Q810B3
Gene name |
Bsx |
Protein name |
Brain-specific homeobox protein homolog |
Names |
|
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:244813 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
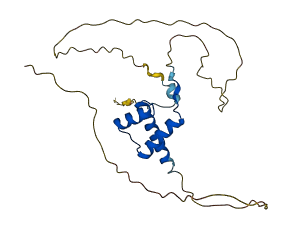
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q810B3
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q810B3-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
8 variants for Q810B3
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs3400037814 | 59 | M>K | No | EVA | |
| rs3389005239 | 62 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389040053 | 65 | L>F | No | EVA | |
| rs3388985970 | 193 | E>V | No | EVA | |
| rs3389035531 | 196 | P>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389031154 | 206 | G>S | No | EVA | |
| rs3389038096 | 219 | I>N | No | EVA | |
| rs3388986022 | 232 | L>F | No | EVA |
No associated diseases with Q810B3
4 regional properties for Q810B3
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Homeobox domain | 108 - 172 | IPR001356 |
| conserved_site | Homeobox, conserved site | 143 - 166 | IPR017970 |
| domain | Homeobox domain, metazoa | 132 - 143 | IPR020479-1 |
| domain | Homeobox domain, metazoa | 147 - 166 | IPR020479-2 |
3 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| transcription regulator complex | A protein complex that is capable of associating with DNA by direct binding, or via other DNA-binding proteins or complexes, and regulating transcription. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA-binding transcription activator activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that activates or increases transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
| sequence-specific double-stranded DNA binding | Binding to double-stranded DNA of a specific nucleotide composition, e.g. GC-rich DNA binding, or with a specific sequence motif or type of DNA, e.g. promotor binding or rDNA binding. |
6 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| brain development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the brain over time, from its formation to the mature structure. Brain development begins with patterning events in the neural tube and ends with the mature structure that is the center of thought and emotion. The brain is responsible for the coordination and control of bodily activities and the interpretation of information from the senses (sight, hearing, smell, etc.). |
| eating behavior | The specific behavior of an organism relating to the intake of food, any substance (usually solid) that can be metabolized by an organism to give energy and build tissue. |
| locomotory behavior | The specific movement from place to place of an organism in response to external or internal stimuli. Locomotion of a whole organism in a manner dependent upon some combination of that organism's internal state and external conditions. |
| mammary gland involution | The tissue remodeling that removes differentiated mammary epithelia during weaning. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
8 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q6RFL5 | BSX | Brain-specific homeobox protein homolog | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | PR |
| Q3C1V8 | BSX | Brain-specific homeobox protein homolog | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9HBU1 | BARX1 | Homeobox protein BarH-like 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UMQ3 | BARX2 | Homeobox protein BarH-like 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q64205 | Dlx3 | Homeobox protein DLX-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P70396 | Dlx5 | Homeobox protein DLX-5 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P70397 | Dlx6 | Homeobox protein DLX-6 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9ER42 | Barx1 | Homeobox protein BarH-like 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MNLNFTSPLH | PASSQRPTSF | FIEDILLHKP | KPLREVAPDH | FASSLASRVP | LLDYGYPLMP |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TPTLLTPHAH | HPLHKGDHHH | PYFLTTSGMP | VPALFPHPQH | AELPGKHCRR | RKARTVFSDS |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| QLSGLEKRFE | IQRYLSTPER | VELATALSLS | ETQVKTWFQN | RRMKHKKQLR | KSQDEPKAAD |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | |
| GPESPEGSPR | APEGAPADAR | LSLPAGAFVL | TEPEDEVDIG | DEGELSSGPH | VL |