Q7ZUQ3
Gene name |
stk3 (zgc:55383) |
Protein name |
Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 |
Names |
EC 2.7.11.1 [Cleaved into: Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 36kDa subunit , MST2/N; Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 20kDa subunit , MST2/C] |
Species |
Danio rerio (Zebrafish) (Brachydanio rerio) |
KEGG Pathway |
dre:324125 |
EC number |
2.7.11.1: Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
Protein Class |
|
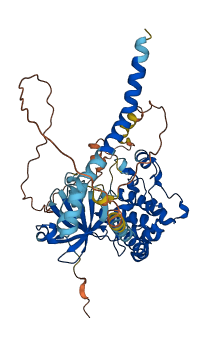
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
26-277 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Cleavage |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
162-185 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
26-277 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
162-185 (Activation loop from InterPro)
Target domain |
26-277 (Protein kinase domain) |
Relief mechanism |
|
Assay |
|
References
- Yeon JH et al. (2016) "Systems-wide Identification of cis-Regulatory Elements in Proteins", Cell systems, 2, 89-100
- Avruch J et al. (2011) "Mst1/2 signalling to Yap: gatekeeper for liver size and tumour development", British journal of cancer, 104, 24-32
- Zhou D et al. (2011) "Mst1 and Mst2 protein kinases restrain intestinal stem cell proliferation and colonic tumorigenesis by inhibition of Yes-associated protein (Yap) overabundance", Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 108, E1312-20
- Creasy CL et al. (1996) "The Ste20-like protein kinase, Mst1, dimerizes and contains an inhibitory domain", The Journal of biological chemistry, 271, 21049-53
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q7ZUQ3
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q7ZUQ3-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q7ZUQ3
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q7ZUQ3 | |||||
6 associated diseases with Q7ZUQ3
[MIM: 209900]: Bardet-Biedl syndrome (BBS)
A syndrome characterized by usually severe pigmentary retinopathy, early-onset obesity, polydactyly, hypogenitalism, renal malformation and intellectual disability. Secondary features include diabetes mellitus, hypertension and congenital heart disease. Bardet-Biedl syndrome inheritance is autosomal recessive, but three mutated alleles (two at one locus, and a third at a second locus) may be required for clinical manifestation of some forms of the disease. . Note=The gene represented in this entry may act as a disease modifier. Heterozygous missense mutations in KIF7 may genetically interact with other BBS genes and contribute to disease manifestation and severity.
[MIM: 614120]: Hydrolethalus syndrome 2 (HLS2)
An embryonic lethal disorder characterized by hydrocephaly or anencephaly, postaxial polydactyly of the upper limbs, and pre- or postaxial polydactyly of the lower limbs. Duplication of the hallux is a common finding. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 200990]: Acrocallosal syndrome (ACLS)
An autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by hypogenesis or agenesis of the corpus callosum. Clinical features include postaxial polydactyly, hallux duplication, macrocephaly, craniofacial abnormalities, severe developmental delay and intellectual disability. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 200990]: Joubert syndrome 12 (JBTS12)
A disorder presenting with cerebellar ataxia, oculomotor apraxia, hypotonia, neonatal breathing abnormalities and psychomotor delay. Neuroradiologically, it is characterized by cerebellar vermian hypoplasia/aplasia, thickened and reoriented superior cerebellar peduncles, and an abnormally large interpeduncular fossa, giving the appearance of a molar tooth on transaxial slices (molar tooth sign). Additional variable features include retinal dystrophy and renal disease. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
[MIM: 607131]: Al-Gazali-Bakalinova syndrome (AGBK)
An autosomal recessive syndrome consisting of macrocephaly, multiple epiphyseal dysplasia and distinctive facial appearance. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
Without disease ID
- A syndrome characterized by usually severe pigmentary retinopathy, early-onset obesity, polydactyly, hypogenitalism, renal malformation and intellectual disability. Secondary features include diabetes mellitus, hypertension and congenital heart disease. Bardet-Biedl syndrome inheritance is autosomal recessive, but three mutated alleles (two at one locus, and a third at a second locus) may be required for clinical manifestation of some forms of the disease. . Note=The gene represented in this entry may act as a disease modifier. Heterozygous missense mutations in KIF7 may genetically interact with other BBS genes and contribute to disease manifestation and severity.
- An embryonic lethal disorder characterized by hydrocephaly or anencephaly, postaxial polydactyly of the upper limbs, and pre- or postaxial polydactyly of the lower limbs. Duplication of the hallux is a common finding. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- An autosomal recessive syndrome characterized by hypogenesis or agenesis of the corpus callosum. Clinical features include postaxial polydactyly, hallux duplication, macrocephaly, craniofacial abnormalities, severe developmental delay and intellectual disability. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- A disorder presenting with cerebellar ataxia, oculomotor apraxia, hypotonia, neonatal breathing abnormalities and psychomotor delay. Neuroradiologically, it is characterized by cerebellar vermian hypoplasia/aplasia, thickened and reoriented superior cerebellar peduncles, and an abnormally large interpeduncular fossa, giving the appearance of a molar tooth on transaxial slices (molar tooth sign). Additional variable features include retinal dystrophy and renal disease. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
- An autosomal recessive syndrome consisting of macrocephaly, multiple epiphyseal dysplasia and distinctive facial appearance. . Note=The disease is caused by variants affecting the gene represented in this entry.
