Q8AYC9
Gene name |
CHEK1 (CHK1) |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1 |
Names |
CHK1 checkpoint homolog, Checkpoint kinase-1 |
Species |
Gallus gallus (Chicken) |
KEGG Pathway |
gga:374260 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
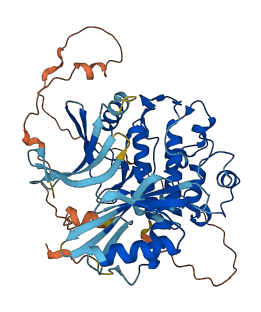
Descriptions
(Annotation based on sequence homology with O14757)
CHEK1 is a serine/threonine protein kinase and is a key mediator that links the DNA stress responses to the cell cycle. Full-length CHEK1 has only low basal activity when expressed. Truncation of the C-terminal regulatory region activates CHEK1 even in the absence of stress.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
147-172 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
9-265 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q8AYC9
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q8AYC9-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
38 variants for Q8AYC9
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs732764600 | 24 | Q>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs736470190 | 47 | D>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs734403832 | 48 | C>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs732304398 | 66 | N>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs737056156 | 76 | E>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs735329243 | 81 | Y>* | No | Ensembl | |
| rs732373230 | 119 | V>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs741214714 | 127 | T>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs733665222 | 128 | H>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs737184686 | 142 | D>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs740224115 | 156 | K>N | No | Ensembl | |
| rs736045480 | 168 | C>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs739446303 | 168 | C>W | No | Ensembl | |
| rs739049862 | 173 | Y>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs731503203 | 174 | V>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs738256463 | 198 | L>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs732083534 | 199 | T>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs741264589 | 201 | M>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs733727526 | 202 | L>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs737876280 | 215 | C>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs730896566 | 247 | T>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs741373133 | 256 | I>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs736991015 | 328 | W>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs736308298 | 329 | D>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs739663479 | 334 | S>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs738429396 | 345 | S>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs741087558 | 346 | Q>H | No | Ensembl | |
| rs730947771 | 346 | Q>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs735072434 | 374 | V>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs739778892 | 375 | R>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs737769601 | 377 | M>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs731579686 | 409 | T>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs740868575 | 415 | S>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs734694470 | 417 | T>P | No | Ensembl | |
| rs732598908 | 420 | R>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs737707079 | 434 | E>G | No | Ensembl | |
| rs735568913 | 440 | D>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs733501777 | 445 | K>Q | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q8AYC9
4 regional properties for Q8AYC9
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
6 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| centrosome | A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle. |
| chromatin | The ordered and organized complex of DNA, protein, and sometimes RNA, that forms the chromosome. |
| condensed nuclear chromosome | A highly compacted molecule of DNA and associated proteins resulting in a cytologically distinct nuclear chromosome. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleoplasm | That part of the nuclear content other than the chromosomes or the nucleolus. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| histone kinase activity (H3-T11 specific) | Catalysis of the transfer of a phosphate group to the threonine-11 residue of the N-terminal tail of histone H3. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
14 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to DNA damage stimulus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating damage to its DNA from environmental insults or errors during metabolism. |
| DNA damage checkpoint signaling | A signal transduction process that contributes to a DNA damage checkpoint. |
| DNA damage induced protein phosphorylation | The widespread phosphorylation of various molecules, triggering many downstream processes, that occurs in response to the detection of DNA damage. |
| DNA repair | The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway. |
| epigenetic maintenance of chromatin in transcription-competent conformation | An epigenetic process that capacitates gene expression by remodelling of chromatin by either modifying the chromatin fiber, the nucleosomal histones, or the DNA. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| mitotic G2 DNA damage checkpoint signaling | A mitotic cell cycle checkpoint that detects and negatively regulates progression through the G2/M transition of the cell cycle in response to DNA damage. |
| negative regulation of mitotic nuclear division | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the rate or extent of mitosis. Mitosis is the division of the eukaryotic cell nucleus to produce two daughter nuclei that, usually, contain the identical chromosome complement to their mother. |
| peptidyl-threonine phosphorylation | The phosphorylation of peptidyl-threonine to form peptidyl-O-phospho-L-threonine. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| regulation of double-strand break repair via homologous recombination | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the error-free repair of a double-strand break in DNA in which the broken DNA molecule is repaired using homologous sequences. |
| regulation of histone H3-K9 acetylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of histone H3-K9 acetylation. |
| regulation of mitotic centrosome separation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of the separation of duplicated centrosome components at the beginning of mitosis. |
| regulation of transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter in response to UV-induced DNA damage | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter as a result of a UV damage stimulus. |
6 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P28708 | PRR1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PRR1 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| P47116 | PTK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase PTK2/STK2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | PR |
| O61661 | grp | Serine/threonine-protein kinase grp | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| O14757 | CHEK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| O35280 | Chek1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q91ZN7 | Chek1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase Chk1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MAVPFVEDWD | LVQTLGEGAY | GEVQLAVNRR | TEEAVAVKIV | DMKRAADCPE | NIKKEICINK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| MLNHENVVKF | YGHRREGATQ | YLFLEYCSGG | ELFDRIEPDI | GMPEPEAQRF | FQQLIAGVVY |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| LHSMGITHRD | LKPENLLLDE | RDNLKISDFG | LATVFKHNGR | ERLLNKMCGT | LPYVAPELLR |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| RPEFRAEPVD | VWACGVVLTA | MLAGELPWDQ | PSDSCQEYSD | WKERKTYLAP | WRKIDSAPLA |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LLHKILTENP | TARITIPDIK | KDRWYCRPLK | KGTKRGRVSS | GGVTESPGAL | PKHIRSDTDF |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| SPVKSALGED | KASYSTSQPE | PGTGGALWDS | STGSIDRLVQ | GISFSQPACP | EHMLLNSQLL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| GTPGSSQSPW | QRLVRRMTRF | FTKLDADGSY | RSLRDVCEKM | GYGWKQSCTN | QVTISTTDRR |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | |
| NNKLIFKVNL | LEMESRILVD | FRLSKGDGLE | FKRHFLKIKG | KLSDVVSTQK | VWLPPP |