Q80WD0
Gene name |
Rtn4rl1 |
Protein name |
Reticulon-4 receptor-like 1 |
Names |
Nogo receptor-like 2, Nogo-66 receptor homolog 2, Nogo-66 receptor-related protein 3, NgR3 |
Species |
Rattus norvegicus (Rat) |
KEGG Pathway |
rno:303311 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
Descriptions
The autoinhibited protein was predicted that may have potential autoinhibitory elements via cis-regPred.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
|
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
cis-regPred |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
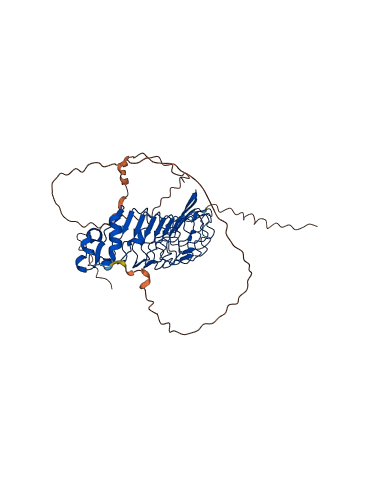
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q80WD0
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q80WD0-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q80WD0
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q80WD0 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q80WD0
10 regional properties for Q80WD0
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 58 - 111 | IPR001611-1 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 126 - 185 | IPR001611-2 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat | 198 - 255 | IPR001611-3 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 76 - 98 | IPR003591-1 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 99 - 123 | IPR003591-2 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 124 - 147 | IPR003591-3 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 148 - 171 | IPR003591-4 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 172 - 195 | IPR003591-5 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 196 - 219 | IPR003591-6 |
| repeat | Leucine-rich repeat, typical subtype | 220 - 243 | IPR003591-7 |
Functions
7 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| anchored component of plasma membrane | The component of the plasma membrane consisting of the gene products that are tethered to the membrane only by a covalently attached anchor, such as a lipid group, that is embedded in the membrane. Gene products with peptide sequences that are embedded in the membrane are excluded from this grouping. |
| cell projection | A prolongation or process extending from a cell, e.g. a flagellum or axon. |
| cell surface | The external part of the cell wall and/or plasma membrane. |
| external side of plasma membrane | The leaflet of the plasma membrane that faces away from the cytoplasm and any proteins embedded or anchored in it or attached to its surface. |
| integral component of membrane | The component of a membrane consisting of the gene products and protein complexes having at least some part of their peptide sequence embedded in the hydrophobic region of the membrane. |
| membrane raft | Any of the small (10-200 nm), heterogeneous, highly dynamic, sterol- and sphingolipid-enriched membrane domains that compartmentalize cellular processes. Small rafts can sometimes be stabilized to form larger platforms through protein-protein and protein-lipid interactions. |
| perikaryon | The portion of the cell soma (neuronal cell body) that excludes the nucleus. |
4 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| chondroitin sulfate binding | Binding to chondroitin sulfate, a glycosaminoglycan made up of two alternating monosaccharides: D-glucuronic acid (GlcA) and N-acetyl-D-galactosamine (GalNAc). |
| heparin binding | Binding to heparin, a member of a group of glycosaminoglycans found mainly as an intracellular component of mast cells and which consist predominantly of alternating alpha-(1->4)-linked D-galactose and N-acetyl-D-glucosamine-6-sulfate residues. |
| Roundabout binding | Binding to Roundabout (ROBO) receptor, a transmembrane receptor. |
| signaling receptor activity | Receiving a signal and transmitting it in the cell to initiate a change in cell activity. A signal is a physical entity or change in state that is used to transfer information in order to trigger a response. |
6 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| axon guidance | The chemotaxis process that directs the migration of an axon growth cone to a specific target site in response to a combination of attractive and repulsive cues. |
| cell surface receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by activation of a receptor on the surface of a cell. The pathway begins with binding of an extracellular ligand to a cell surface receptor, or for receptors that signal in the absence of a ligand, by ligand-withdrawal or the activity of a constitutively active receptor. The pathway ends with regulation of a downstream cellular process, e.g. transcription. |
| corpus callosum development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the corpus callosum over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The corpus callosum is a thick bundle of nerve fibers comprising a commissural plate connecting the two cerebral hemispheres. It consists of contralateral axon projections that provide communication between the right and left cerebral hemispheres. |
| negative chemotaxis | The directed movement of a motile cell or organism towards a lower concentration of a chemical. |
| negative regulation of axon regeneration | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of axon regeneration. |