5 regional properties for Q7ZUQ3
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Peptidase S8/S53 domain | 179 - 417 | IPR000209 |
| domain | Peptidase S8 propeptide/proteinase inhibitor I9 | 75 - 147 | IPR010259 |
| domain | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9, C-terminal domain 3 | 600 - 680 | IPR041051 |
| domain | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9, C-terminal domain 2 | 533 - 598 | IPR041052 |
| domain | Proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin type 9, C-terminal domain 1 | 448 - 529 | IPR041254 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 2.7.11.1 | Protein-serine/threonine kinases |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | ||
| PANTHER Subfamily | ||
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cytoplasm | The contents of a cell excluding the plasma membrane and nucleus, but including other subcellular structures. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
5 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| ATP binding | Binding to ATP, adenosine 5'-triphosphate, a universally important coenzyme and enzyme regulator. |
| metal ion binding | Binding to a metal ion. |
| protein kinase activity | Catalysis of the phosphorylation of an amino acid residue in a protein, usually according to the reaction |
| protein serine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
| protein serine/threonine kinase activity | Catalysis of the reactions |
7 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| apoptotic process | A programmed cell death process which begins when a cell receives an internal (e.g. DNA damage) or external signal (e.g. an extracellular death ligand), and proceeds through a series of biochemical events (signaling pathway phase) which trigger an execution phase. The execution phase is the last step of an apoptotic process, and is typically characterized by rounding-up of the cell, retraction of pseudopodes, reduction of cellular volume (pyknosis), chromatin condensation, nuclear fragmentation (karyorrhexis), plasma membrane blebbing and fragmentation of the cell into apoptotic bodies. When the execution phase is completed, the cell has died. |
| camera-type eye development | The process whose specific outcome is the progression of the camera-type eye over time, from its formation to the mature structure. The camera-type eye is an organ of sight that receives light through an aperture and focuses it through a lens, projecting it on a photoreceptor field. |
| hippo signaling | The series of molecular signals mediated by the serine/threonine kinase Hippo or one of its orthologs. In Drosophila, Hippo in complex with the scaffold protein Salvador (Sav), phosphorylates and activates Warts (Wts), which in turn phosphorylates and inactivates the Yorkie (Yki) transcriptional activator. The core fly components hippo, sav, wts and mats are conserved in mammals as STK4/3 (MST1/2), SAV1/WW45, LATS1/2 and MOB1. |
| intracellular signal transduction | The process in which a signal is passed on to downstream components within the cell, which become activated themselves to further propagate the signal and finally trigger a change in the function or state of the cell. |
| phosphorylation | The process of introducing a phosphate group into a molecule, usually with the formation of a phosphoric ester, a phosphoric anhydride or a phosphoric amide. |
| protein tetramerization | The formation of a protein tetramer, a macromolecular structure consisting of four noncovalently associated identical or nonidentical subunits. |
| regulation of MAPK cascade | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of signal transduction mediated by the MAP kinase (MAPK) cascade. |
17 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q5E9L6 | STK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q3SWY6 | STK25 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 25 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | PR |
| Q5ZJK4 | STK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q13043 | STK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q13188 | STK3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q9Y6E0 | STK24 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 24 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| O00506 | STK25 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 25 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9JI11 | Stk4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q9JI10 | Stk3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q9Z2W1 | Stk25 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 25 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q99JT2 | Stk26 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 26 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q99KH8 | Stk24 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 24 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| O54748 | Stk3 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| A4K2T0 | STK4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Macaca mulatta (Rhesus macaque) | PR |
| H2L099 | gck-1 | Germinal center kinase 1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q9NB31 | cst-1 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase cst-1 | Caenorhabditis elegans | PR |
| Q6P3Q4 | stk4 | Serine/threonine-protein kinase 4 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MEHSVPKNKL | KKLSEDSLTK | QPEEVFDVLE | KLGEGSYGSV | FKAIHKESGQ | VVAIKQVPVE |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| SDLQEIIKEI | SIMQQCDSPY | VVKYYGSYFK | NTDLWIVMEY | CGAGSVSDII | RLRNKTLTED |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| EIATVLKSTL | KGLEYLHFMR | KIHRDIKAGN | ILLNTEGHAK | LADFGVAGQL | TDTMAKRNTV |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| IGTPFWMAPE | VIQEIGYNCV | ADIWSLGITS | IEMAEGKPPY | ADIHPMRAIF | MIPTNPPPTF |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| RKPEHWSDDF | TDFVKKCLVK | NPEQRATATQ | LLQHPFIVGA | KPVSILRDLI | TEAMDMKAKR |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| QQEQQRELEE | DDENSEEEVE | VDSHTMVKSG | SESAGTMRAT | GTMSDGAQTM | IEHGSTMLES |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | 420 |
| NLGTMVINSD | DEEEEEDLGS | MRRNPTSQQI | QRPSFMDYFD | KQDSNKAQEG | FNHNQQDPCL |
| 430 | 440 | 450 | 460 | 470 | 480 |
| ISKTAFPDNW | KVPQDGDFDF | LKNLDFEELQ | MRLTALDPMM | EREIEELRQR | YTAKRQPILD |
| 490 | |||||
| AMDAKKRRQQ | NF |