme that catalyzes of the hydrolysis of a lipid within a lipoprotein. |
| lipoprotein particle receptor binding | Binding to a lipoprotein particle receptor. |
| low-density lipoprotein particle receptor binding | Binding to a low-density lipoprotein receptor. |
| phosphatidylcholine binding | Binding to a phosphatidylcholine, a glycophospholipid in which a phosphatidyl group is esterified to the hydroxyl group of choline. |
| phosphatidylcholine-sterol O-acyltransferase activator activity | Increases the activity of phosphatidylcholine-sterol O-acyltransferase, an enzyme that converts cholesterol and phosphatidylcholine (lecithins) to cholesteryl esters and lyso-phosphatidylcholines. |
| phospholipid binding | Binding to a phospholipid, a class of lipids containing phosphoric acid as a mono- or diester. |
23 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| acylglycerol homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of acylglycerol within an organism or cell. |
| cholesterol biosynthetic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3 beta-ol, the principal sterol of vertebrates and the precursor of many steroids, including bile acids and steroid hormones. |
| cholesterol efflux | The directed movement of cholesterol, cholest-5-en-3-beta-ol, out of a cell or organelle. |
| cholesterol homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of cholesterol within an organism or cell. |
| high-density lipoprotein particle assembly | The non-covalent aggregation and arrangement of proteins and lipids to form a high-density lipoprotein particle. |
| lipid transport | The directed movement of lipids into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. Lipids are compounds soluble in an organic solvent but not, or sparingly, in an aqueous solvent. |
| lipoprotein metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving any conjugated, water-soluble protein in which the covalently attached nonprotein group consists of a lipid or lipids. |
| phosphatidylcholine metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving phosphatidylcholines, any of a class of glycerophospholipids in which the phosphatidyl group is esterified to the hydroxyl group of choline. They are important constituents of cell membranes. |
| phospholipid efflux | The directed movement of a phospholipid out of a cell or organelle. |
| positive regulation of cholesterol esterification | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of cholesterol esterification. Cholesterol esterification is the lipid modification process in which a sterol ester is formed by the combination of a carboxylic acid (often a fatty acid) and cholesterol. In the blood this process is associated with the conversion of free cholesterol into cholesteryl ester, which is then sequestered into the core of a lipoprotein particle. |
| positive regulation of fatty acid biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of fatty acids. |
| positive regulation of lipid biosynthetic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the formation of lipids. |
| positive regulation of lipid catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of lipids. |
| positive regulation of lipoprotein lipase activity | Any process that activates or increases the activity of the enzyme lipoprotein lipase. |
| positive regulation of triglyceride catabolic process | Any process that increases the frequency, rate, or extent of the chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of triglyceride. |
| positive regulation of very-low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling | Any process that increases the rate, frequency or extent of very-low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling. Very-low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling is the acquisition, loss or modification of a protein or lipid within a very-low-density lipoprotein particle, including the hydrolysis of triglyceride by hepatic lipase or lipoprotein lipase and the subsequent loss of free fatty acid. |
| regulation of intestinal cholesterol absorption | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of absorption of cholesterol into the blood, and the exclusion of other sterols from absorption. |
| tissue regeneration | The regrowth of lost or destroyed tissues. |
| triglyceride catabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways resulting in the breakdown of a triglyceride, any triester of glycerol. |
| triglyceride homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of triglyceride within an organism or cell. |
| triglyceride metabolic process | The chemical reactions and pathways involving triglyceride, any triester of glycerol. The three fatty acid residues may all be the same or differ in any permutation. Triglycerides are important components of plant oils, animal fats and animal plasma lipoproteins. |
| triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle remodeling | The acquisition, loss or modification of a protein or lipid within a triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle, including the hydrolysis of triglyceride by lipoprotein lipase, with the subsequent loss of free fatty acid, and the transfer of cholesterol esters to a triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle by cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP), with the simultaneous transfer of triglyceride from a triglyceride-rich lipoprotein particle. |
| very-low-density lipoprotein particle remodeling | The acquisition, loss or modification of a protein or lipid within a very-low-density lipoprotein particle, including the hydrolysis of triglyceride by hepatic lipase or lipoprotein lipase and the subsequent loss of free fatty acid. |
4 homologous proteins in AiPD
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAAVITWALA | LLAVFASTQA | RKSLWDYFSQ | NSWSKGVMGQ | PQKLAQENLK | GSFEQDLYNM |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NNYLEKLGPL | RGPGKEPPLL | AQDPEGIRKQ | LQQELGEVSS | RLEPYMAAKH | QQVGWNLEGL |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| RQQLKPYTAE | LMEQVGLSVQ | ELQEQLRVVG | EDTKAQLLGG | VDEALNLLQD | MQSRVLHHTD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| RVKELFHPYA | ERLVTGIGHH | VQELHRSVAP | HAAASPARLS | RCVQTLSHKL | TRKAKDLHTS |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| IQRNLDQLRD | ELSAFIRVST | DGAEDGDSLD | PQALSEEVRQ | RLQAFRHDTY | LQIAAFTQAI |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| DQETEEIQHQ | LAPPPPSHSA | FAPELGHSDS | NKALSRLQSR | LDDLWEDIAY | GLQDQGHSHL |
| SDPEGHSG |