Q7ZVK3
Gene name |
sirt2 (zgc:77003) |
Protein name |
NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-2 |
Names |
EC 2.3.1.286 , NAD-dependent protein defatty-acylase sirtuin-2 , EC 2.3.1.- , Regulatory protein SIR2 homolog 2 , SIR2-like protein 2 |
Species |
Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) |
KEGG Pathway |
dre:322309 |
EC number |
2.3.1.286: Transferring groups other than amino-acyl groups |
Protein Class |
|
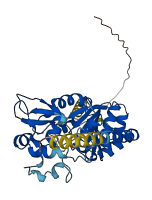
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
25-316 (Catalytic core domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Others |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Li J et al. (2015) "Insight into the Mechanism of Intramolecular Inhibition of the Catalytic Activity of Sirtuin 2 (SIRT2)", PloS one, 10, e0139095
- Xu Y et al. (2014) "Oxidative stress activates SIRT2 to deacetylate and stimulate phosphoglycerate mutase", Cancer research, 74, 3630-42
- Finnin MS et al. (2001) "Structure of the histone deacetylase SIRT2", Nature structural biology, 8, 621-5
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q7ZVK3
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q7ZVK3-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q7ZVK3
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q7ZVK3 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q7ZVK3
1 regional properties for Q7ZVK3
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Sirtuin family, catalytic core domain | 55 - 335 | IPR026590 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.3.1.286 | Transferring groups other than amino-acyl groups |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
19 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| centriole | A cellular organelle, found close to the nucleus in many eukaryotic cells, consisting of a small cylinder with microtubular walls, 300-500 nm long and 150-250 nm in diameter. It contains nine short, parallel, peripheral microtubular fibrils, each fibril consisting of one complete microtubule fused to two incomplete microtubules. Cells usually have two centrioles, lying at right angles to each other. At division, each pair of centrioles generates another pair and the twin pairs form the pole of the mitotic spindle. |
| centrosome | A structure comprised of a core structure (in most organisms, a pair of centrioles) and peripheral material from which a microtubule-based structure, such as a spindle apparatus, is organized. Centrosomes occur close to the nucleus during interphase in many eukaryotic cells, though in animal cells it changes continually during the cell-division cycle. |
| chromosome | A structure composed of a very long molecule of DNA and associated proteins (e.g. histones) that carries hereditary information. |
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| cytosol | The part of the cytoplasm that does not contain organelles but which does contain other particulate matter, such as protein complexes. |
| glial cell projection | A prolongation or process extending from a glial cell. |
| heterochromatin | A compact and highly condensed form of chromatin that is refractory to transcription. |
| juxtaparanode region of axon | A region of an axon near a node of Ranvier that is between the paranode and internode regions. |
| meiotic spindle | A spindle that forms as part of meiosis. Several proteins, such as budding yeast Spo21p, fission yeast Spo2 and Spo13, and C. elegans mei-1, localize specifically to the meiotic spindle and are absent from the mitotic spindle. |
| midbody | A thin cytoplasmic bridge formed between daughter cells at the end of cytokinesis. The midbody forms where the contractile ring constricts, and may persist for some time before finally breaking to complete cytokinesis. |
| mitotic spindle | A spindle that forms as part of mitosis. Mitotic and meiotic spindles contain distinctive complements of proteins associated with microtubules. |
| myelin sheath | An electrically insulating fatty layer that surrounds the axons of many neurons. It is an outgrowth of glial cells |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
| paranodal junction | A highly specialized cell-cell junction found in vertebrates, which forms between a neuron and a glial cell, and has structural similarity to Drosophila septate junctions. It flanks the node of Ranvier in myelinated nerve and electrically isolates the myelinated from unmyelinated nerve segments and physically separates the voltage-gated sodium channels at the node from the cluster of potassium channels underneath the myelin sheath. |
| paranode region of axon | An axon part that is located adjacent to the nodes of Ranvier and surrounded by lateral loop portions of myelin sheath. |
| perikaryon | The portion of the cell soma (neuronal cell body) that excludes the nucleus. |
| perinuclear region of cytoplasm | Cytoplasm situated near, or occurring around, the nucleus. |
| Schmidt-Lanterman incisure | Regions within compact myelin in which the cytoplasmic faces of the enveloping myelin sheath are not tightly juxtaposed, and include cytoplasm from the cell responsible for making the myelin. Schmidt-Lanterman incisures occur in the compact myelin internode, while lateral loops are analogous structures found in the paranodal region adjacent to the nodes of Ranvier. |
| spindle | The array of microtubules and associated molecules that forms between opposite poles of a eukaryotic cell during mitosis or meiosis and serves to move the duplicated chromosomes apart. |
9 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| histone deacetylase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| NAD+ binding | Binding to the oxidized form, NAD, of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide, a coenzyme involved in many redox and biosynthetic reactions. |
