Q80UE6
Gene name |
Wnk4 |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK4 |
Names |
Protein kinase lysine-deficient 4, Protein kinase with no lysine 4 |
Species |
Mus musculus (Mouse) |
KEGG Pathway |
mmu:69847 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
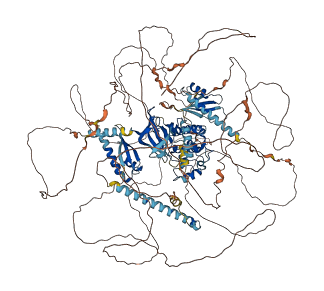
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
171-429 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
317-338 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
171-429 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q80UE6
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q80UE6-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
15 variants for Q80UE6
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| rs217080242 | 109 | M>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs213942067 | 133 | S>F | No | Ensembl | |
| rs250224787 | 543 | L>M | No | Ensembl | |
| rs232403658 | 611 | E>D | No | Ensembl | |
| rs235569209 | 661 | V>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs27073460 | 742 | T>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs256215640 | 766 | A>T | No | Ensembl | |
| rs27073455 | 782 | I>V | No | Ensembl | |
| rs234187710 | 839 | S>L | No | Ensembl | |
| rs254823119 | 844 | Q>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs216388261 | 859 | V>A | No | Ensembl | |
| rs52181149 | 870 | A>S | No | Ensembl | |
| rs214688602 | 940 | G>D | No | Ensembl | |
| rs230203846 | 942 | L>R | No | Ensembl | |
| rs242671939 | 970 | R>C | No | Ensembl |
No associated diseases with Q80UE6
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
4 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| bicellular tight junction | An occluding cell-cell junction that is composed of a branching network of sealing strands that completely encircles the apical end of each cell in an epithelial sheet; the outer leaflets of the two interacting plasma membranes are seen to be tightly apposed where sealing strands are present. Each sealing strand is composed of a long row of transmembrane adhesion proteins embedded in each of the two interacting plasma membranes. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| membrane | A lipid bilayer along with all the proteins and protein complexes embedded in it an attached to it. |
6 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| chloride channel inhibitor activity | Binds to and stops, prevents, or reduces the activity of a chloride channel. |
| potassium channel inhibitor activity | Binds to and stops, prevents, or reduces the activity of a potassium channel. |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate, and ATP + protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate. |
| protein serine/threonine/tyrosine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions: ATP + a protein serine = ADP + protein serine phosphate; ATP + a protein threonine = ADP + protein threonine phosphate; and ATP + a protein tyrosine = ADP + protein tyrosine phosphate. |
14 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular cation homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of cations at the level of a cell. |
| cellular chloride ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of chloride ions at the level of a cell. |
| chloride transport | The directed movement of chloride into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| distal tubule morphogenesis | The process in which the anatomical structures of a distal tubule are generated and organized. The distal tubule is a nephron tubule that begins at the macula densa and extends to the connecting tubule. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| ion homeostasis | Any process involved in the maintenance of an internal steady state of ions within an organism or cell. |
| ion transport | The directed movement of charged atoms or small charged molecules into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| negative regulation of pancreatic juice secretion | Any process that decreases the rate, frequency or extent of pancreatic juice secretion, the regulated release of pancreatic juice by the exocrine pancreas into the upper part of the intestine. |
| negative regulation of sodium ion transport | Any process that decreases the frequency, rate or extent of the directed movement of sodium ions (Na+) into, out of or within a cell, or between cells, by means of some agent such as a transporter or pore. |
| positive regulation of potassium ion import across plasma membrane | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of potassium ion import across the plasma membrane. |