| negative regulation of neuron projection development | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of neuron projection development. Neuron projection development is the process whose specific outcome is the progression of a neuron projection over time, from its formation to the mature structure. A neuron projection is any process extending from a neural cell, such as axons or dendrites (collectively called neurites). |
36 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q3MHH9 | ECM2 | Extracellular matrix protein 2 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| P58874 | OPTC | Opticin | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q24K06 | LRRC10 | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 10 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q9V780 | Lap1 | Protein lap1 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | PR |
| Q96NW7 | LRRC7 | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 7 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8IWT6 | LRRC8A | Volume-regulated anion channel subunit LRRC8A | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9HCJ2 | LRRC4C | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 4C | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UFC0 | LRWD1 | Leucine-rich repeat and WD repeat-containing protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96L50 | LRR1 | Leucine-rich repeat protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8IWK6 | ADGRA3 | Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor A3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q7L1W4 | LRRC8D | Volume-regulated anion channel subunit LRRC8D | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q96FE5 | LINGO1 | Leucine-rich repeat and immunoglobulin-like domain-containing nogo receptor-interacting protein 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q8TDW0 | LRRC8C | Volume-regulated anion channel subunit LRRC8C | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q38SD2 | LRRK1 | Leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q86UN2 | RTN4RL1 | Reticulon-4 receptor-like 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| A6H694 | Lrrc63 | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 63 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9D9Q0 | Lrrc69 | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 69 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8BGI7 | Lrrc39 | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 39 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q7TT36 | Adgra3 | Adhesion G protein-coupled receptor A3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P59383 | Lrrn4 | Leucine-rich repeat neuronal protein 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9D1T0 | Lingo1 | Leucine-rich repeat and immunoglobulin-like domain-containing nogo receptor-interacting protein 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8R502 | Lrrc8c | Volume-regulated anion channel subunit LRRC8C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q80WG5 | Lrrc8a | Volume-regulated anion channel subunit LRRC8A | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q80TE7 | Lrrc7 | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 7 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q5DU41 | Lrrc8b | Volume-regulated anion channel subunit LRRC8B | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q5RKR3 | Islr2 | Immunoglobulin superfamily containing leucine-rich repeat protein 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8C031 | Lrrc4c | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 4C | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q8K0S5 | Rtn4rl1 | Reticulon-4 receptor-like 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| P70587 | Lrrc7 | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 7 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q4V8G0 | Lrrc63 | Leucine-rich repeat-containing protein 63 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| Q9TZM3 | lrk-1 | Leucine-rich repeat serine/threonine-protein kinase 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q9SHI4 | RLP3 | Receptor-like protein 3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | SS |
| Q5G5E0 | PIRL5 | Plant intracellular Ras-group-related LRR protein 5 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| B0JZ65 | lrwd1 | Leucine-rich repeat and WD repeat-containing protein 1 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| Q68F79 | lrrc8e | Volume-regulated anion channel subunit LRRC8E | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | PR |
| B0R160 | lrwd1 | Leucine-rich repeat and WD repeat-containing protein 1 | Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MLRKGCCVEL | LLLLLAGELP | LSGGCPRDCV | CYPSPMTVSC | QAHNFAAIPE | GIPEDSERIF |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| LQNNHITFLQ | QGHFSPAMVT | LWIYSNNITF | IAPNTFEGFV | HLEELDLGDN | RQLRTLAPET |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| FQGLVKLHAL | YLYKCGLSSL | PAGIFGGLHS | LQYLYLQDNH | IEYLQDDIFV | DLVNLSHLFL |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| HGNKLWSLGQ | GIFRGLVNLD | RLLLHENQLQ | WVHHKAFHDL | HRLTTLFLFN | NSLTELQGDC |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LAPLVALEFL | RLNGNAWDCG | CRARSLWEWL | RRFRGSSSVV | PCATPELRQG | QDLKSLRVED |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| FRNCTGPASP | HQIKSHTLST | SDRAARKEHH | PSHGASRDKG | HPHGHLPGSR | SGSKKPGKNC |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| TSHRNRNQIS | KGSAGKELPE | LQDYAPDYQH | KFSFDIMPTA | RPKRKGKCAR | RTPIRAPSGV |
| 430 | 440 | ||||
| QQASSGTALG | VSLLAWILGL | VVSLR |