| NAD-dependent histone deacetylase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| NAD-dependent histone H4K16 deacetylase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| NAD-dependent protein deacetylase activity | Catalysis of the removal of one or more acetyl groups from a protein, requiring NAD. |
| NAD-dependent protein demyristoylase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| NAD-dependent protein depalmitoylase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
| tubulin deacetylase activity | Catalysis of the reaction |
20 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to caloric restriction | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a of caloric restriction, insufficient food energy intake. |
| cellular response to hypoxia | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus indicating lowered oxygen tension. Hypoxia, defined as a decline in O2 levels below normoxic levels of 20.8 - 20.95%, results in metabolic adaptation at both the cellular and organismal level. |
| cellular response to oxidative stress | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of oxidative stress, a state often resulting from exposure to high levels of reactive oxygen species, e.g. superoxide anions, hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals. |
| cilium assembly | The assembly of a cilium, a specialized eukaryotic organelle that consists of a filiform extrusion of the cell surface. Each cilium is bounded by an extrusion of the cytoplasmic membrane, and contains a regular longitudinal array of microtubules, anchored basally in a centriole. |
| hemopoiesis | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the myeloid and lymphoid derived organ/tissue systems of the blood and other parts of the body over time, from formation to the mature structure. The site of hemopoiesis is variable during development, but occurs primarily in bone marrow or kidney in many adult vertebrates. |
| negative regulation of angiogenesis | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of angiogenesis. |
| negative regulation of autophagy | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of autophagy. Autophagy is the process in which cells digest parts of their own cytoplasm. |
| negative regulation of oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation | Any process that stops or decreases the rate or extent of oligodendrocyte progenitor proliferation. |
| negative regulation of protein catabolic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of protein catabolic process. |
| negative regulation of reactive oxygen species metabolic process | Any process that stops, prevents or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of reactive oxygen species metabolic process. |
| negative regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that stops, prevents, or reduces the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| positive regulation of DNA binding | Any process that increases the frequency, rate or extent of DNA binding. DNA binding is any process in which a gene product interacts selectively with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| positive regulation of execution phase of apoptosis | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of execution phase of apoptosis. |
| positive regulation of proteasomal ubiquitin-dependent protein catabolic process | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of the breakdown of a protein or peptide by hydrolysis of its peptide bonds, initiated by the covalent attachment of ubiquitin, and mediated by the proteasome. |
| positive regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate or extent of transcription from an RNA polymerase II promoter. |
| protein deacetylation | The removal of an acetyl group from a protein amino acid. An acetyl group is CH3CO-, derived from acetic acid. |
| regulation of cell cycle | Any process that modulates the rate or extent of progression through the cell cycle. |
| regulation of tubulin deacetylation | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of tubulin deacetylation. Tubulin deacetylation is the removal of an acetyl group from a protein amino acid. |
| swimming behavior | The response to external or internal stimuli that results in the locomotory process of swimming. Swimming is the self-propelled movement of an organism through the water. |
| tubulin deacetylation | The removal of an acetyl group from tubulin. An acetyl group is CH3CO-, derived from acetic acid. |
7 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| P53686 | HST2 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase HST2 | Saccharomyces cerevisiae (strain ATCC 204508 / S288c) (Baker's yeast) | SS |
| Q9I7I7 | Sirt2 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase Sirt2 | Drosophila melanogaster (Fruit fly) | SS |
| Q9NTG7 | SIRT3 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-3, mitochondrial | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q8IXJ6 | SIRT2 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q8R104 | Sirt3 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8VDQ8 | Sirt2 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q5RJQ4 | Sirt2 | NAD-dependent protein deacetylase sirtuin-2 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | PR |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MSEEVSKRVE | EEADTPGLEG | QSDDSSDEGD | ASGDTEMDFL | RSLFSRTLGL | SPGDKVLDEL |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| TLDSVARYIL | SGKCKNIICM | VGAGISTSAG | IPDFRSPGTG | LYANLQKYNL | PYPEAIFQID |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| YFKKHPEPFF | ALARELYPGQ | FKPTVYHYFI | KMLKDKGLLR | RCYSQNIDTL | ERVAGLEGED |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| LIEAHGTFHT | SHCVSFLCRK | EYSMDWMKNQ | IFSEEIPKCD | SCGSLVKPDI | VFFGESLPSR |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| FFTSMKADFP | QCDLLIIMGT | SLQVQPFASL | VSRVSNRCPR | LLINMEKTGQ | SEFGMGLFSF |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| GGGMDFDSDK | AYRDVAHLST | CDDGCMTLAE | LLGWKKELEE | MVKREHALID | SKDAKKTDKE |
| 370 | |||||
| ASQSSKSAVA | EAEKTDKTE |