| positive regulation of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of sodium ion transmembrane transporter activity. |
| protein localization | Any process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a specific location. |
| protein phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group on to a protein. |
| renal sodium ion absorption | A renal system process in which sodium ions are taken up from the collecting ducts and proximal and distal loops of the nephron. In non-mammalian species, absorption may occur in related structures. |
17 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q9Y3S1 | WNK2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9H4A3 | WNK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9BYP7 | WNK3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q96J92 | WNK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q99J45 | Nrbp1 | Nuclear receptor-binding protein | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q80XP9 | Wnk3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| P83741 | Wnk1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q3UH66 | Wnk2 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6R2V0 | WNK1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK1 | Sus scrofa (Pig) | SS |
| Q9JIH7 | Wnk1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | EV |
| Q7TPK6 | Wnk4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK4 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| X5M5N0 | wnk-1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK | Caenorhabditis elegans | SS |
| Q8RXE5 | WNK10 | Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK10 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q944Q0 | WNK8 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK8 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9LVL5 | WNK4 | Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK4 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q9STK6 | WNK3 | Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK3 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| Q8LST2 | WNK7 | Probable serine/threonine-protein kinase WNK7 | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MLAPRNTETG | VPMSQTEADL | ALRPSPALTS | TGPTRLGPPP | RRVRRFSGKA | EPRPRSSRPS |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| RRSSVDLGLL | SSWSQPASLL | PEPPDPPDSA | GPTRSPPSSS | KEPPEGTWMG | AAPVKAVDSA |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| CPELTGSSGG | PGSREPPRVP | DAAARERRRE | QEEKEDTETQ | AVATSPDGRY | LKFDIEIGRG |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| SFKTVYRGLD | TDTTVEVAWC | ELQTRKLSRA | ERQRFSEEVE | MLKGLQHPNI | VRFYDSWKSV |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| LRGQVCIVLV | TELMTSGTLK | TYLRRFREMK | PRVLQRWSRQ | ILRGLHFLHS | RVPPILHRDL |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| KCDNVFITGP | SGSVKIGDLG | LATLKRASFA | KSVIGTPEFM | APEMYEEKYD | EAVDVYAFGM |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| CMLEMATSEY | PYSECQNAAQ | IYRKVTSGTK | PNSFYKVKMP | EVKEIIEGCI | RTDKNERFTI |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| QDLLAHAFFR | EERGVHVELA | EEDDGEKPGL | KLWLRMEDAR | RGGRPRDNQA | IEFLFQLGRD |
| 490 | 500 | 510 | 520 | 530 | 540 |
| AAEEVAQEMV | ALGLVCEADY | QPVARAVRER | VAAIQRKREK | LRKARELEVL | PPDSGPPPAT |
| 550 | 560 | 570 | 580 | 590 | 600 |
| VSLAPGPPSA | FPPEPEEPEA | DQHQSFLFRH | ASYSSTTSDC | ETDGYLSSSG | FLDASDPALQ |
| 610 | 620 | 630 | 640 | 650 | 660 |
| PPGGLPSSPA | ESHLCLPSGF | ALSIPRSGPG | SDFSPGDSYA | SDAASGLSDM | GEGGQMRKNP |
| 670 | 680 | 690 | 700 | 710 | 720 |
| VKTLRRRPRS | RLRVTSVSDQ | SDRVVECQLQ | THNSKMVTFR | FDLDGDSPEE | IAAAMVYNEF |
| 730 | 740 | 750 | 760 | 770 | 780 |
| ILPSERDGFL | SRIREIIQRV | ETLLKRDAGP | PEAAEDALSP | QEEPAALPAL | PGPPNAEPQR |
| 790 | 800 | 810 | 820 | 830 | 840 |
| SISPEQRSWA | AFSTSPSSPG | TPLSPGAPFS | PGTPPVFPCP | IFPITSPSCY | PCPFSQVSSN |
| 850 | 860 | 870 | 880 | 890 | 900 |
| PYPQAPSSLL | PLSSSASQVP | LPSSSLPISA | PLPFSPSYPQ | DPLSPTSLPV | CPSPPSLPST |
| 910 | 920 | 930 | 940 | 950 | 960 |
| TAAPLLSLAS | AFSLAVMTVA | QSLLSPSPGL | LSQSPPAPPG | PLPSLPLSLA | SCDQESLSAQ |
| 970 | 980 | 990 | 1000 | 1010 | 1020 |
| TAETENEASR | NPAQPLLGDA | RLAPISEEGK | PQLVGRFQVT | SSKEPAEPPL | QPASPTLSRS |
| 1030 | 1040 | 1050 | 1060 | 1070 | 1080 |
| LKLPSPPLTS | ESSDTEDSAA | GGPETREALA | ESDRAAEGLG | VAVDDEKDEG | KEPLLGGSSP |
| 1090 | 1100 | 1110 | 1120 | 1130 | 1140 |
| ILSHPSPVWM | NYSYSSLCLS | SEESESSGED | EEFWAELQNL | RQKHLSEVEA | LQTLQKKEIE |
| 1150 | 1160 | 1170 | 1180 | 1190 | 1200 |
| DLYSRLGKQP | PPGIVAPAAM | LSCRQRRLSK | GSFPTSRRNS | LQRSDLPGPG | IMRRNSLSGS |
| 1210 | 1220 | ||||
| STGSQEQRAS | KGVTFAGDIG | RM |