Q764M6
Gene name |
IRF3 |
Protein name |
Interferon regulatory factor 3 |
Names |
IRF-3 |
Species |
Sus scrofa (Pig) |
KEGG Pathway |
ssc:396656 |
EC number |
|
Protein Class |
|
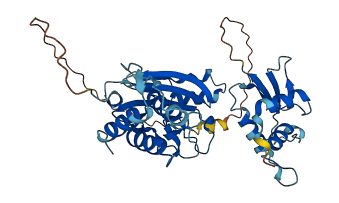
Descriptions
Autoinhibitory domains (AIDs)
Target domain |
199-378 (IFN association domain) |
Relief mechanism |
PTM |
Assay |
|
Accessory elements
No accessory elements
References
- Lin R et al. (1999) "Structural and functional analysis of interferon regulatory factor 3: localization of the transactivation and autoinhibitory domains", Molecular and cellular biology, 19, 2465-74
- Shah M et al. (2015) "In silico mechanistic analysis of IRF3 inactivation and high-risk HPV E6 species-dependent drug response", Scientific reports, 5, 13446
- Liu S et al. (2015) "Phosphorylation of innate immune adaptor proteins MAVS, STING, and TRIF induces IRF3 activation", Science (New York, N.Y.), 347, aaa2630
Autoinhibited structure

Activated structure

1 structures for Q764M6
| Entry ID | Method | Resolution | Chain | Position | Source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AF-Q764M6-F1 | Predicted | AlphaFoldDB |
No variants for Q764M6
| Variant ID(s) | Position | Change | Description | Diseaes Association | Provenance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No variants for Q764M6 | |||||
No associated diseases with Q764M6
Functions
2 GO annotations of cellular component
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| mitochondrion | A semiautonomous, self replicating organelle that occurs in varying numbers, shapes, and sizes in the cytoplasm of virtually all eukaryotic cells. It is notably the site of tissue respiration. |
| nucleus | A membrane-bounded organelle of eukaryotic cells in which chromosomes are housed and replicated. In most cells, the nucleus contains all of the cell's chromosomes except the organellar chromosomes, and is the site of RNA synthesis and processing. In some species, or in specialized cell types, RNA metabolism or DNA replication may be absent. |
2 GO annotations of molecular function
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| DNA-binding transcription factor activity, RNA polymerase II-specific | A DNA-binding transcription factor activity that modulates the transcription of specific gene sets transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
| RNA polymerase II cis-regulatory region sequence-specific DNA binding | Binding to a specific upstream regulatory DNA sequence (transcription factor recognition sequence or binding site) located in cis relative to the transcription start site (i.e., on the same strand of DNA) of a gene transcribed by RNA polymerase II. |
10 GO annotations of biological process
| Name | Definition |
|---|---|
| cellular response to virus | Any process that results in a change in state or activity of a cell (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a stimulus from a virus. |
| defense response to virus | Reactions triggered in response to the presence of a virus that act to protect the cell or organism. |
| immune system process | Any process involved in the development or functioning of the immune system, an organismal system for calibrated responses to potential internal or invasive threats. |
| innate immune response | Innate immune responses are defense responses mediated by germline encoded components that directly recognize components of potential pathogens. |
| positive regulation of interferon-alpha production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interferon-alpha production. |
| positive regulation of interferon-beta production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of interferon-beta production. |
| positive regulation of type I interferon production | Any process that activates or increases the frequency, rate, or extent of type I interferon production. Type I interferons include the interferon-alpha, beta, delta, episilon, zeta, kappa, tau, and omega gene families. |
| regulation of apoptotic process | Any process that modulates the occurrence or rate of cell death by apoptotic process. |
| regulation of transcription by RNA polymerase II | Any process that modulates the frequency, rate or extent of transcription mediated by RNA polymerase II. |
| TRIF-dependent toll-like receptor signaling pathway | The series of molecular signals initiated by a ligand binding to a toll-like receptor where the TRIF adaptor mediates transduction of the signal. Toll-like receptors directly bind pattern motifs from a variety of microbial sources to initiate an innate immune response. |
| 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 |
| MGTQKPRILP | WLISQLNQGQ | LEGVAWLDEG | HTRFRIPWKH | GLRQDAQQED | FGIFQAWAEA |
| 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 |
| SGAYTPGKDK | PDLPTWKRNF | RSALNRKEAL | RLAEDHSKDP | HDPHKIYEFV | TSGVGDFPEP |
| 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 |
| DTSLDLSGRY | STSDTHEDSL | DKLLSGMDLA | SDAGPQSLTL | ALEQPPQLSL | SPSVDAPASC |
| 190 | 200 | 210 | 220 | 230 | 240 |
| PNLGVRENPL | KQLLANDDEW | EFQVTVFYRG | CQVFQQTVCS | PGGLRLVGSE | AEDGTLAGQP |
| 250 | 260 | 270 | 280 | 290 | 300 |
| VRLPDPAASL | TDRGVADYVR | RVLSCLGGGL | ALWRAGQWLW | AQRLGHCHVY | WAMGEELIPD |
| 310 | 320 | 330 | 340 | 350 | 360 |
| SGHKPDGEVP | KDREGGVFDL | GPFIEDLIAF | IEGSRRSPRY | TLWFCMGQSW | PQDEPWVKRL |
| 370 | 380 | 390 | 400 | 410 | |
| VMVKVVPMCL | RALVDMARDG | GASSLENTVD | LHISNSHPLS | LTSDQYKACL | RDLVEDMDF |