Q7XJ60
Gene name |
EB1A |
Protein name |
Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 1A |
Names |
APC-binding protein EB1A, End-binding protein 1A, AtEB1A, Protein ATEB1 homolog 2, AtEB1H2 |
Species |
Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) |
KEGG Pathway |
ath:AT3G47690 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
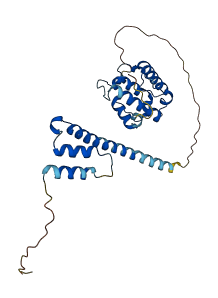
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
13-115 (CH domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Partner binding |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Komaki S et al. (2010) "Nuclear-localized subtype of end-binding 1 protein regulates spindle organization in Arabidopsis", Journal of cell science, 123, 451-9
- Kanaba T et al. (2013) "Microtubule-binding sites of the CH domain of EB1 and its autoinhibition revealed by NMR", Biochimica et biophysica acta, 1834, 499-507
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q7XJ60
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q7XJ60-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
23 variants for Q7XJ60
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENSVATH14395588 | 67 | E>K | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH12618347 | 76 | V>I | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH14395589 | 133 | S>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH12618351 | 139 | R>K | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH12618352 | 145 | N>Y | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_3_17582438_C_T | 148 | P>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06262246 | 153 | T>A | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06262247 | 170 | A>S | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06262249 | 171 | S>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH02464040 | 175 | S>P | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_3_17582629_G_A | 181 | V>M | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_3_17582649_G_T | 187 | E>D | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06262254 | 197 | L>H | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06262255 | 222 | D>E | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06262265 | 227 | V>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_3_17583210_A_C | 232 | K>T | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH00406214 | 243 | A>V | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_3_17583250_A_T | 245 | E>D | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_3_17583261_A_G | 249 | E>G | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH06262266 | 267 | E>G | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_3_17583318_A_T | 268 | Q>L | No | 1000Genomes | |
| tmp_3_17583321_T_G | 269 | L>R | No | 1000Genomes | |
| ENSVATH12618396 | 276 | A>T | No | 1000Genomes |
No associated diseases with Q7XJ60
14 regional properties for Q7XJ60
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Protein kinase domain | 621 - 882 | IPR000719 |
| domain | Ephrin receptor ligand binding domain | 29 - 206 | IPR001090 |
| domain | Serine-threonine/tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 622 - 878 | IPR001245 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class V, conserved site | 182 - 202 | IPR001426-1 |
| conserved_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, receptor class V, conserved site | 243 - 263 | IPR001426-2 |
| domain | Sterile alpha motif domain | 908 - 975 | IPR001660 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 324 - 434 | IPR003961-1 |
| domain | Fibronectin type III | 435 - 530 | IPR003961-2 |
| active_site | Tyrosine-protein kinase, active site | 742 - 754 | IPR008266 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase ephrin type A/B receptor-like | 269 - 302 | IPR011641 |
| binding_site | Protein kinase, ATP binding site | 627 - 653 | IPR017441 |
| domain | Tyrosine-protein kinase, catalytic domain | 621 - 878 | IPR020635 |
| domain | Ephrin receptor, transmembrane domain | 543 - 618 | IPR027936 |
| domain | Ephrin type-A receptor 3, ligand binding domain | 29 - 200 | IPR034266 |
Functions
9 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cortical microtubule, transverse to long axis | Arrays of microtubules underlying and connected to the plasma membrane, in the cortical cytosol, oriented mainly with their axes transverse to the long axis of the cell (and root in plants). In plants it influences the direction of cellulose microfibril deposition. |
| cytoplasmic microtubule | Any microtubule in the cytoplasm of a cell. |
| microtubule organizing center | An intracellular structure that can catalyze gamma-tubulin-dependent microtubule nucleation and that can anchor microtubules by interacting with their minus ends, plus ends or sides. |
