Q7LXU0
Gene name |
hjc (SSO0575, ORF-c21_024) |
Protein name |
Holliday junction resolvase Hjc |
Names |
Hjc |
Species |
Saccharolobus solfataricus (strain ATCC 35092 / DSM 1617 / JCM 11322 / P2) (Sulfolobus solfataricus) |
KEGG Pathway |
sso:SSO0575 |
EC number |
3.1.21.10: Endodeoxyribonucleases producing 5'-phosphomonoesters |
Protein Class |
HOLLIDAY JUNCTION RESOLVASE HJC (PTHR39651) |
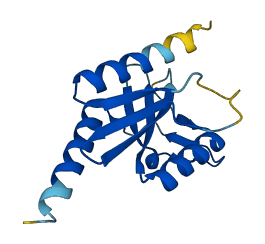
Descriptions
The Holliday junction-resolving enzyme Hjc specifically recognizes four-way DNA junctions, cleaving them without sequence preference to generate recombinant DNA duplex products. Hjc imposes an X-shaped global conformation on the bound DNA junction and distorts base stacking around the point of cleavage, three nucleotides 3' of the junction center.
Hjc is autoinhibited in the conformation of the junction upon binding multiple Hjc dimers, in which Hjc fails to cleave the DNA because of the inaccurate positioning of the enzyme catalytic center over the targeted scissile bond, and this can be relieved by the addition of either competitor duplex DNA or the architectural double-stranded DNA-binding protein Sso7d.
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
11-103 (Hjc domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, Partner binding |
Assay |
Structural analysis |
Target domain |
11-103 (Hjc domain) |
Relief mechanism |
Ligand binding, Partner binding |
Assay |
Structural analysis |
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

4 structures for Q7LXU0
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1HH1 | X-ray | 215 A | A | 1-143 | PDB |
| 4TKD | X-ray | 201 A | A/B/C/D | 1-143 | PDB |
| 4TKK | X-ray | 240 A | A/B | 1-143 | PDB |
| AF-Q7LXU0-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q7LXU0
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q7LXU0 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q7LXU0
16 regional properties for Q7LXU0
| Type | Name | Position | InterPro Accession |
|---|---|---|---|
| domain | Death domain | 2326 - 2420 | IPR000488 |
| domain | ZU5 domain | 990 - 1147 | IPR000906-1 |
| domain | ZU5 domain | 1149 - 1296 | IPR000906-2 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 47 - 138 | IPR002110-1 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 139 - 200 | IPR002110-2 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 201 - 274 | IPR002110-3 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 272 - 340 | IPR002110-4 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 338 - 406 | IPR002110-5 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 407 - 472 | IPR002110-6 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 473 - 505 | IPR002110-7 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 506 - 604 | IPR002110-8 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 604 - 670 | IPR002110-9 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 671 - 769 | IPR002110-10 |
| repeat | Ankyrin repeat | 770 - 802 | IPR002110-11 |
| domain | Ankyrin-3, death domain | 2334 - 2417 | IPR037971 |
| domain | Ankyrin, UPA domain | 1316 - 1445 | IPR040745 |
Functions
| Description | ||
|---|---|---|
| EC Number | 3.1.21.10 | Endodeoxyribonucleases producing 5'-phosphomonoesters |
| Subcellular Localization |
|
|
| PANTHER Family | PTHR39651 | HOLLIDAY JUNCTION RESOLVASE HJC |
| PANTHER Subfamily | PTHR39651:SF1 | HOLLIDAY JUNCTION RESOLVASE HJC |
| PANTHER Protein Class | ||
| PANTHER Pathway Category | No pathway information available | |
No GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| No GO annotations for cellular component |
3 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| crossover junction DNA endonuclease activity | Catalysis of the endonucleolytic cleavage at a junction such as a reciprocal single-stranded crossover between two homologous DNA duplexes (Holliday junction). |
| DNA binding | Any molecular function by which a gene product interacts selectively and non-covalently with DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid). |
| magnesium ion binding | Binding to a magnesium (Mg) ion. |
2 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA recombination | Any process in which a new genotype is formed by reassortment of genes resulting in gene combinations different from those that were present in the parents. In eukaryotes genetic recombination can occur by chromosome assortment, intrachromosomal recombination, or nonreciprocal interchromosomal recombination. Interchromosomal recombination occurs by crossing over. In bacteria it may occur by genetic transformation, conjugation, transduction, or F-duction. |
| DNA repair | The process of restoring DNA after damage. Genomes are subject to damage by chemical and physical agents in the environment (e.g. UV and ionizing radiations, chemical mutagens, fungal and bacterial toxins, etc.) and by free radicals or alkylating agents endogenously generated in metabolism. DNA is also damaged because of errors during its replication. A variety of different DNA repair pathways have been reported that include direct reversal, base excision repair, nucleotide excision repair, photoreactivation, bypass, double-strand break repair pathway, and mismatch repair pathway. |
No homologous proteins in AiPD
| UniProt AC | Gene Name | Protein Name | Species | Evidence Code |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No homologous proteins | ||||
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MNAKKRKGSA | VERNIVSRLR | DKGFAVVRAP | ASGSKRKDPI | PDIIALKNGV | IILIEMKSRK |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| DIEGKIYVRR | EQAEGIIEFA | RKSGGSLFLG | VKKPGVLKFI | PFEKLRRTET | GNYVADSEIE |
| 130 | 140 | ||||
| GLDLEDLVRL | VEAKISRTLD | NFL |