| microtubule plus-end | The growing (plus) end of a microtubule. In vitro, microtubules polymerize more quickly at the plus end than at the minus end. In vivo, microtubule growth occurs only at the plus end, and the plus end switches between periods of growth and shortening, a behavior known as dynamic instability. |
| phragmoplast | Fibrous structure (light microscope view) that arises between the daughter nuclei at telophase and within which the initial partition (cell plate), dividing the mother cell in two (cytokinesis), is formed. Appears at first as a spindle connected to the two nuclei, but later spreads laterally in the form of a ring. Consists of microtubules. |
| preprophase band | A dense band of microtubules, 1-3 pm wide, that appears just beneath the cell membrane before the start of cell division in the cells of higher plants. It precedes the onset of prophase and then disappears as mitosis begins, yet it somehow determines the plane of orientation of the new cell plate forming in late telophase and marks the zone of the parental cell wall where fusion with the growing cell plate ultimately occurs. |
| spindle microtubule | Any microtubule that is part of a mitotic or meiotic spindle; anchored at one spindle pole. |
| spindle midzone | The area in the center of the spindle where the spindle microtubules from opposite poles overlap. |
| spindle pole | Either of the ends of a spindle, where spindle microtubules are organized; usually contains a microtubule organizing center and accessory molecules, spindle microtubules and astral microtubules. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| microtubule binding | Binding to a microtubule, a filament composed of tubulin monomers. |
| microtubule plus-end binding | Binding to the plus end of a microtubule. |
6 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cell division | The process resulting in division and partitioning of components of a cell to form more cells; may or may not be accompanied by the physical separation of a cell into distinct, individually membrane-bounded daughter cells. |
| microtubule bundle formation | A process that results in a parallel arrangement of microtubules. |
| protein localization to microtubule plus-end | A process in which a protein is transported to, or maintained in, a location at a microtubule plus-end. |
| regulation of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of microtubule polymerization or depolymerization by the addition or removal of tubulin heterodimers from a microtubule. |
| spindle assembly | The aggregation, arrangement and bonding together of a set of components to form the spindle, the array of microtubules and associated molecules that serves to move duplicated chromosomes apart. |
| thigmotropism | The movement of an organism, or part of an organism, such as leaves or tendrils, in response to a touch stimulus, usually toward or away from it. |
12 homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q3ZBD9 | MAPRE1 | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 1 | Bos taurus (Bovine) | SS |
| Q5ZLC7 | MAPRE1 | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 1 | Gallus gallus (Chicken) | SS |
| Q15691 | MAPRE1 | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | EV |
| Q15555 | MAPRE2 | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 2 | Homo sapiens (Human) | PR |
| Q9UPY8 | MAPRE3 | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 3 | Homo sapiens (Human) | SS |
| Q61166 | Mapre1 | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 1 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q6PER3 | Mapre3 | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 3 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | SS |
| Q8R001 | Mapre2 | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 2 | Mus musculus (Mouse) | PR |
| Q5XIT1 | Mapre3 | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 3 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q66HR2 | Mapre1 | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 1 | Rattus norvegicus (Rat) | SS |
| Q9FJJ5 | EB1B | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 1B | Arabidopsis thaliana (Mouse-ear cress) | EV |
| Q6P848 | mapre1 | Microtubule-associated protein RP/EB family member 1 | Xenopus tropicalis (Western clawed frog) (Silurana tropicalis) | SS |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MATNIGMMDS | AYFVGRNEIL | TWINDRLHLN | LSRVEEAASG | AVQCQMLDMT | FPGVVPMHKV |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| NFDAKNEYDM | IQNYKVLQDV | FNKLKITKPL | EINRLVKGRP | LDNLEFLQWL | KRFCDSINGG |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| IMNENYNPVE | RRSRNGKERS | VKGSNKIPKS | LQTNNNHPPP | NSSSVGLSKA | SGPKSAKAAE |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| VQALSKELVD | LKISTDLLEK | ERDFYFSKLR | DVEILCQTPE | LDDLPIVVAV | KKILYATDAN |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | |||
| ESALEDAQEY | LNQSLGVEDD | EAEGNGEQLE | EEKTQA |